Cannabis Use Disorder:
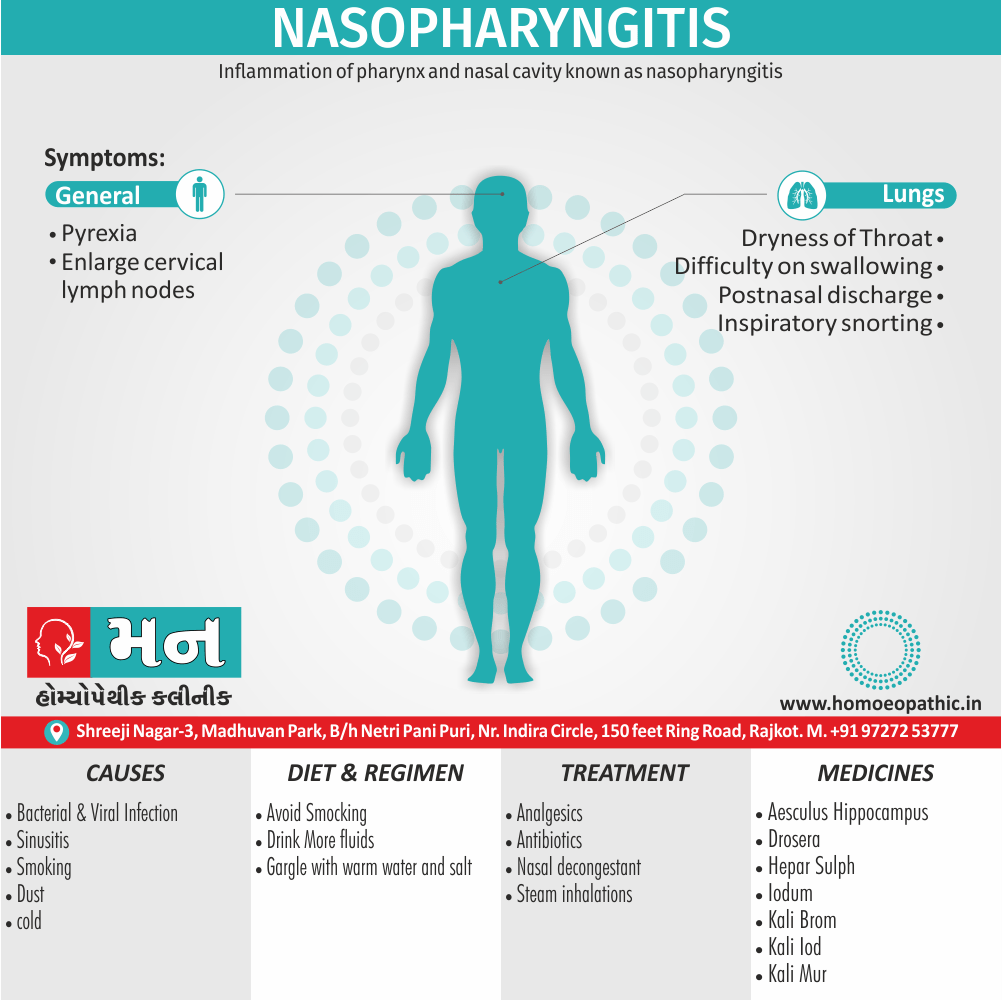
Definition of Cannabis Use Disorder:
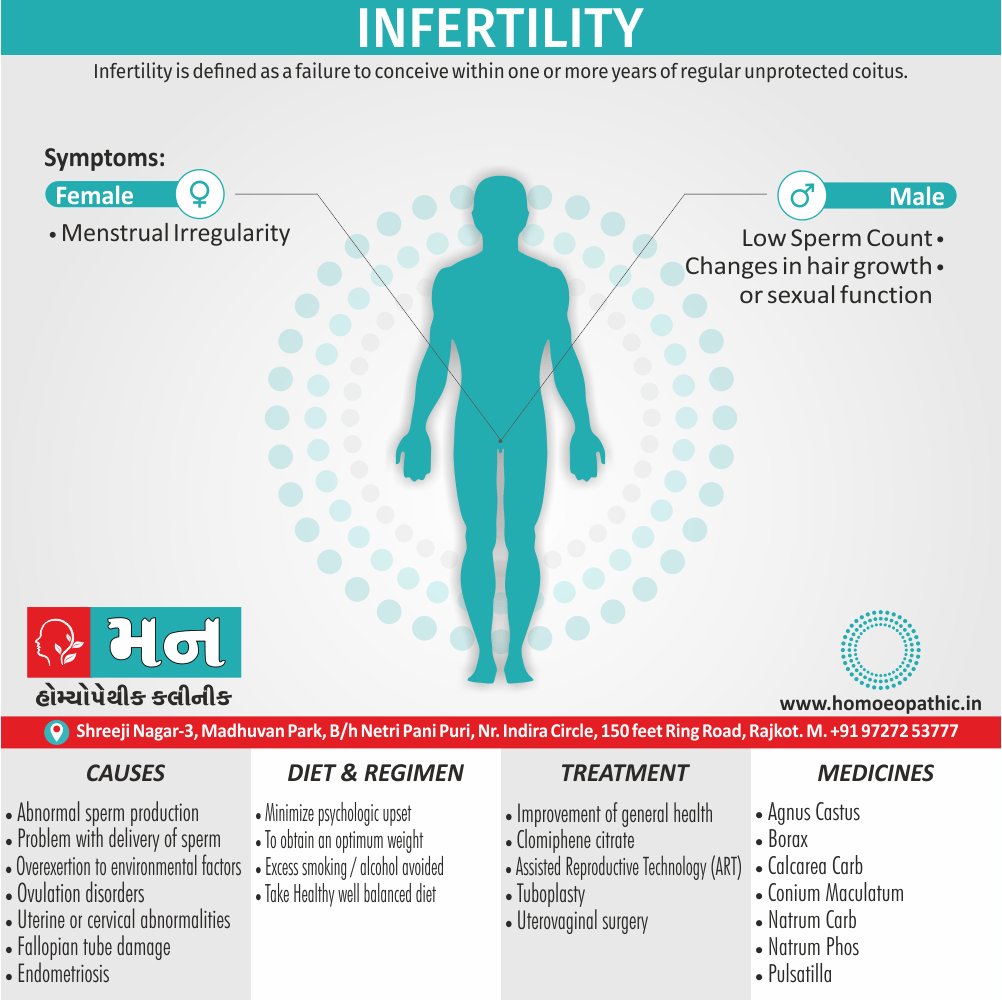
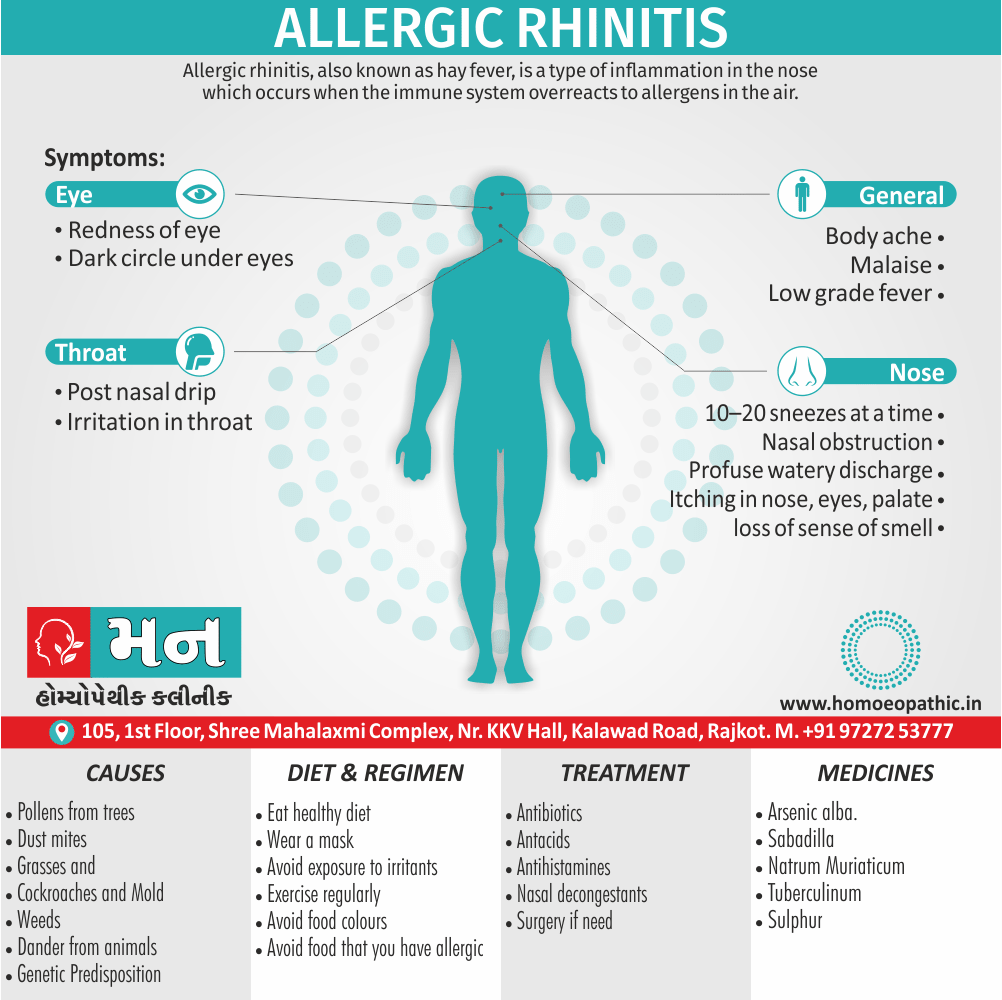
People who use marijuana will develop marijuana use disorder, meaning that they are unable to stop using marijuana even though it’s causing health and social problems in their lives.
Overview of Cannabis Use Disorder:
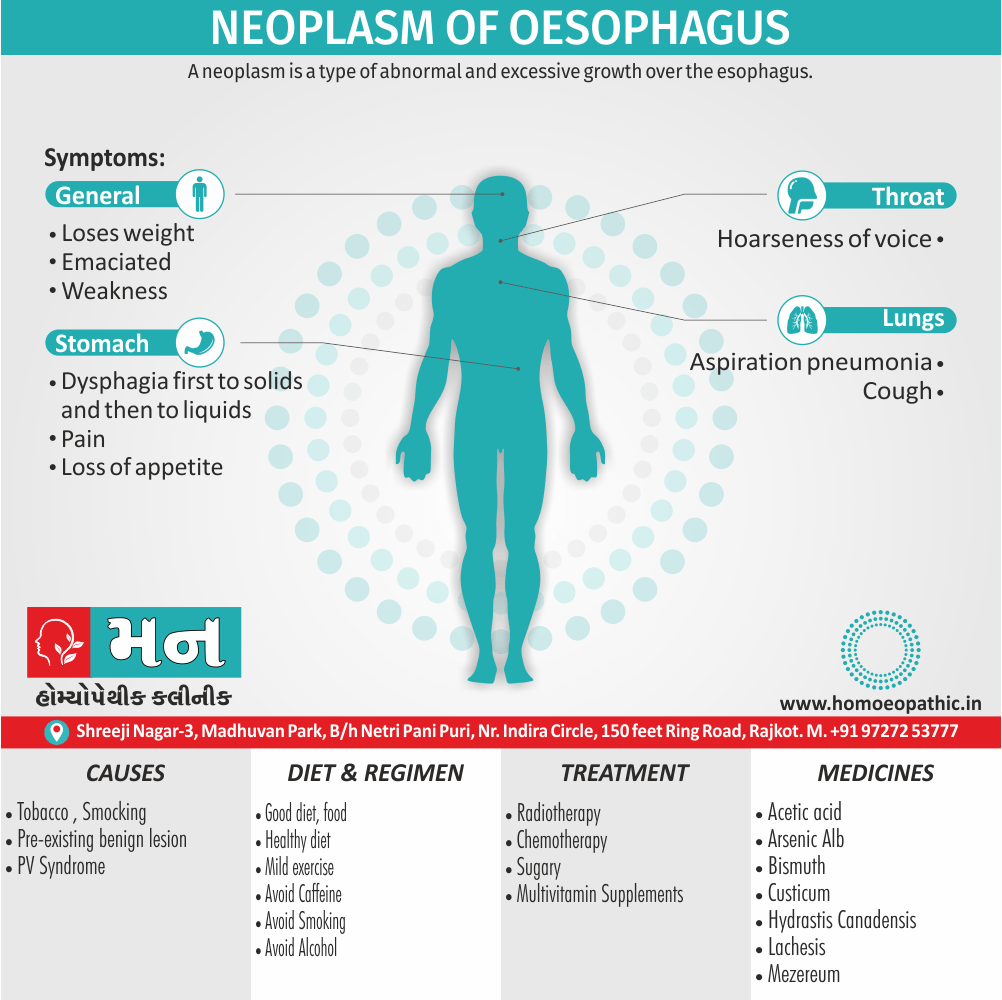
In Cannabis use disorder, Cannabis is derived from the hemp plant, Cannabis sativa, which has several varieties named after the region in which it is found (e.g. sativa indica in India and Pakistan, and americana in America).
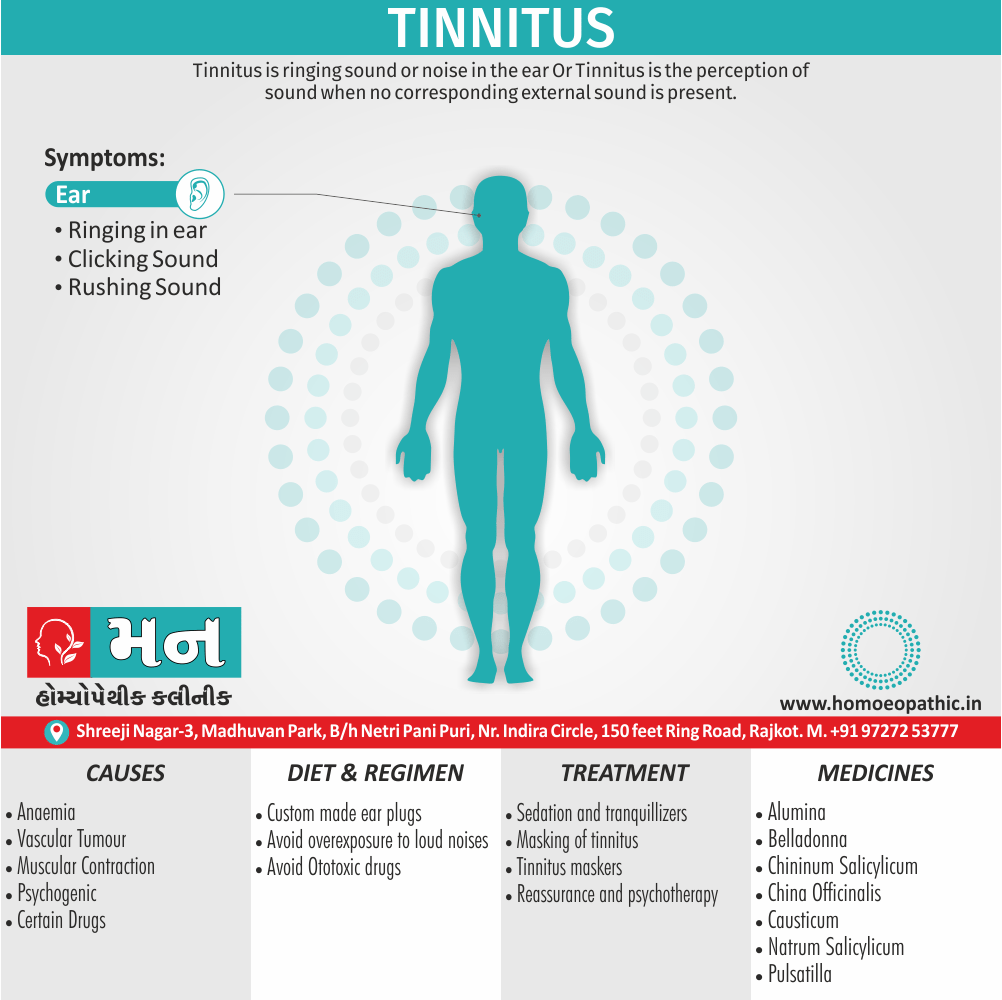
Street names: Grass, Hash or Hashish, Marijuana.
Cannabis produces more than 400 identifiable chemicals of which about 50 are cannabinoids, the most active being Δ-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC). The pistillate form of the female plant is more important in cannabis production.
Recently, a Gi-protein (in other words, inhibitory G-protein) linked cannabinoid receptor has found (especially, in basal ganglia, hippocampus and cerebellum) which inhibits the adenylate cyclase activity in a dose-dependent manner.
Cannabis produces a very mild physical dependence, with a relatively mild withdrawal syndrome, i.e.
- Fine tremors
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
- Decreased appetite also craving
In detail, this syndrome begins within few hours of stopping cannabis use also lasts for 4 to 5 days. However, some health professionals feel that there is no true physical dependence with cannabis.
On the other hand, psychological dependence ranges from mild (in other words, occasional ‘trips’) to marked (e.g. compulsive use). Furthermore, All the active ingredients called as marijuana or marihuana.
It can detected in urine for up to 3 weeks after chronic heavy use.
