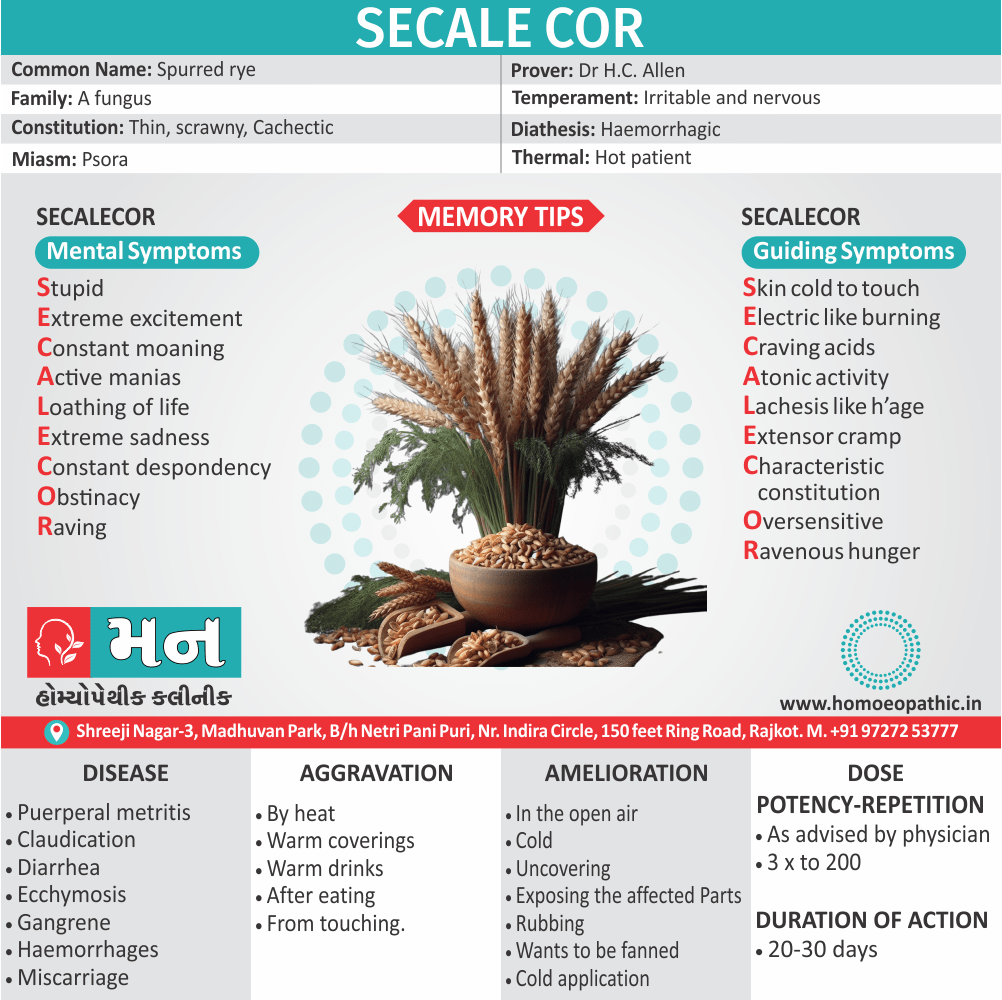
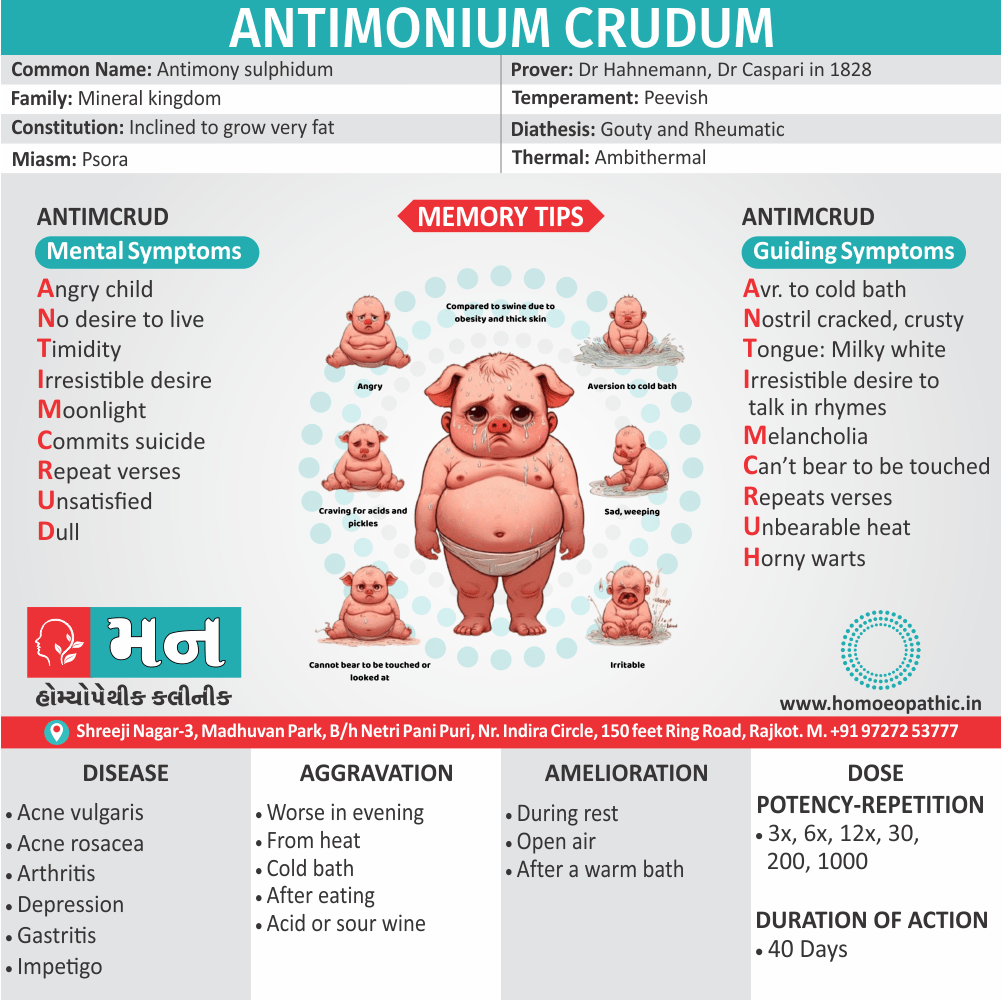