Preparation of Cannabis :
| Cannabis Preparations |
Portion of Plant |
THC Content(%) |
Potency(as compared to ‘Bhang’) |
| 1. Hashish or Charas | Resinous exudate especially from the flowering tops of cultivated plants |
8-14 |
10 |
| 2. Ganja | Small leaves also brackets of inflorescence of highly cultivated plants |
1-2 |
2 |
| 3. Bhang | Dried leaves, flowering shoots also cut tops of uncultivated plants |
1 |
1 |
| 4. Hash oil | Specifically Lipid soluble plant extract |
15-40 |
25 |
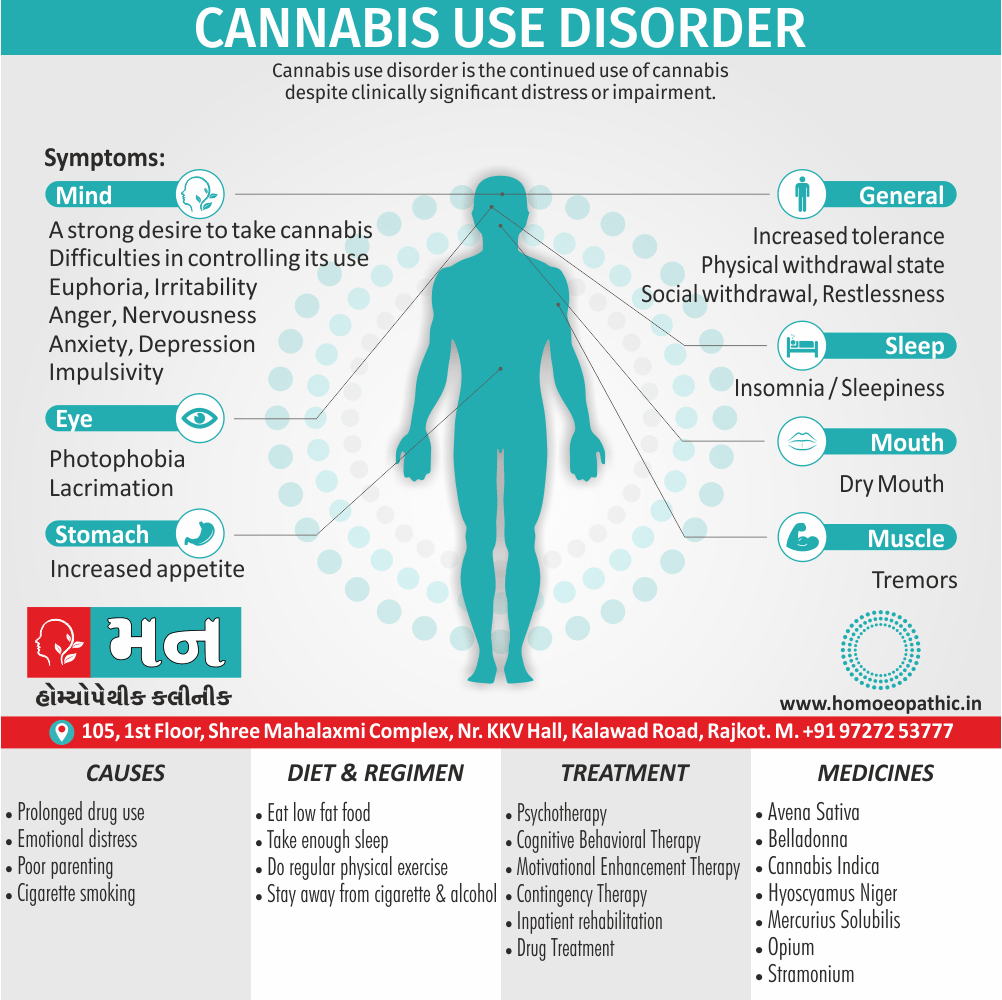
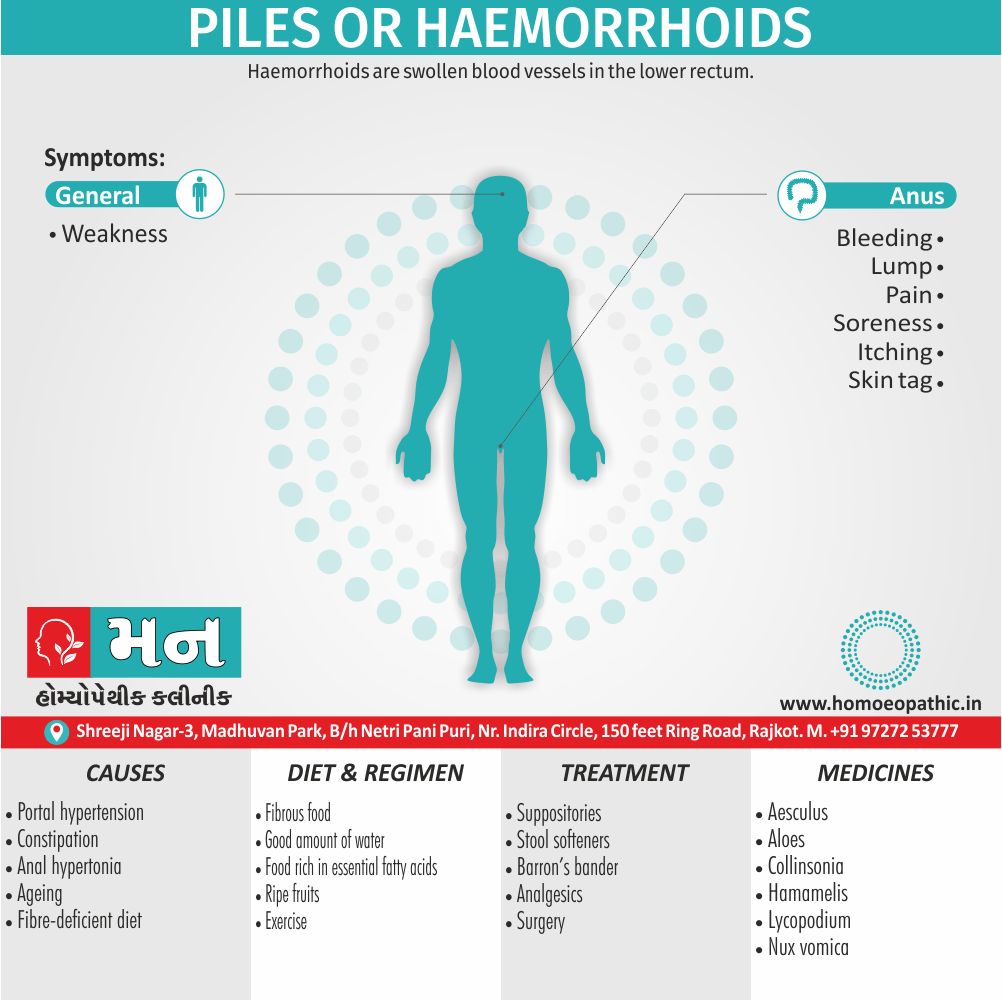
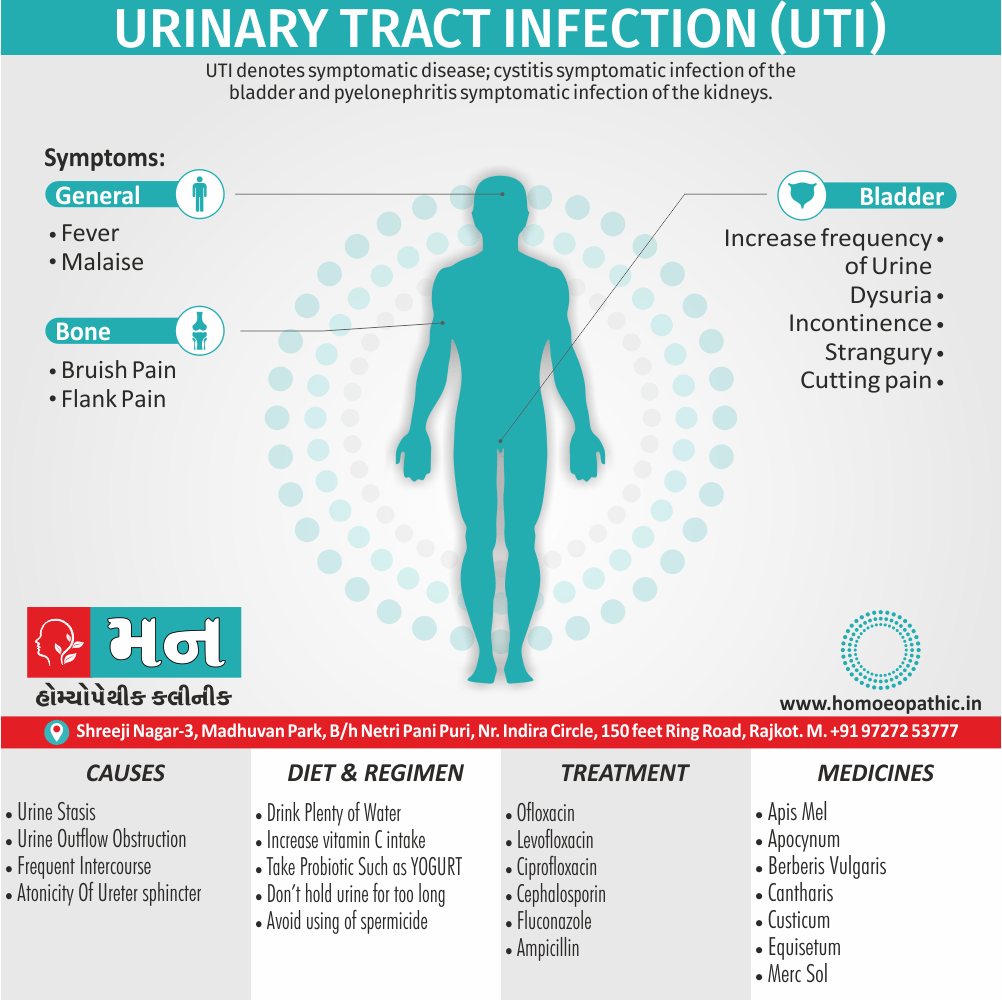
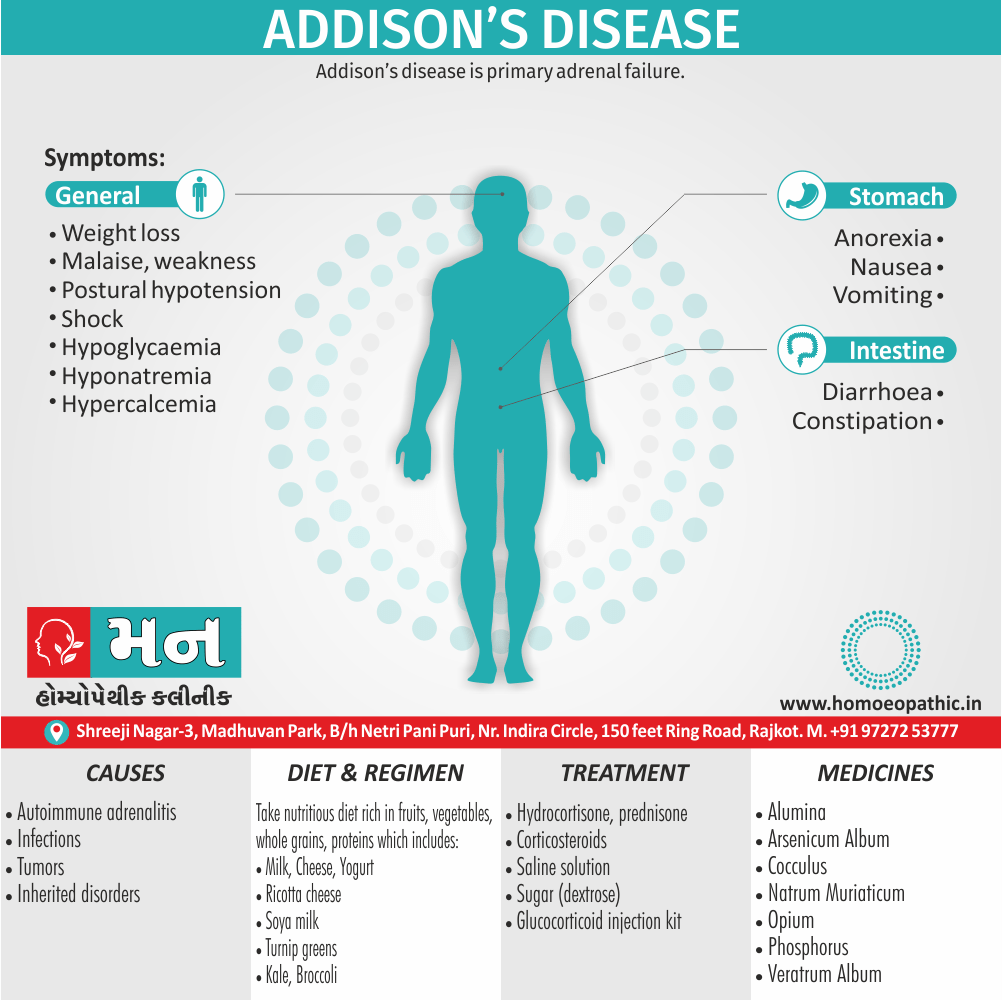
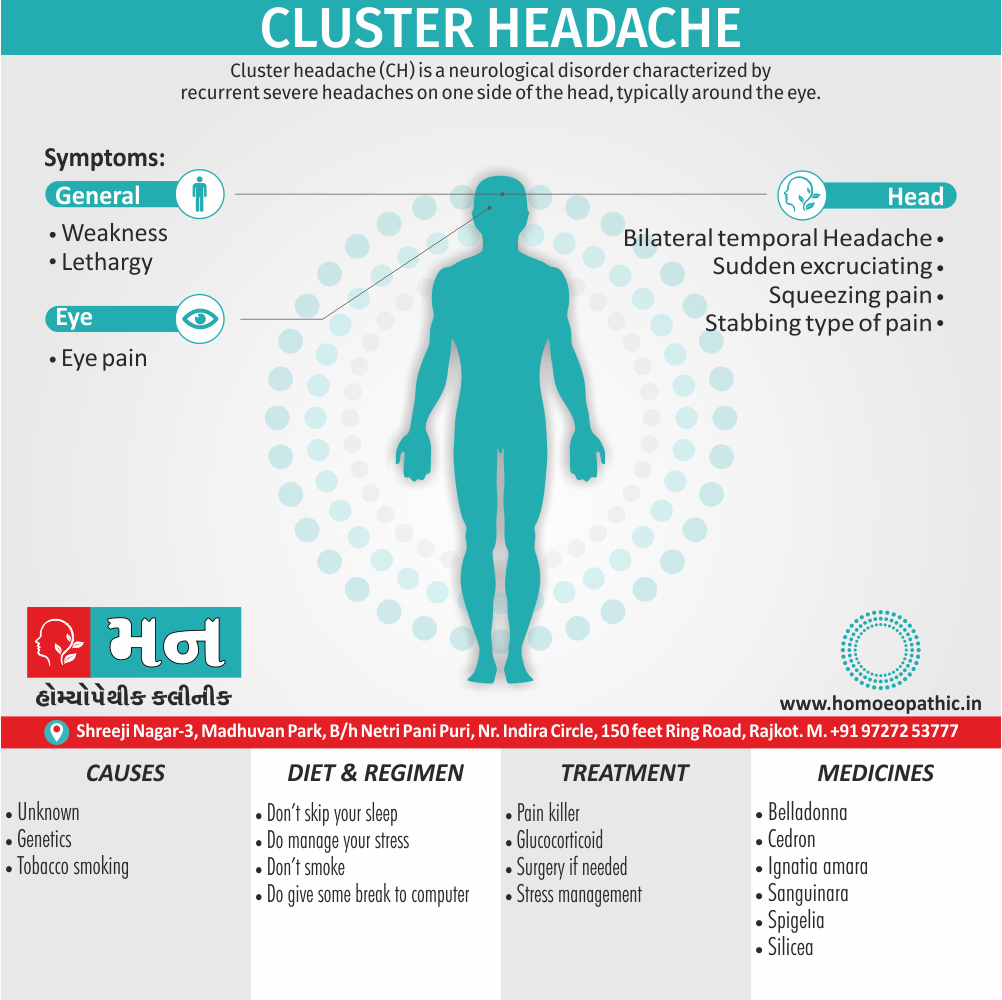
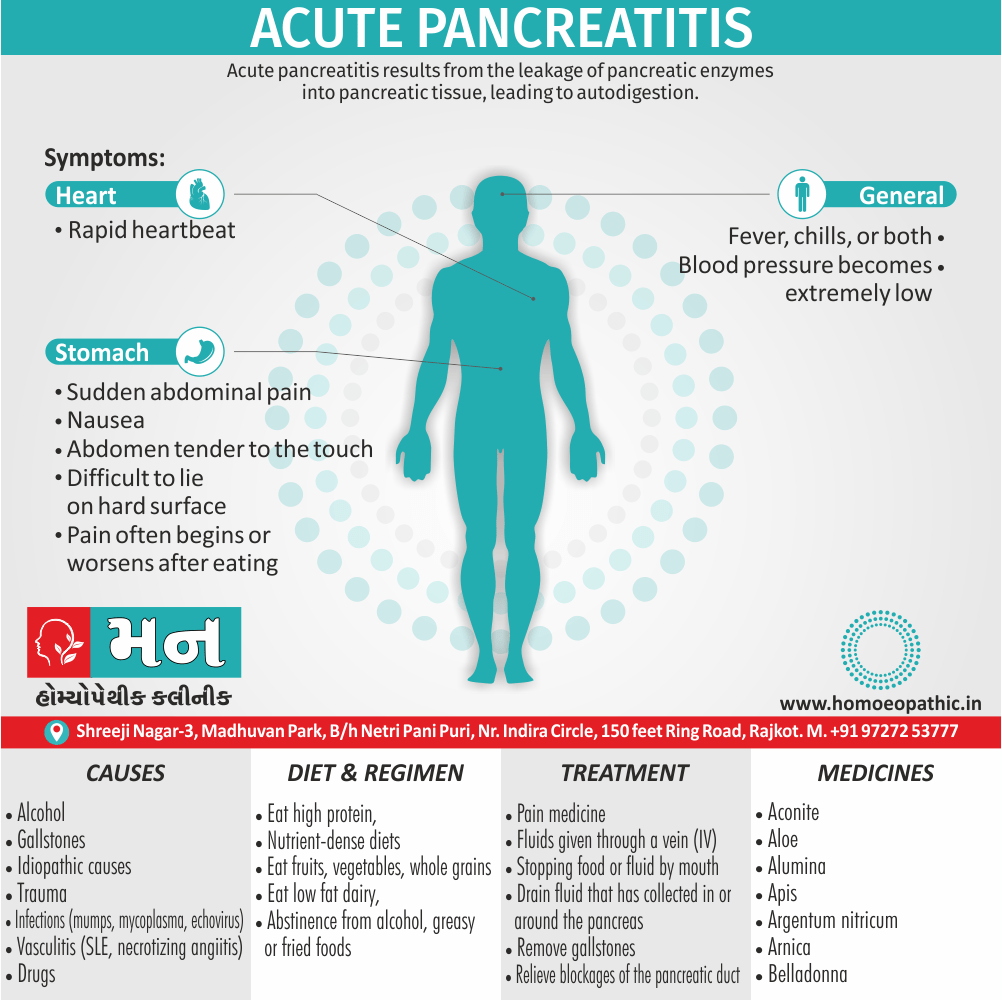
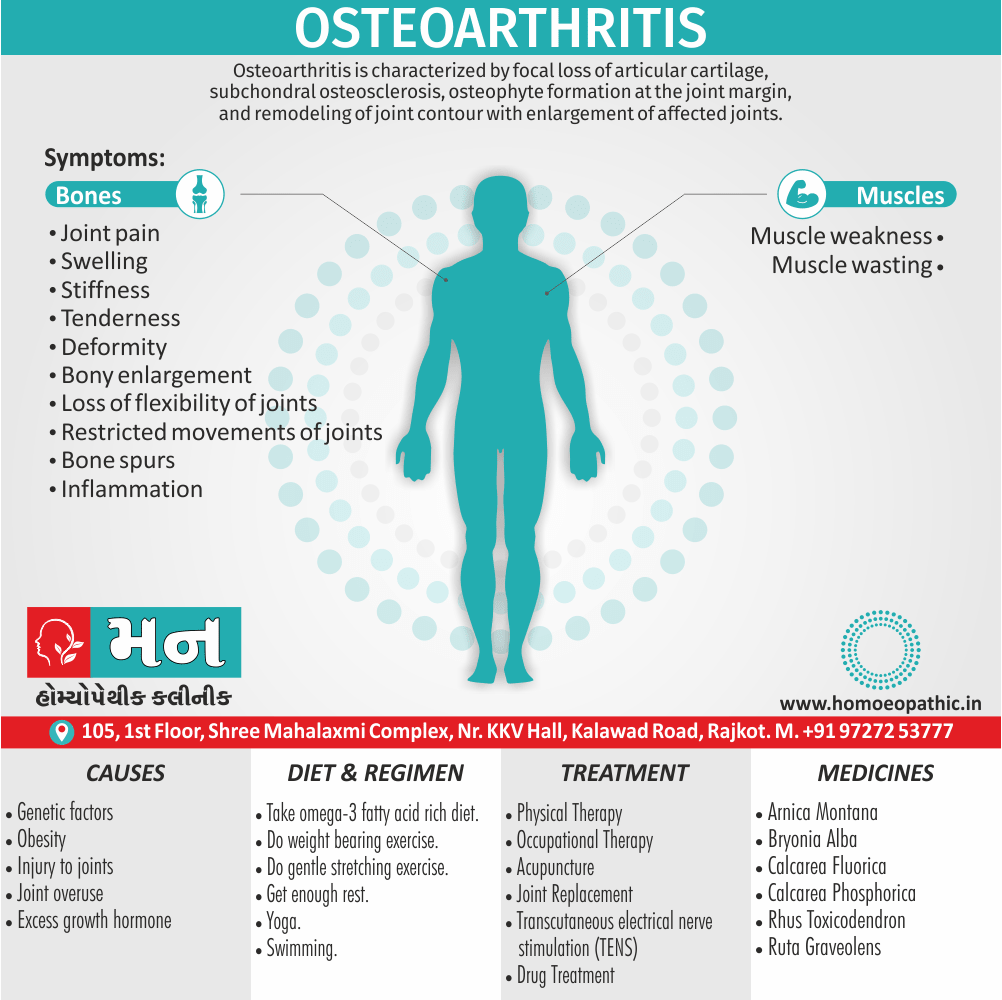
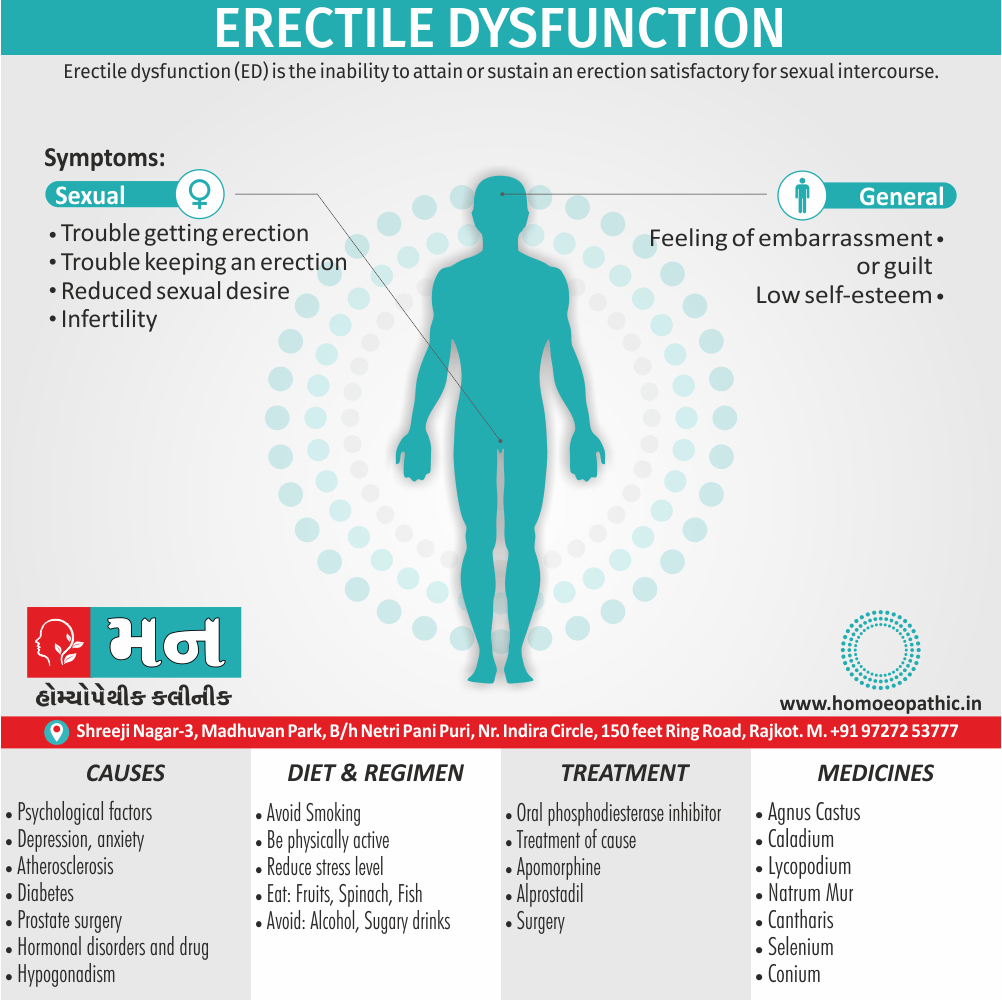
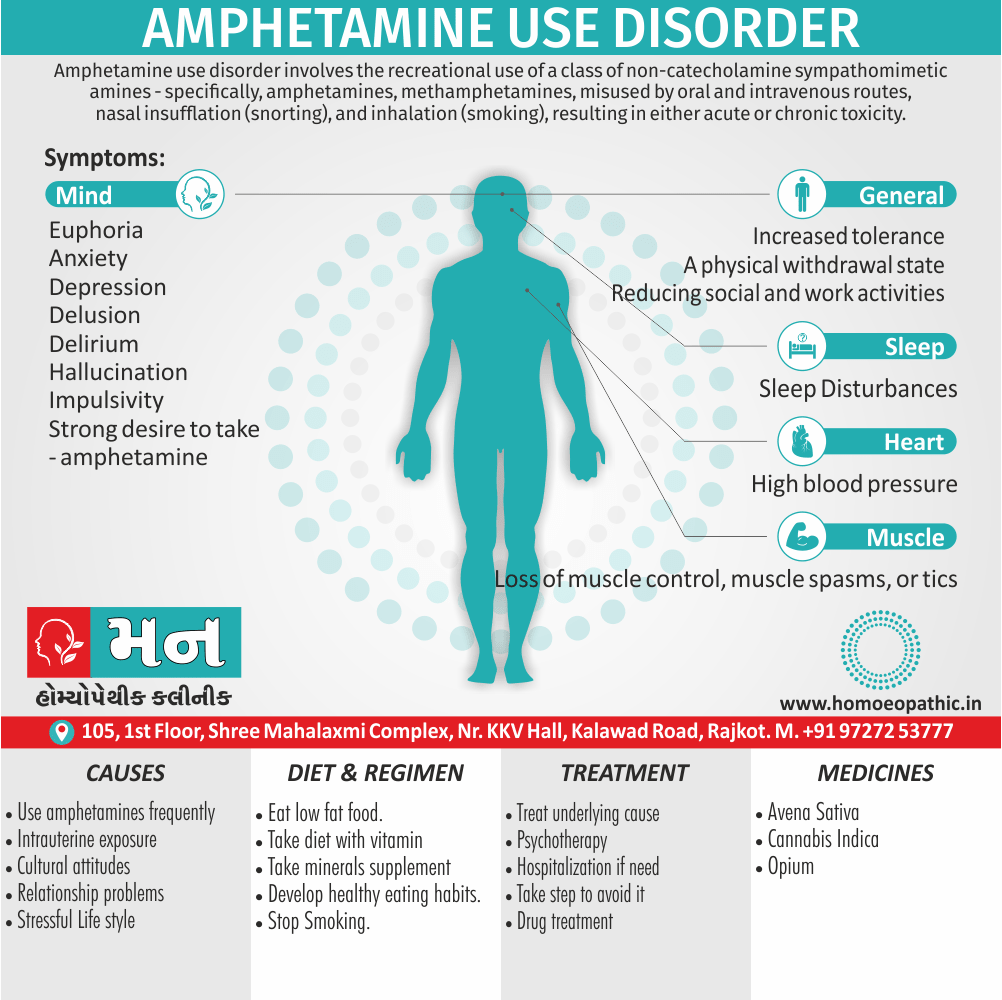
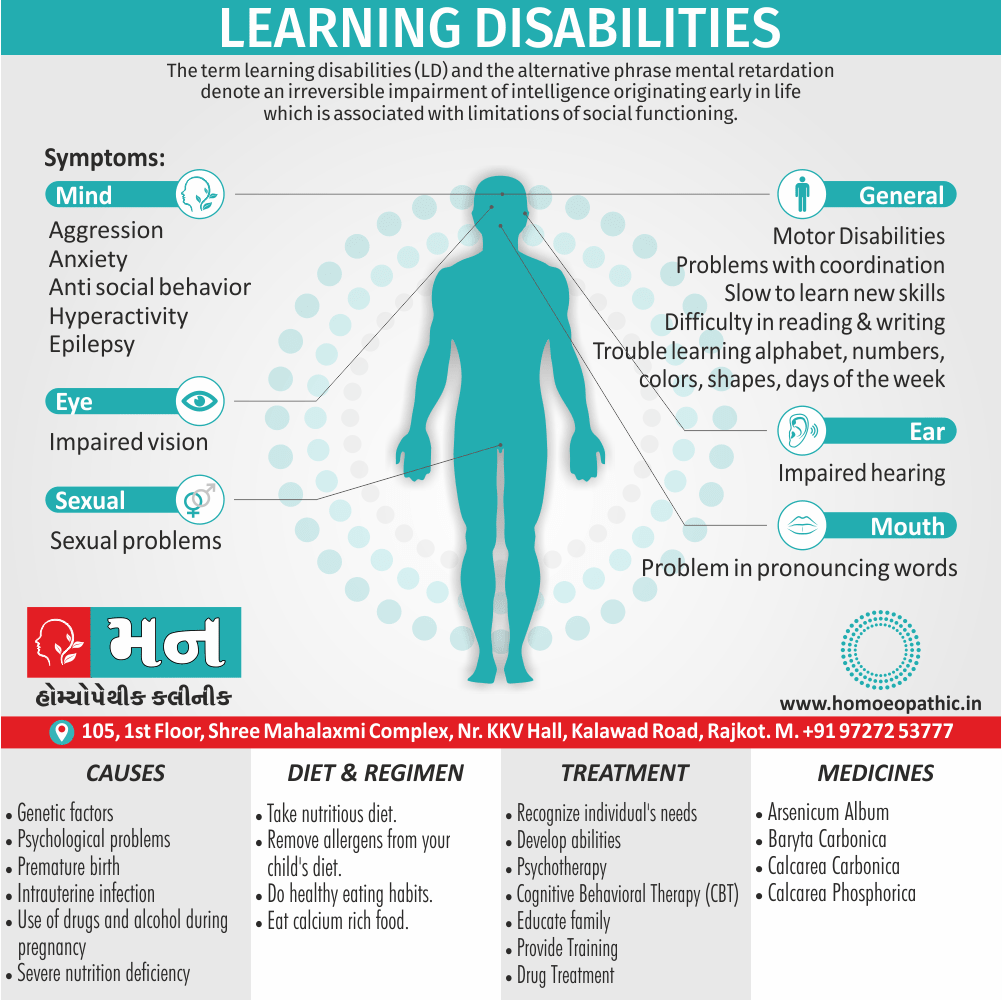
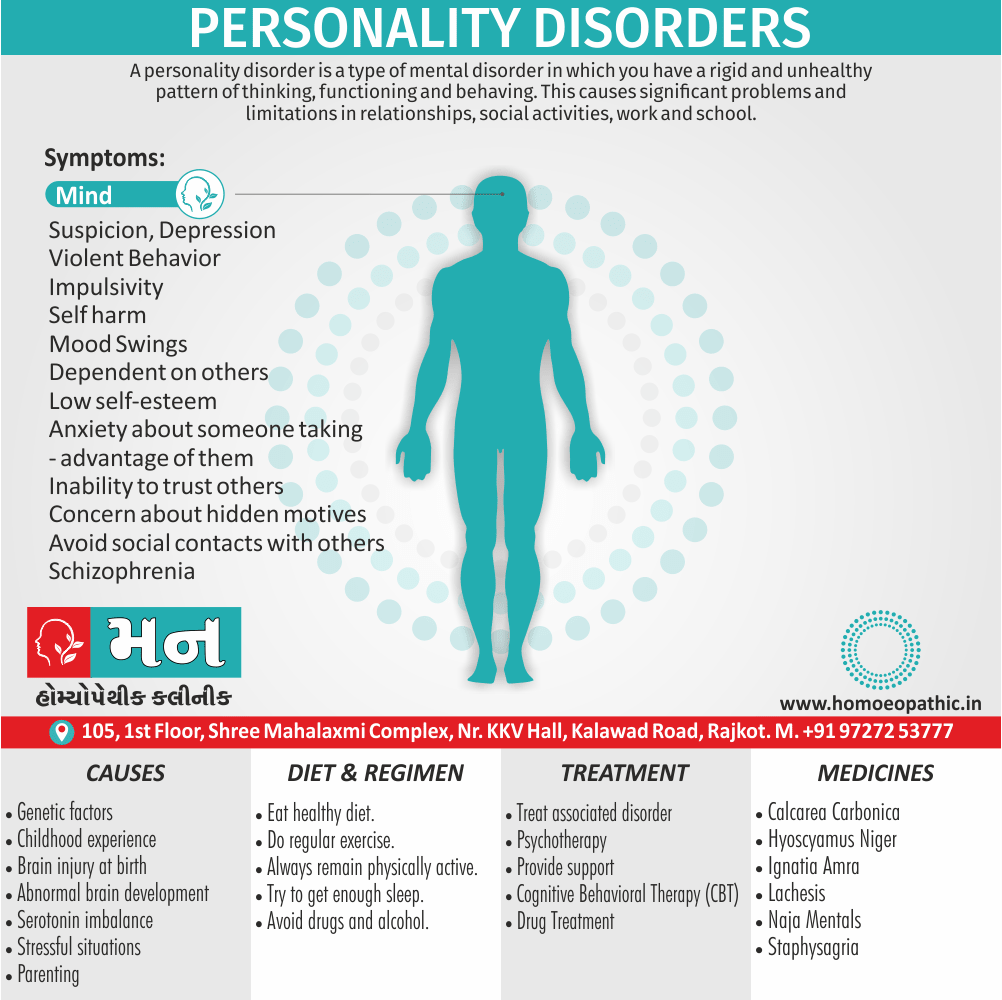
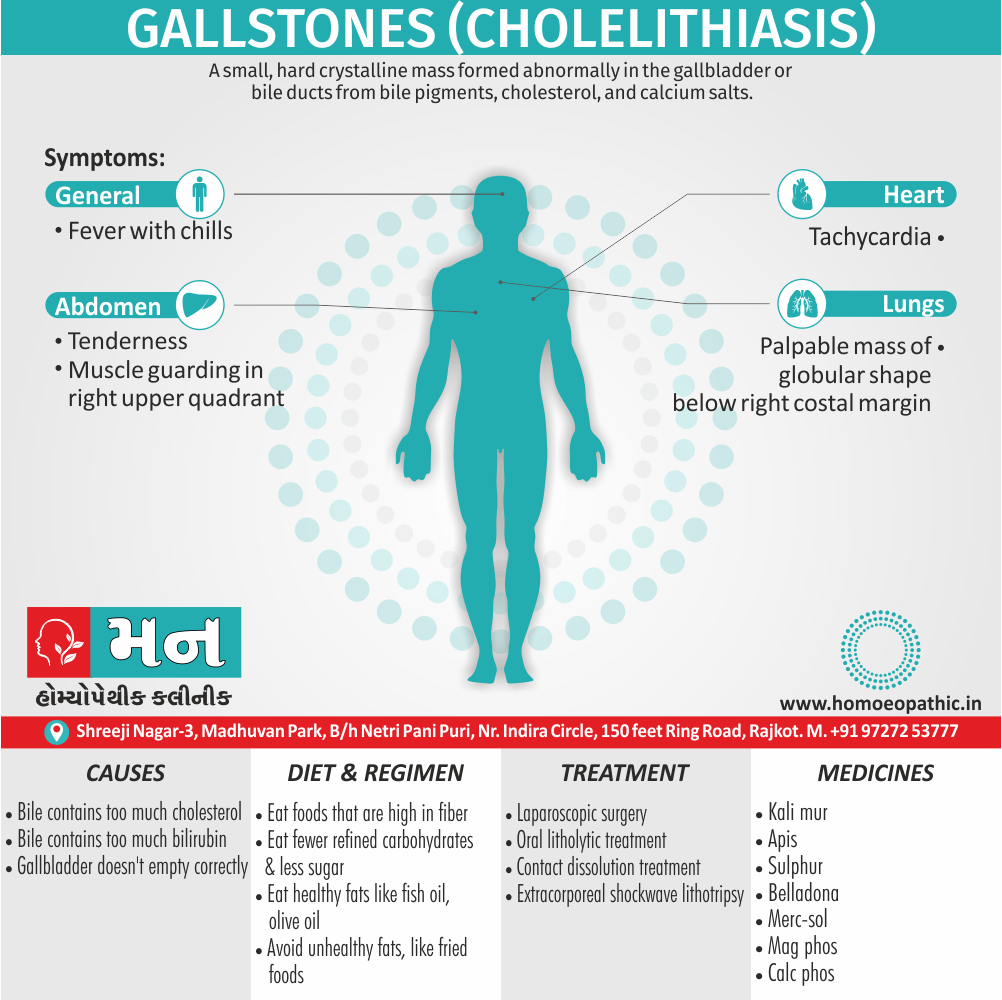
Causes of Cannabis Use Disorder
There are many causes of this Disorder:
- The leading cause of this disorder is using marijuana for longer periods of time.
- Using larger amounts of cannabis over time.
- History of cannabis abuse among family members or friends.
- Lack of support during times of stress.
- Genetic factors can be responsible since there is some research that shows the risk of substance abuse increases with genetics.(4)
Risk factors of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Certain factors are considered to heighten the risk of developing cannabis dependence and longitudinal studies over a number of years have enabled researchers to track aspects of social and psychological development concurrently with cannabis use.
- Increasing evidence is being shown for the elevation of associated problems by the frequency and age at which cannabis is used, with young and frequent users being at most risk.
- The main factors in Australia, for example, related to a heightened risk for developing problems with cannabis use include frequent use at a young age; personal maladjustment; emotional distress; poor parenting; school drop-out; affiliation with drug-using peers; moving away from home at an early age; daily cigarette smoking; and ready access to cannabis.
- The researchers concluded there is emerging evidence that positive experiences to early cannabis use are a significant predictor of late dependence and that genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of problematic use.(2)
Pathophysiology of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Prolonged and heavy cannabis use can alter brain circuitry. However, the specific pathophysiological mechanisms are yet unclear.
- In terms of addiction, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary molecule responsible for the reinforcing properties of marijuana.
- Interestingly, despite the striatal dopamine system typically being involved with substances of abuse such as alcohol and opioids, meta-analysis reveals insufficient evidence at this time to support such a conclusion for cannabis. And also that dopamine receptors may not be involved.
- At a symptomatic level, heavy use modifies conscious experience by altering the brain’s network for self-awareness. By reducing anxiety and impairing memory, it also affects motivation and personal experience. At a molecular level, the story is more complex.
- The botanical provides over 500 different active chemical compounds, which interact with numerous molecular targets, thereby modulating the transmission of endocannabinoids, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and serotonin.
- Psychoactive effects are primarily derived from tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which binds cannabinoid receptors (CB)1 and CB2.CB1 receptors are located throughout the central nervous system (CNS), lungs, liver, and kidneys. CB2 receptors predominate within the immune hematopoietic cells.
- Binding these receptors modulates G-protein-coupled inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, thereby influencing pain, mood, appetite, nausea, and sexual activity.
- CNS effects also appear to be mediated by glial cells, particularly microglia and astrocytes. In vitro studies show microglial to produce greater endocannabinoids than neurons, and astrocytes may play a role in signaling by regulating endocannabinoid turnover.
- Thus an influence of the neuropil, not just the neurons, may better describe the CNS changes mediated by cannabis. (3)
Types of Cannabis Use Disorder
There are three types of cannabis use disorder:
- Mild (2 or 3 criteria)
- Moderate (4 or 5 criteria)
- Severe (6 or more criteria)
The list of the criteria used is:
Unsafe use, social problems, avoidance of major responsibilities, withdrawal of the drug, tolerance level to drug use, usage of large amounts of the drug, usage for long periods of time, effort to quit using, reserving more time for use, physical or mental health problems due to using the drug or dependence, giving up activities, and cravings. (4)
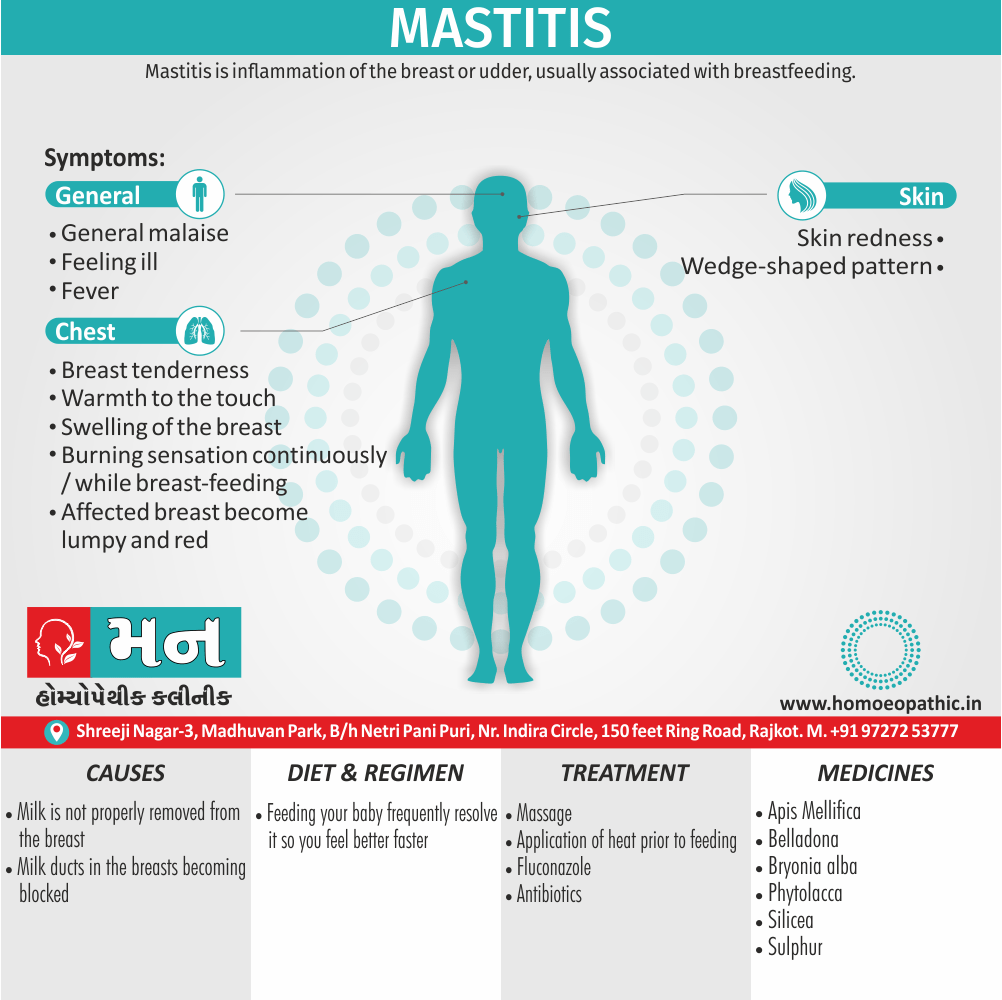
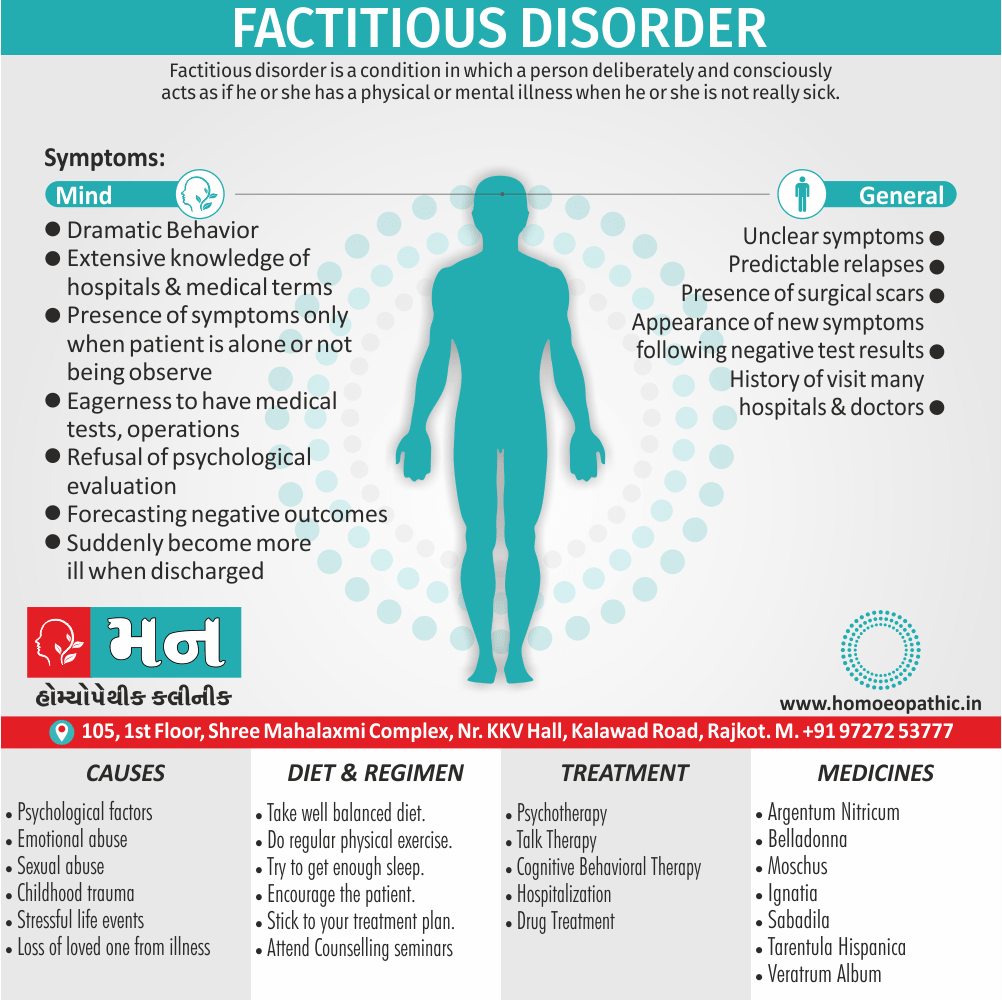
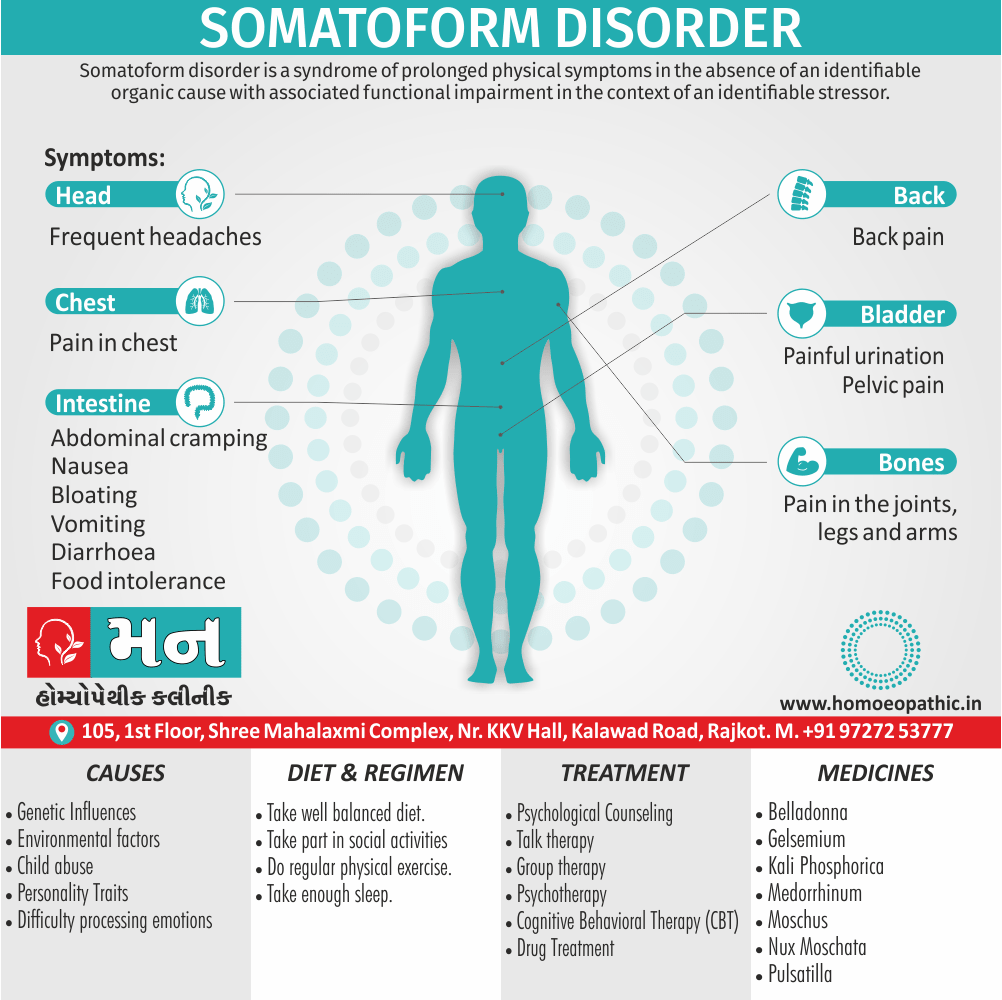
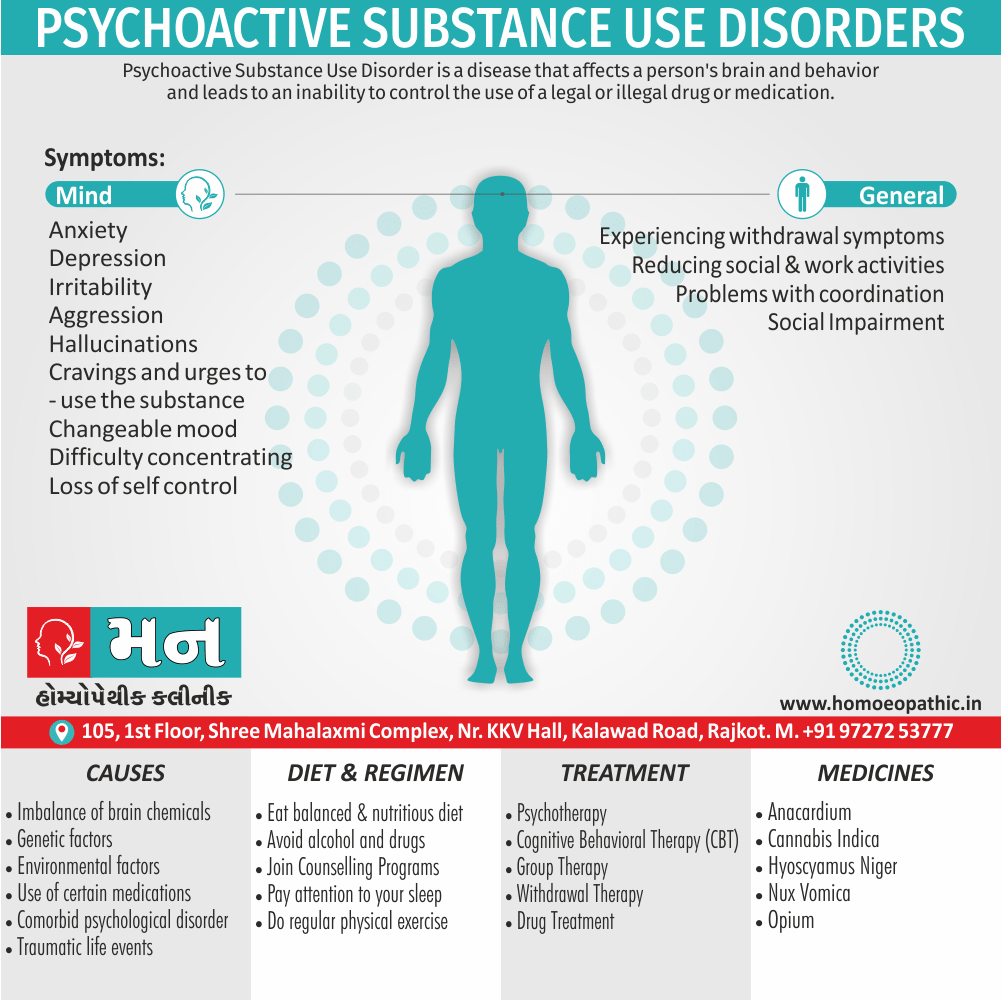
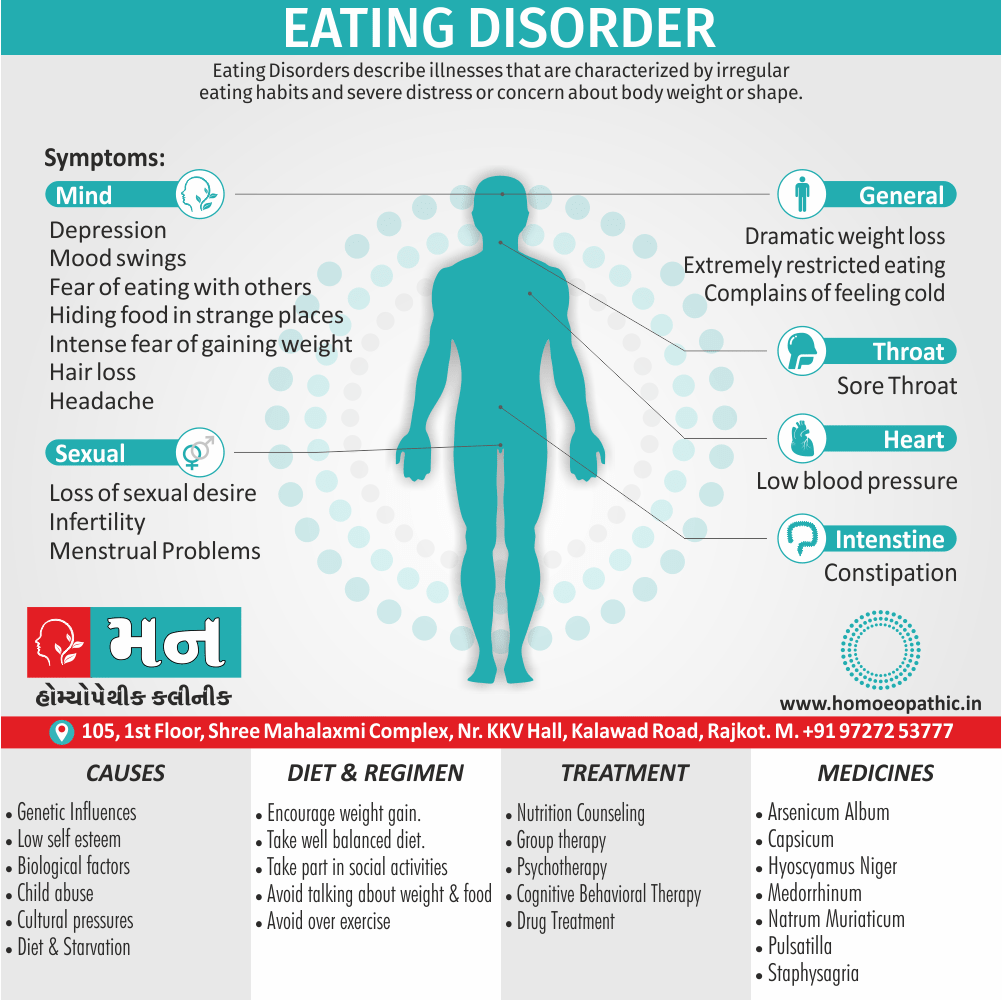
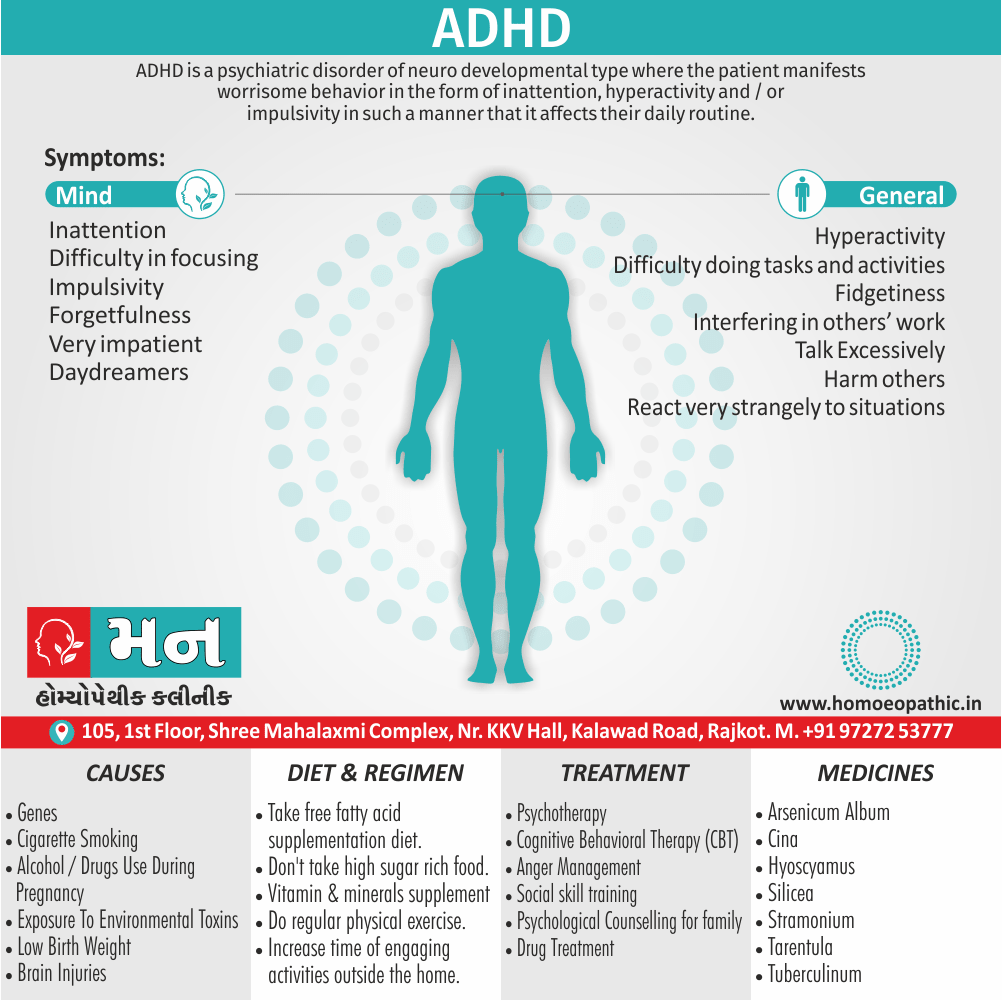
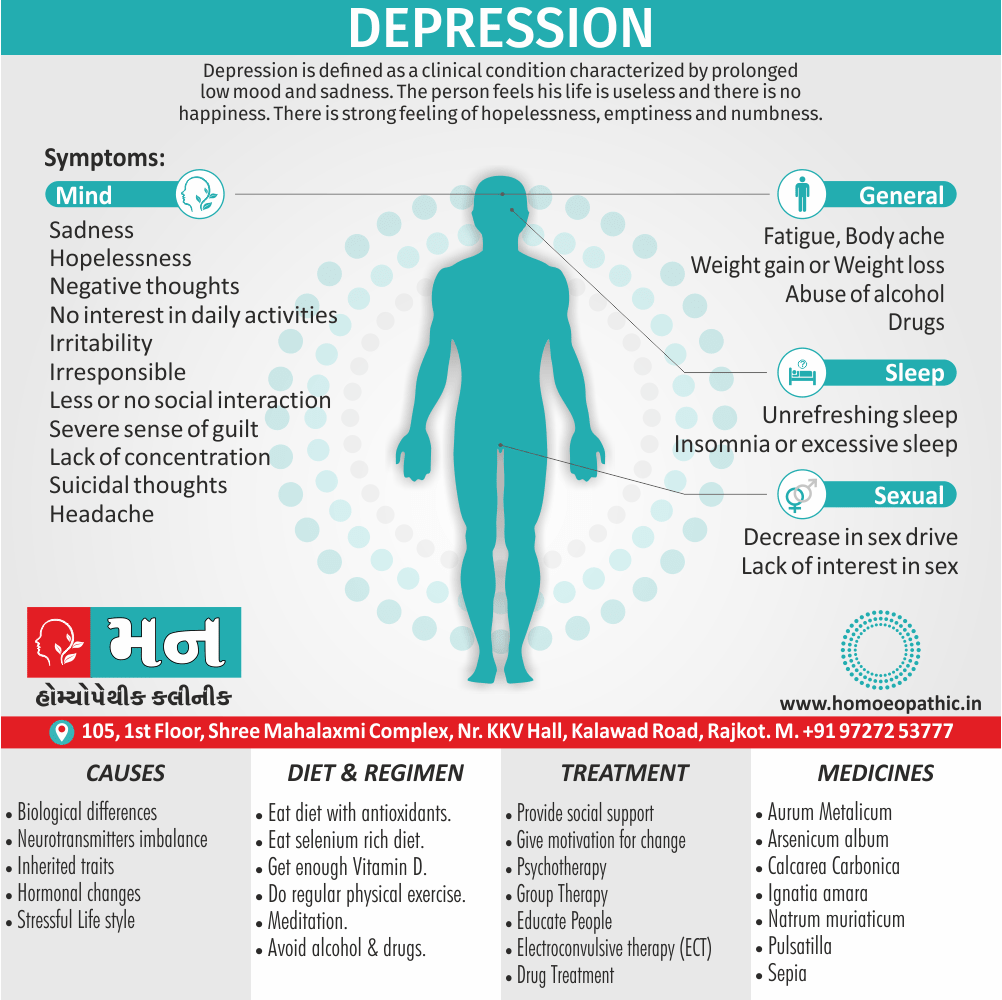
Sign & Symptoms of Cannabis Use Disorder
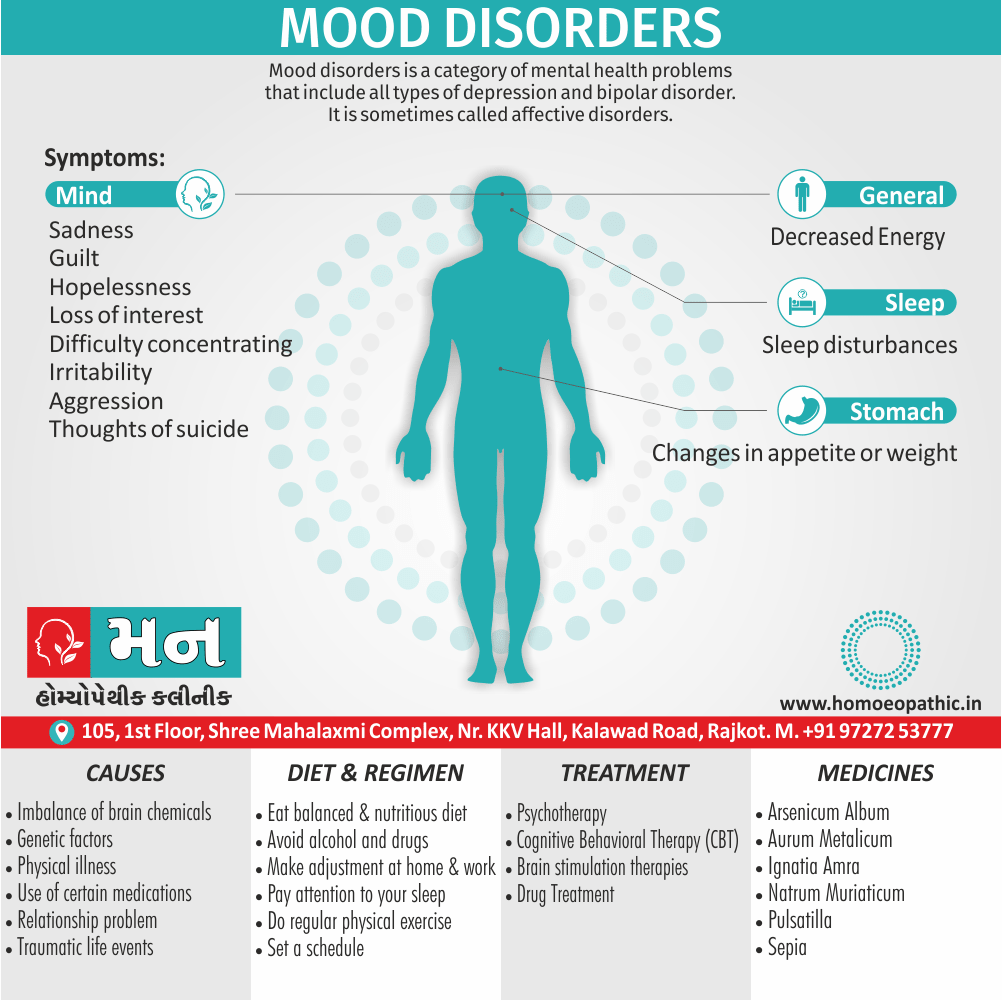
Using cannabis can result in psychological problems or disorders. Some of these are:
- Mood swings
- Panic attacks
- Personality disorders
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Dysphoria
- Irritability
- Anger
- Nervousness
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Impulsivity
- Sleep difficulties
- Loss of appetite and eating disorders
- Cognitive issues
- Social withdrawal
- Poor judgment and decision making skills
- Criminal behavior
- Driving issues
- Damage to short-term memory
- Learning difficulties
- Delusions / illusions
- Hallucinations
- Euphoria
- Respiratory issues
- Lung cancer
- Trouble concentrating
- Tooth decay
- Restlessness
- Gums disease
- Poor performance at school
- Photophobia
- Lacrimation (4)
Diagnosis of Cannabis Use Disorder
An accurate self-diagnosis is not possible. A diagnosis must be determined by a mental health or health care professional.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the criteria is:
- Persistent or recent use of cannabis (marijuana)
- Changes in behavior which are clinically significant, and are developed after using the drug
- Development of following two or more signs within two hours of cannabis use. Irritation of conjunctiva of the eye, increased appetite, dryness of the mouth, increased heart rate (tachycardia) (4)
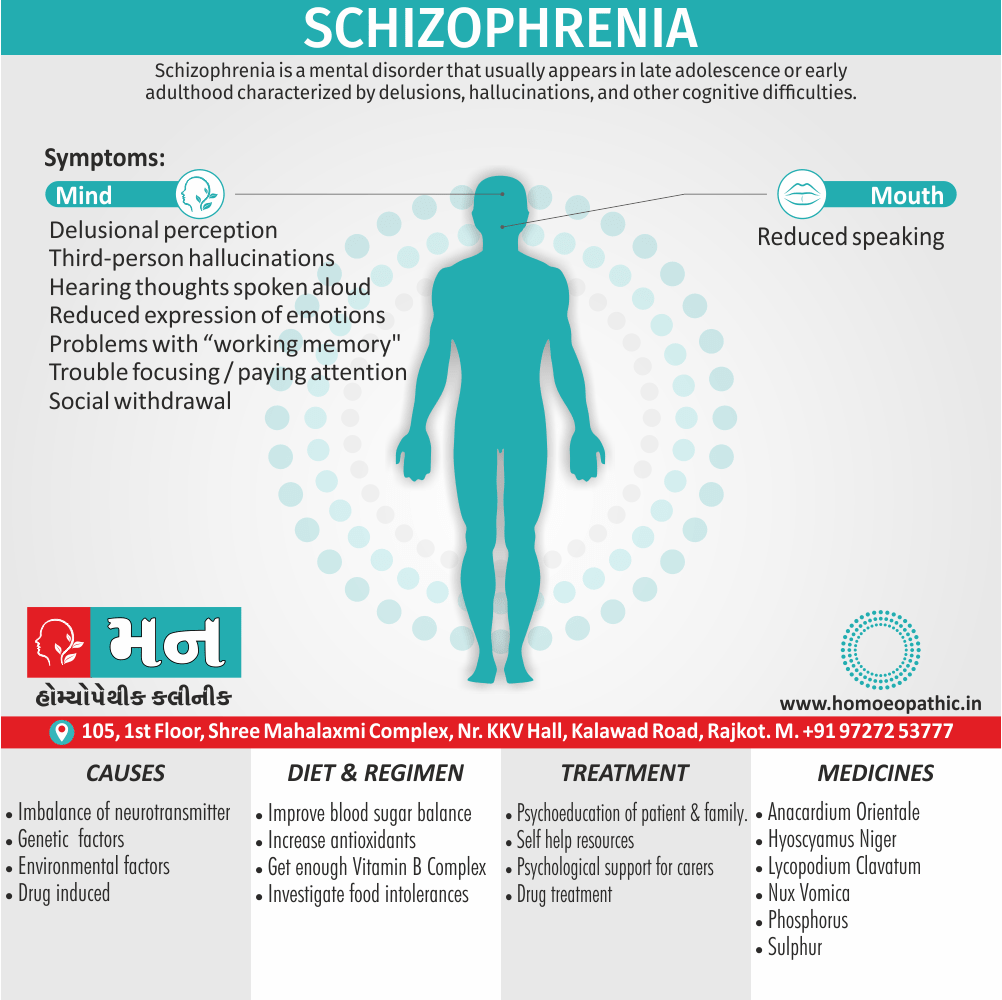
Differential diagnosis of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Intoxication syndromes
- Amphetamine or cocaine intoxication
- Endogenous psychiatric disorders
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Schizophrenia spectrum disorder
Treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder
Contingency Management:
- This is when a person is monitored for their behavior and is rewarded for positive behavior. If drug use occurs the reward is taken back.
Motivational Enhancement Therapy:
- This therapy is targeted at the mindset of the person which brings about greater inspiration and greater contribution in the Cannabis Use Disorder treatment. It is intended to produce rapid results.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy:
- In cognitive-behavioral therapy, the affected individual learns different methods to cope with the negative feelings and how to replace them with positive ones rather than using marijuana as an escape or way to cope with their problems.
Medications:
- There are no medications available for treating cannabis use disorder. Medication can only be used to help minimize withdrawal symptoms.(4)
Prevention of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Parents should monitor their children’s activities. They should supervise and maintain proper communication so that children share their struggles and problems freely with them rather than using marijuana to escape their problems or to cope with anxiety.
- Children should be made aware of the harmful effects of cannabis use. Efforts are needed to prevent the criminal sale of this drug.
Self Help:
- People who want to stop using cannabis can join a group in which other members provide motivation to stop, support, and care about each other.
- If a person is heavily dependent on cannabis, self-help is not a good option and the person would be better suited by participating in a substance abuse cannabis use disorder treatment program. (4)
Complications of cannabis use disorders
1. Transient or short-lasting psychiatric disorders e.g.:
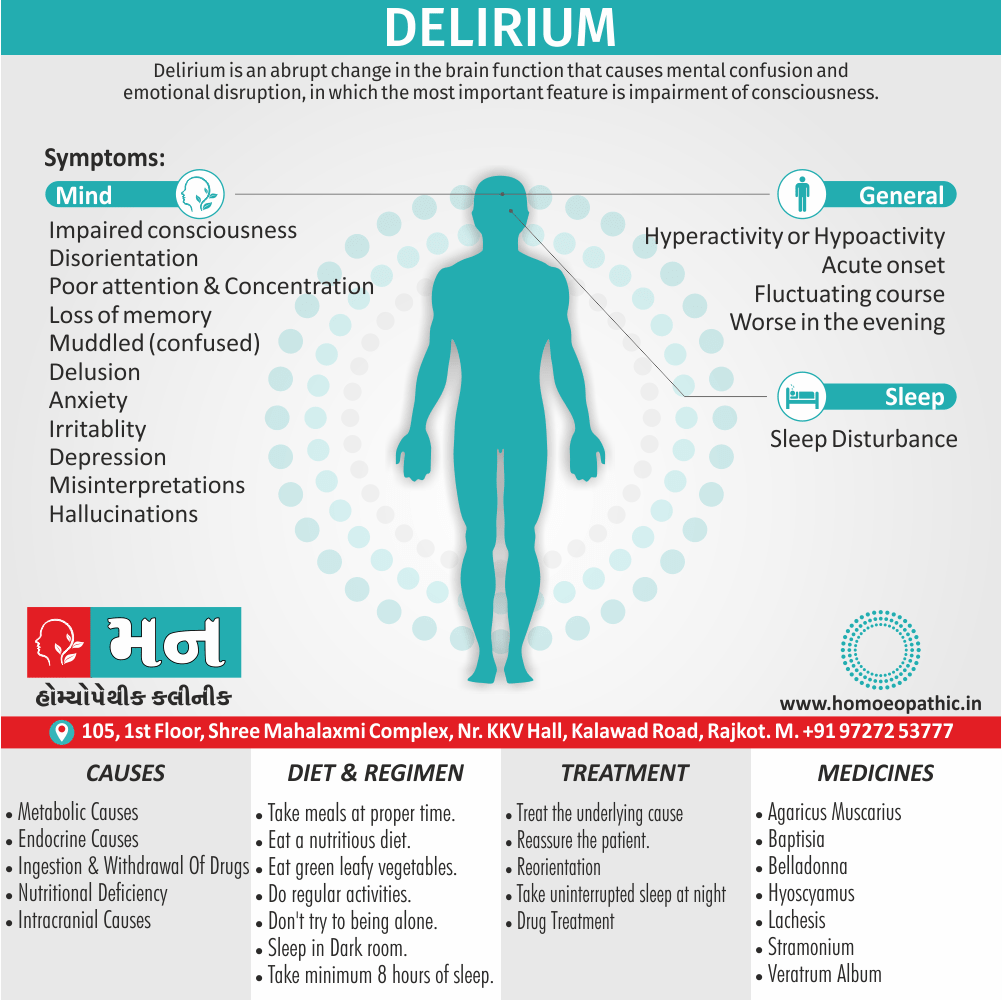
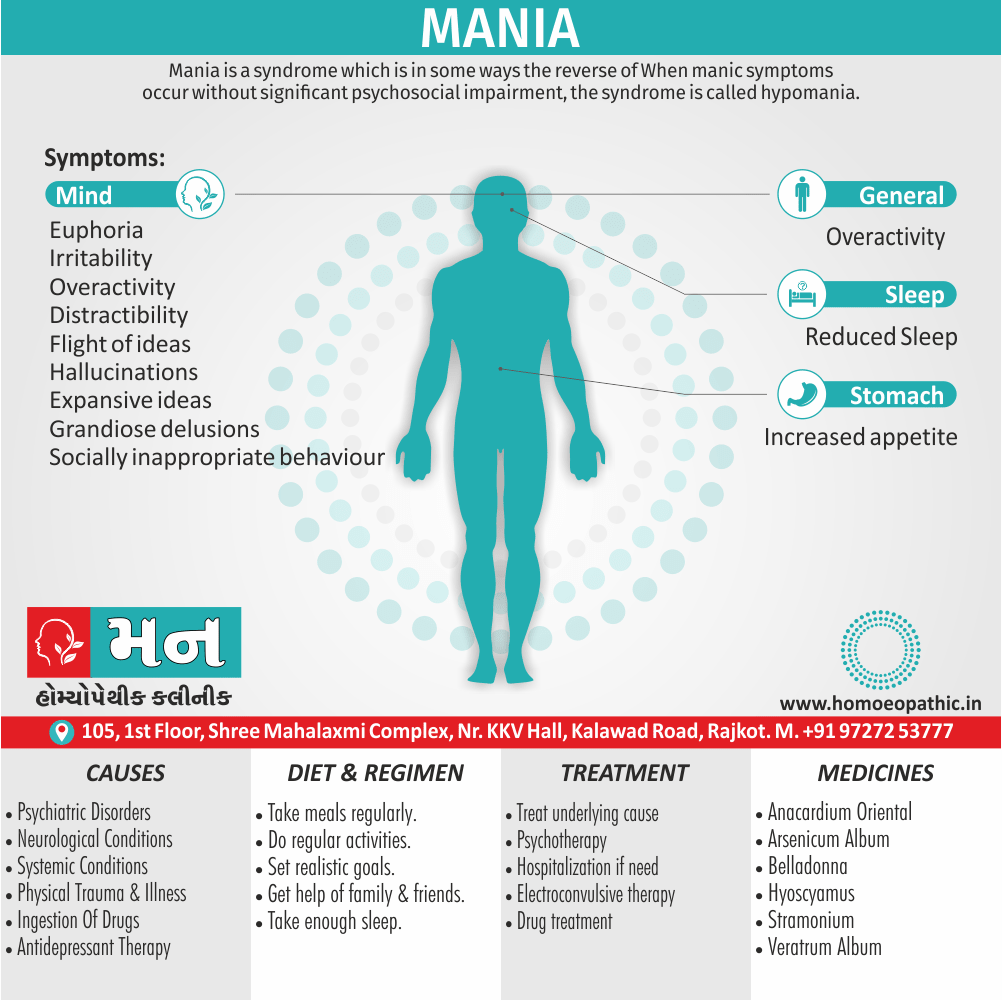
Acute anxiety, overly suspicious psychosis, vehement fugue-like states, suicidal ideation, hypomania, schizophrenia-like state (e.g. persecutory delusions, hallucinations and at times catatonic symptoms), acute organic psychosis and, very rarely, depression.
2. A motivational syndrome e.g.:
Chronic cannabis use is postulated to cause lethargy, apathy, loss of interest, anergia, reduced drive and lack of ambition. Additionally, The aetiological role of cannabis in this disorder is however far from proven.
3. ‘Hemp insanity’ or cannabis psychosis i.e.:
It was described as being similar to an acute schizophreniform disorder with disorientation and confusion, and with a good prognosis. Furthermore, The validity of this specific disorder is currently doubted.
4. Other complications i.e.:
Chronic cannabis use sometimes leads to memory impairment, either worsening or relapse in schizophrenia or mood disorder, chronic obstructive airway disease, pulmonary malignancies, alteration in both the humoral also cell-mediated immunity, decreased testosterone levels, anovulatory cycles, reversible inhibition of spermatogenesis, blockade of gonadotropin releasing hormone, also increased risk for the developing foetus (if taken during pregnancy).
Homoeopathic Treatment:
Homeopathic Treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
Which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Cannabis Use Disorder:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
Medicines:
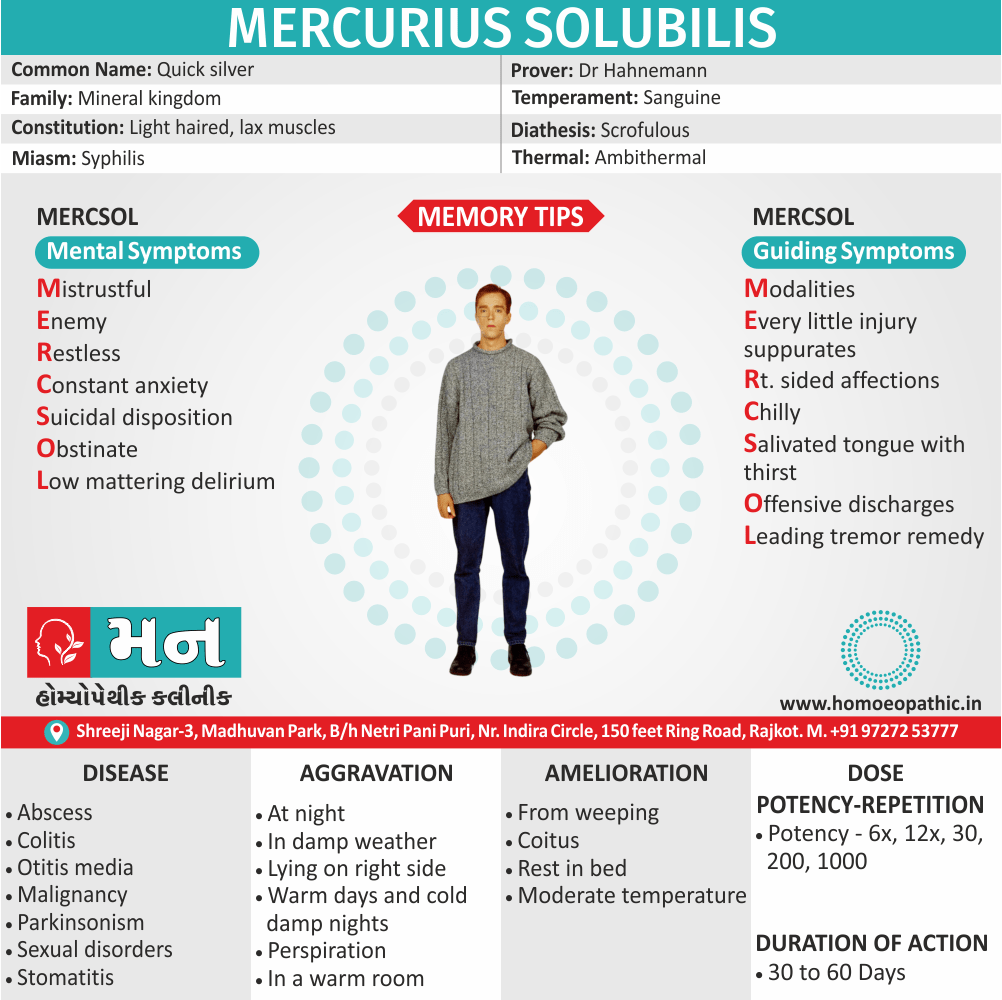
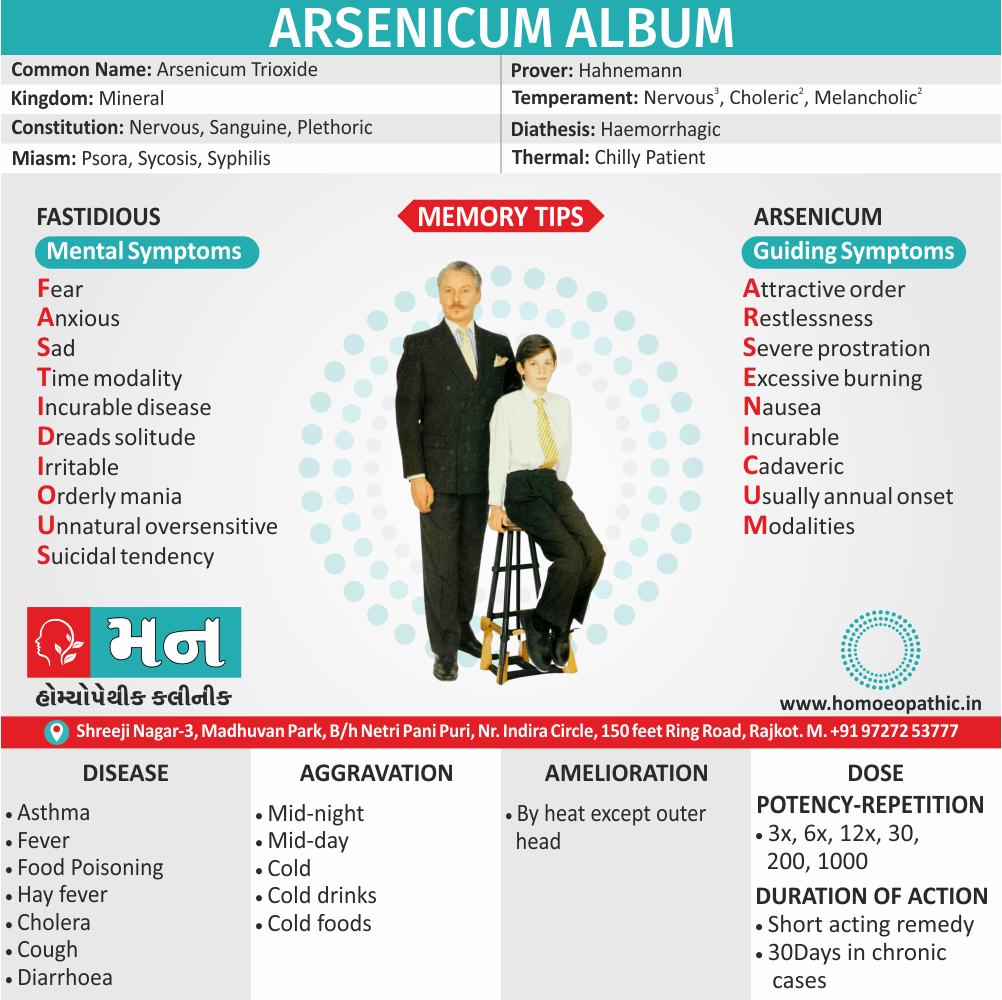
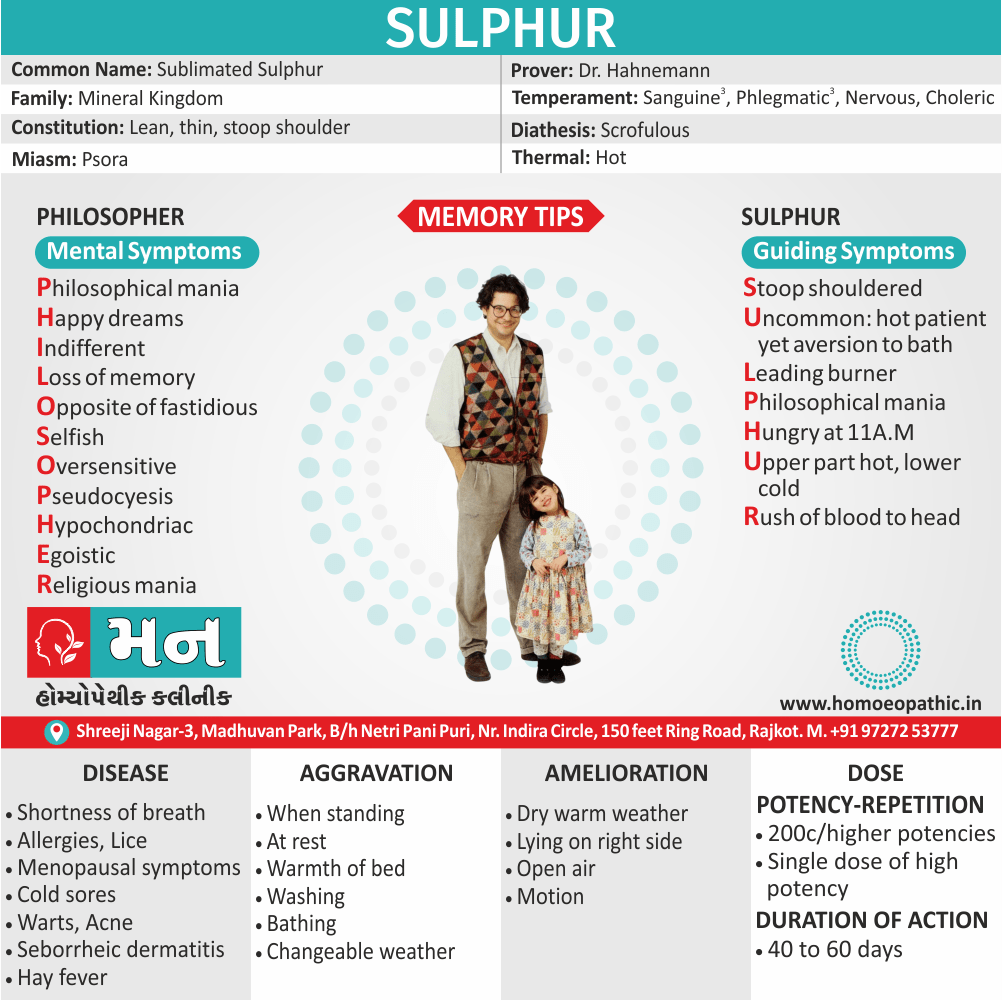
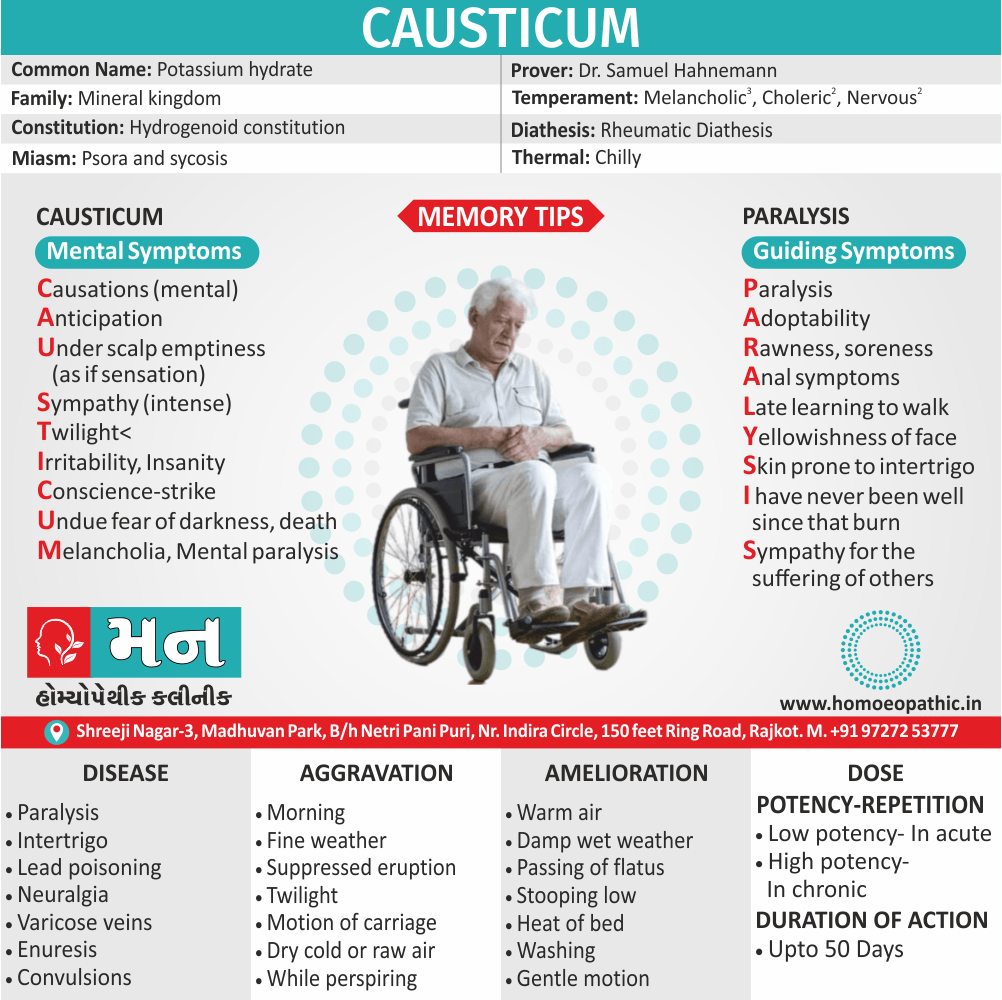
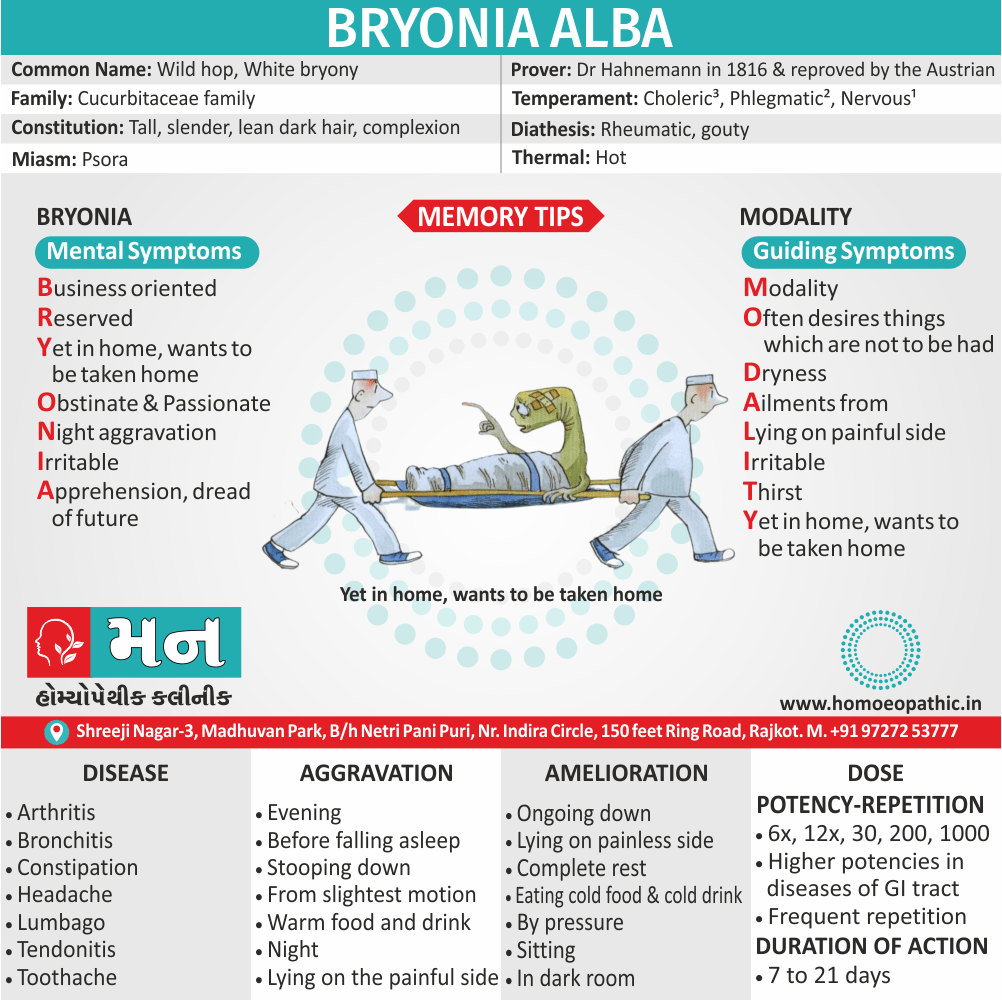
Avena Sativa: Best homeopathic medicine for drug addiction when dealing with withdrawal symptoms.
- The effects of morphine or heroin, as well as of cocaine, tobacco, marijuana, and valium, are treated effectively with Avena Sativa.
- It is one of the best ways to overcome morphine addiction.
- Avena Sativa works very well in treating insomnia due to drugs or alcohol.
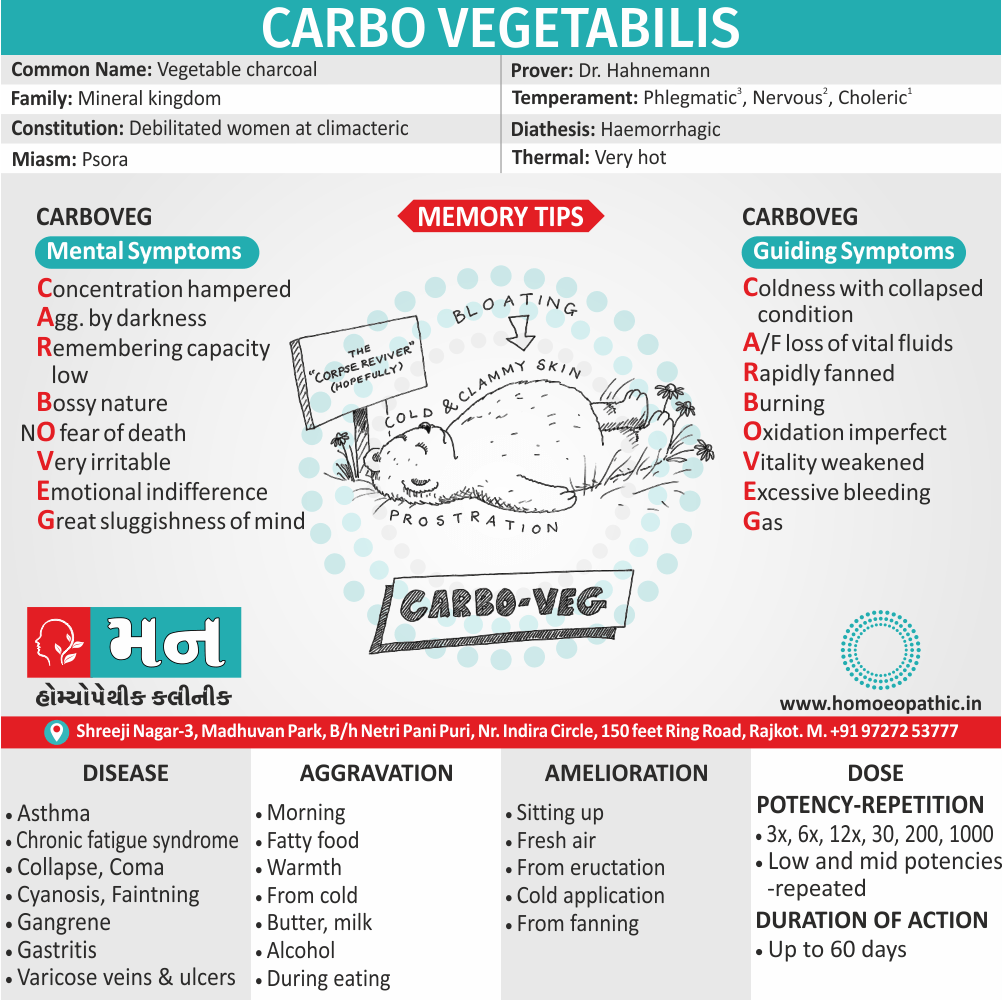
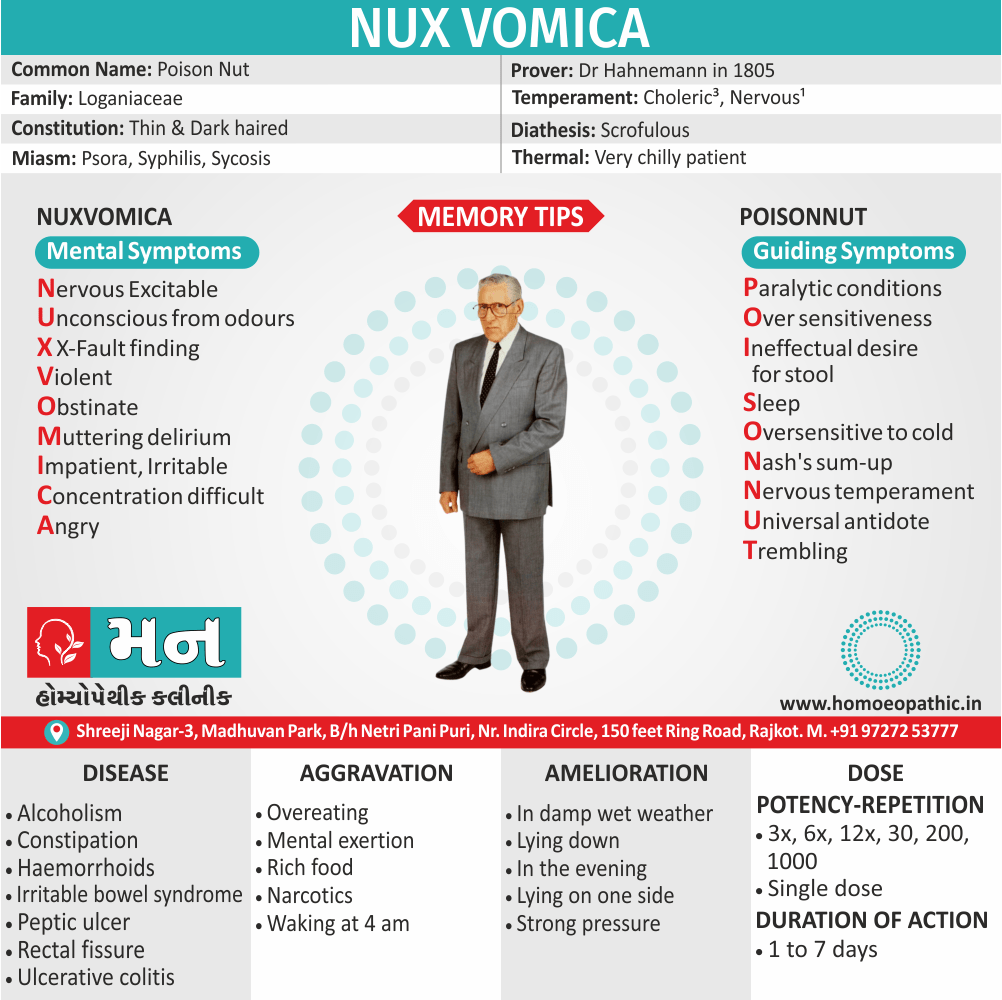
Nux Vomica: Homeopathic treatment for drug addiction with abdominal symptoms, nausea and vomiting.
- Sour taste and nausea in the morning, accompanied by retching, is an indicator for the use of Nux Vomica.
- The stomach is very sensitive to pressure when applied externally.
- The patient feels Intoxicated; the feeling is worse in the morning.
- The patient may complain of vertigo with momentary loss of consciousness.
- Indigestion caused by alcohol, coffee, and other drugs is treated well with Nux Vomica.
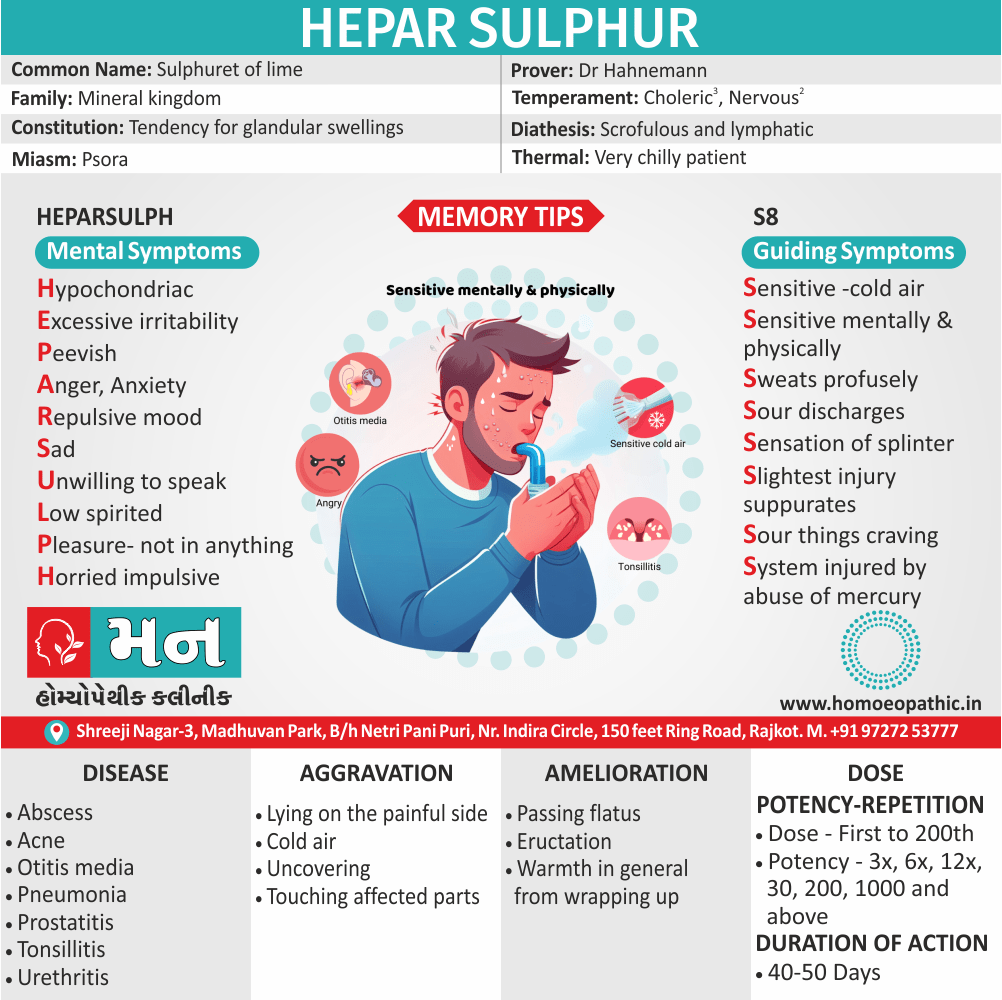
Morphinum: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with heart symptoms.
- In cases indicating the use of homeopathic medicine Morphinum, there is a violent throbbing in the heart along with a small and weak pulse.
- There may be a sudden alteration in the heart rate which is known as tachycardia or fast heart rate, and bradycardia or slow heart rate.
- The patient may be delirious and suffer from depression.
- Morphinum also works well for cases of drug addiction in which the patient is in a dream-like state and feels indifference.
Coffea: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with marked insomnia after a phase of excitement.
- The patient experiences increased energy, ecstasy, sleeplessness on account of excess mental activity, and an increased flow of ideas.
- He is unable to sleep from an excessive intake of coffee.
- The patient experiences great loquacity, his brain feels clear, and he is extremely active.
- The patient also feels strong enough to do anything.
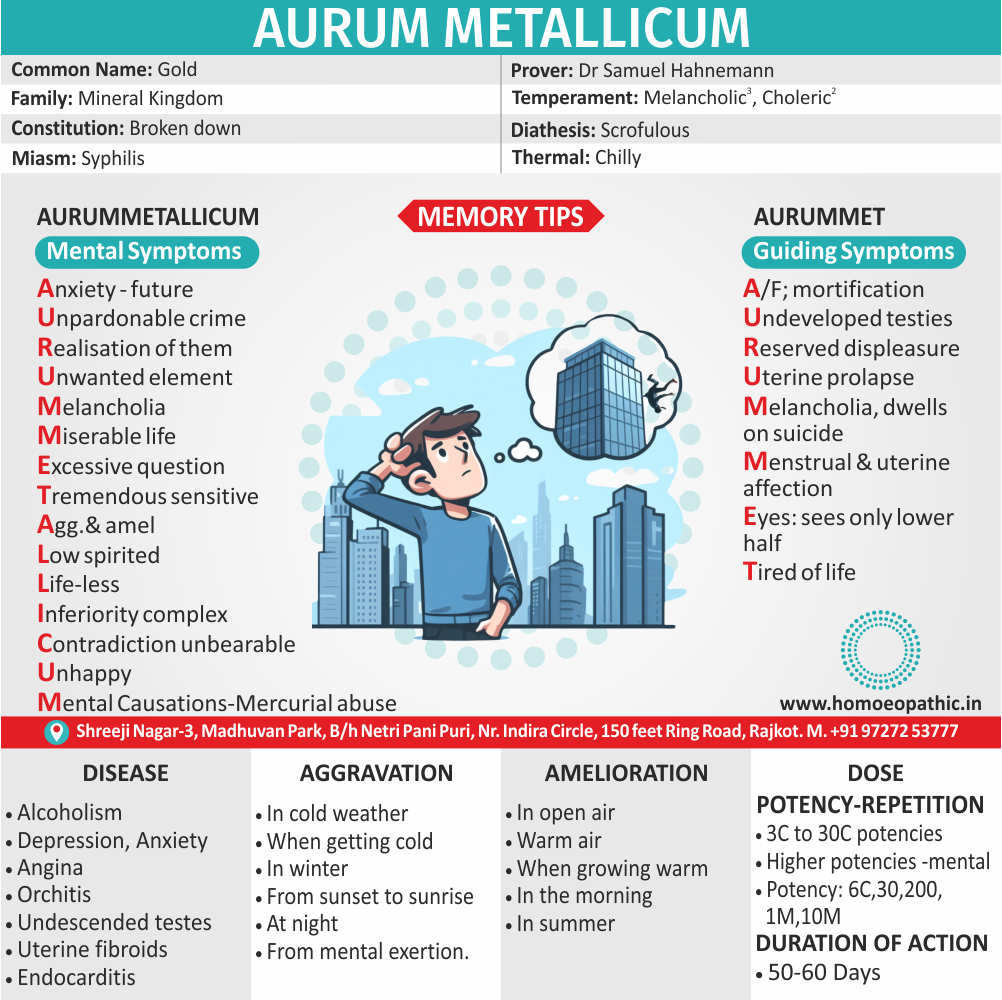
Hyoscyamus: Homeopathic treatment for drug addiction accompanied by hallucinations and delusions.
- The patient experiences a confused mind and seems intoxicated, laughs, sings, recites poetry, and babbles deliriously.
- The patient does foolish things and does not behave normal.
- Hyoscyamus also helps patients with an addiction to alcohol and those who experience intoxicated rages.
- In such cases, there is involuntary urination along with hallucinations.
Opium: Suitable homeopathic medicine for drug addiction accompanied by drowsiness.
- The patient falls into a heavy and deep sleep, he wants nothing, and says that nothing ails him.
- The patient is hot, sweaty, drowsy and has cold limbs.
- The complaints are accompanied by a heavy, deep sleep, and noisy, laboured breathing.
- Loss of consciousness and a coma from drug overdose is also treated well with Opium.
Sulphuricum Acidum: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with a craving for alcoholic stimulants.
- The patient experiences hot flushes, trembling, and cold sweats, accompanied by humming and tickling in the ears.
- Sour vomiting and hiccoughs, along with nausea and shivering, is effectively treated with Sulphuricum Acidum.(5)
Diet & Regimen of Cannabis use disorder
- Eat law fat food
- Take enough sleep
- Do regular physical exercise
- Stay away from cigarette & alcohol
Reference:
- Short Textbook of Psychiatry by Niraj Ahuja / Ch 4
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabis_use_disorder
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538131/
- https://www.firstlightpsych.com/blog/addictions/cannabis-use-disorder-and-cannabis-dependence-disorder#factors
- https://www.drhomeo.com/homeopathic-treatment/homeopathic-treatment-drug-addiction/
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cannabis Use Disorder?
In Cannabis use disorder, Cannabis is derived from the hemp plant, Cannabis sativa, which has several varieties named after the region in which it is found.
What is Acute intoxication of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Impairment of consciousness also orientation
- Lightheadedness
- Tachycardia
- Sense of floating in the air
- Euphoric dream-like state
- Alternation in psychomotor activity and tremors
- Photophobia, also Lacrimation
- Reddening of conjunctiva
- Dry mouth, also Increased appetite
Give complications of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Either Transient or short-lasting psychiatric disorders
- Motivational syndrome
- Either ‘Hemp insanity’ or cannabis psychosis
- Schizophrenia
- Chronic obstructive airway disease
- Pulmonary malignancies
What is the treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Firstly, Psychotropic medication
- Secondly, Sometimes hospitalization
- Thirdly, Psychotherapy
- Lastly, Psychoeducation
Definition:
People who use marijuana will develop marijuana use disorder, meaning that they are unable to stop using marijuana even though it’s causing health and social problems in their lives.
Overview
Epidemiology
Causes
Risk Factors
Types
Pathophysiology
Clinical Features
Sign & Symptoms
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Investigations
Treatment
Prevention
Homeopathic Treatment
Diet & Regimen
Do’s and Dont’s
Terminology
References
FAQ
Also Search As
Overview
Overview of Cannabis Use Disorder:
In Cannabis use disorder, Cannabis is derived from the hemp plant, Cannabis sativa, which has several varieties named after the region in which it is found (e.g. sativa indica in India and Pakistan, and americana in America).
Street names: Grass, Hash or Hashish, Marijuana.
Cannabis produces more than 400 identifiable chemicals of which about 50 are cannabinoids, the most active being Δ-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC). The pistillate form of the female plant is more important in cannabis production.
Recently, a Gi-protein (in other words, inhibitory G-protein) linked cannabinoid receptor has found (especially, in basal ganglia, hippocampus and cerebellum) which inhibits the adenylate cyclase activity in a dose-dependent manner.
Cannabis produces a very mild physical dependence, with a relatively mild withdrawal syndrome, i.e.
- Fine tremors
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
- Decreased appetite also craving
In detail, this syndrome begins within few hours of stopping cannabis use also lasts for 4 to 5 days. However, some health professionals feel that there is no true physical dependence with cannabis.
On the other hand, psychological dependence ranges from mild (in other words, occasional ‘trips’) to marked (e.g. compulsive use). Furthermore, All the active ingredients called as marijuana or marihuana.
It can detected in urine for up to 3 weeks after chronic heavy use.
Preparation of Cannabis :
| Cannabis Preparations | Portion of Plant | THC Content(%) |
Potency(as compared to ‘Bhang’) |
| 1. Hashish or Charas | Resinous exudate especially from the flowering tops of cultivated plants | 8-14 | 10 |
| 2. Ganja | Small leaves also brackets of inflorescence of highly cultivated plants | 1-2 | 2 |
| 3. Bhang | Dried leaves, flowering shoots also cut tops of uncultivated plants | 1 | 1 |
| 4. Hash oil | Specifically Lipid soluble plant extract | 15-40 | 25 |
Epidemiology
Indian epidemiology then other
Causes
Causes of Cannabis Use Disorder
There are many causes of this Disorder:
- The leading cause of this disorder is using marijuana for longer periods of time.
- Using larger amounts of cannabis over time.
- History of cannabis abuse among family members or friends.
- Lack of support during times of stress.
- Genetic factors can be responsible since there is some research that shows the risk of substance abuse increases with genetics.(4)
Risk Factors
Risk factors of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Certain factors are considered to heighten the risk of developing cannabis dependence and longitudinal studies over a number of years have enabled researchers to track aspects of social and psychological development concurrently with cannabis use.
- Increasing evidence is being shown for the elevation of associated problems by the frequency and age at which cannabis is used, with young and frequent users being at most risk.
- The main factors in Australia, for example, related to a heightened risk for developing problems with cannabis use include frequent use at a young age; personal maladjustment; emotional distress; poor parenting; school drop-out; affiliation with drug-using peers; moving away from home at an early age; daily cigarette smoking; and ready access to cannabis.
- The researchers concluded there is emerging evidence that positive experiences to early cannabis use are a significant predictor of late dependence and that genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of problematic use.(2)
Types
Types of Cannabis Use Disorder
There are three types of cannabis use disorder:
- Mild (2 or 3 criteria)
- Moderate (4 or 5 criteria)
- Severe (6 or more criteria)
The list of the criteria used is:
Unsafe use, social problems, avoidance of major responsibilities, withdrawal of the drug, tolerance level to drug use, usage of large amounts of the drug, usage for long periods of time, effort to quit using, reserving more time for use, physical or mental health problems due to using the drug or dependence, giving up activities, and cravings. (4)
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Prolonged and heavy cannabis use can alter brain circuitry. However, the specific pathophysiological mechanisms are yet unclear.
- In terms of addiction, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary molecule responsible for the reinforcing properties of marijuana.
- Interestingly, despite the striatal dopamine system typically being involved with substances of abuse such as alcohol and opioids, meta-analysis reveals insufficient evidence at this time to support such a conclusion for cannabis. And also that dopamine receptors may not be involved.
- At a symptomatic level, heavy use modifies conscious experience by altering the brain’s network for self-awareness. By reducing anxiety and impairing memory, it also affects motivation and personal experience. At a molecular level, the story is more complex.
- The botanical provides over 500 different active chemical compounds, which interact with numerous molecular targets, thereby modulating the transmission of endocannabinoids, gamma-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and serotonin.
- Psychoactive effects are primarily derived from tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which binds cannabinoid receptors (CB)1 and CB2.CB1 receptors are located throughout the central nervous system (CNS), lungs, liver, and kidneys. CB2 receptors predominate within the immune hematopoietic cells.
- Binding these receptors modulates G-protein-coupled inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, thereby influencing pain, mood, appetite, nausea, and sexual activity.
- CNS effects also appear to be mediated by glial cells, particularly microglia and astrocytes. In vitro studies show microglial to produce greater endocannabinoids than neurons, and astrocytes may play a role in signaling by regulating endocannabinoid turnover.
- Thus an influence of the neuropil, not just the neurons, may better describe the CNS changes mediated by cannabis. (3)
Clinical Features
Tab Content
Sign & Symptoms
Sign & Symptoms of Cannabis Use Disorder
Using cannabis can result in psychological problems or disorders. Some of these are:
- Mood swings
- Panic attacks
- Personality disorders
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Dysphoria
- Irritability
- Anger
- Nervousness
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Impulsivity
- Sleep difficulties
- Loss of appetite and eating disorders
- Cognitive issues
- Social withdrawal
- Poor judgment and decision making skills
- Criminal behavior
- Driving issues
- Damage to short-term memory
- Learning difficulties
- Delusions / illusions
- Hallucinations
- Euphoria
- Respiratory issues
- Lung cancer
- Trouble concentrating
- Tooth decay
- Restlessness
- Gums disease
- Poor performance at school
- Photophobia
- Lacrimation (4)
Clinical Examination
Tab Content
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Cannabis Use Disorder
An accurate self-diagnosis is not possible. A diagnosis must be determined by a mental health or health care professional.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the criteria is:
- Persistent or recent use of cannabis (marijuana)
- Changes in behavior which are clinically significant, and are developed after using the drug
- Development of following two or more signs within two hours of cannabis use. Irritation of conjunctiva of the eye, increased appetite, dryness of the mouth, increased heart rate (tachycardia) (4)
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Intoxication syndromes
- Amphetamine or cocaine intoxication
- Endogenous psychiatric disorders
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Schizophrenia spectrum disorder
Complications
Complications of cannabis use disorders
1. Transient or short-lasting psychiatric disorders e.g.:
Acute anxiety, overly suspicious psychosis, vehement fugue-like states, suicidal ideation, hypomania, schizophrenia-like state (e.g. persecutory delusions, hallucinations and at times catatonic symptoms), acute organic psychosis and, very rarely, depression.
2. A motivational syndrome e.g.:
Chronic cannabis use is postulated to cause lethargy, apathy, loss of interest, anergia, reduced drive and lack of ambition. Additionally, The aetiological role of cannabis in this disorder is however far from proven.
3. ‘Hemp insanity’ or cannabis psychosis i.e.:
It was described as being similar to an acute schizophreniform disorder with disorientation and confusion, and with a good prognosis. Furthermore, The validity of this specific disorder is currently doubted.
4. Other complications i.e.:
Chronic cannabis use sometimes leads to memory impairment, either worsening or relapse in schizophrenia or mood disorder, chronic obstructive airway disease, pulmonary malignancies, alteration in both the humoral also cell-mediated immunity, decreased testosterone levels, anovulatory cycles, reversible inhibition of spermatogenesis, blockade of gonadotropin releasing hormone, also increased risk for the developing foetus (if taken during pregnancy).
Investigations
Tab Content
Treatment
Treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder
Contingency Management:
- This is when a person is monitored for their behavior and is rewarded for positive behavior. If drug use occurs the reward is taken back.
Motivational Enhancement Therapy:
- This therapy is targeted at the mindset of the person which brings about greater inspiration and greater contribution in the Cannabis Use Disorder treatment. It is intended to produce rapid results.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy:
- In cognitive-behavioral therapy, the affected individual learns different methods to cope with the negative feelings and how to replace them with positive ones rather than using marijuana as an escape or way to cope with their problems.
Medications:
- There are no medications available for treating cannabis use disorder. Medication can only be used to help minimize withdrawal symptoms.(4)
Prevention
Prevention of Cannabis Use Disorder
- Parents should monitor their children’s activities. They should supervise and maintain proper communication so that children share their struggles and problems freely with them rather than using marijuana to escape their problems or to cope with anxiety.
- Children should be made aware of the harmful effects of cannabis use. Efforts are needed to prevent the criminal sale of this drug.
Self Help:
- People who want to stop using cannabis can join a group in which other members provide motivation to stop, support, and care about each other.
- If a person is heavily dependent on cannabis, self-help is not a good option and the person would be better suited by participating in a substance abuse cannabis use disorder treatment program. (4)
Homeopathic Treatment
Homoeopathic Treatment:
Homeopathic Treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
Which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Cannabis Use Disorder:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
Medicines:
Avena Sativa: Best homeopathic medicine for drug addiction when dealing with withdrawal symptoms.
- The effects of morphine or heroin, as well as of cocaine, tobacco, marijuana, and valium, are treated effectively with Avena Sativa.
- It is one of the best ways to overcome morphine addiction.
- Avena Sativa works very well in treating insomnia due to drugs or alcohol.
Nux Vomica: Homeopathic treatment for drug addiction with abdominal symptoms, nausea and vomiting.
- Sour taste and nausea in the morning, accompanied by retching, is an indicator for the use of Nux Vomica.
- The stomach is very sensitive to pressure when applied externally.
- The patient feels Intoxicated; the feeling is worse in the morning.
- The patient may complain of vertigo with momentary loss of consciousness.
- Indigestion caused by alcohol, coffee, and other drugs is treated well with Nux Vomica.
Morphinum: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with heart symptoms.
- In cases indicating the use of homeopathic medicine Morphinum, there is a violent throbbing in the heart along with a small and weak pulse.
- There may be a sudden alteration in the heart rate which is known as tachycardia or fast heart rate, and bradycardia or slow heart rate.
- The patient may be delirious and suffer from depression.
- Morphinum also works well for cases of drug addiction in which the patient is in a dream-like state and feels indifference.
Coffea: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with marked insomnia after a phase of excitement.
- The patient experiences increased energy, ecstasy, sleeplessness on account of excess mental activity, and an increased flow of ideas.
- He is unable to sleep from an excessive intake of coffee.
- The patient experiences great loquacity, his brain feels clear, and he is extremely active.
- The patient also feels strong enough to do anything.
Hyoscyamus: Homeopathic treatment for drug addiction accompanied by hallucinations and delusions.
- The patient experiences a confused mind and seems intoxicated, laughs, sings, recites poetry, and babbles deliriously.
- The patient does foolish things and does not behave normal.
- Hyoscyamus also helps patients with an addiction to alcohol and those who experience intoxicated rages.
- In such cases, there is involuntary urination along with hallucinations.
Opium: Suitable homeopathic medicine for drug addiction accompanied by drowsiness.
- The patient falls into a heavy and deep sleep, he wants nothing, and says that nothing ails him.
- The patient is hot, sweaty, drowsy and has cold limbs.
- The complaints are accompanied by a heavy, deep sleep, and noisy, laboured breathing.
- Loss of consciousness and a coma from drug overdose is also treated well with Opium.
Sulphuricum Acidum: Homeopathic medicine for drug addiction with a craving for alcoholic stimulants.
- The patient experiences hot flushes, trembling, and cold sweats, accompanied by humming and tickling in the ears.
- Sour vomiting and hiccoughs, along with nausea and shivering, is effectively treated with Sulphuricum Acidum.(5)
Diet & Regimen
Diet & Regimen of Cannabis use disorder
- Eat law fat food
- Take enough sleep
- Do regular physical exercise
- Stay away from cigarette & alcohol
Do’s and Dont’s
Tab Content
Terminology
Tab Content
References
Reference:
- Short Textbook of Psychiatry by Niraj Ahuja / Ch 4
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabis_use_disorder
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538131/
- https://www.firstlightpsych.com/blog/addictions/cannabis-use-disorder-and-cannabis-dependence-disorder#factors
- https://www.drhomeo.com/homeopathic-treatment/homeopathic-treatment-drug-addiction/
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cannabis Use Disorder?
In Cannabis use disorder, Cannabis is derived from the hemp plant, Cannabis sativa, which has several varieties named after the region in which it is found.
What is Acute intoxication of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Impairment of consciousness also orientation
- Lightheadedness
- Tachycardia
- Sense of floating in the air
- Euphoric dream-like state
- Alternation in psychomotor activity and tremors
- Photophobia, also Lacrimation
- Reddening of conjunctiva
- Dry mouth, also Increased appetite
Give complications of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Either Transient or short-lasting psychiatric disorders
- Motivational syndrome
- Either ‘Hemp insanity’ or cannabis psychosis
- Schizophrenia
- Chronic obstructive airway disease
- Pulmonary malignancies
What is the treatment of Cannabis Use Disorder?
- Firstly, Psychotropic medication
- Secondly, Sometimes hospitalization
- Thirdly, Psychotherapy
- Lastly, Psychoeducation
Also Search As
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
XYZ
XXX
XYZ
XXX
XYZ
XXX
People found Homeopathic Clinic For XXXX by searching for
XXX
People found Homeopathic Doctors for XXXX by searching for
XXX
People found Homeopathic treatment for XXXX by searching for
XXX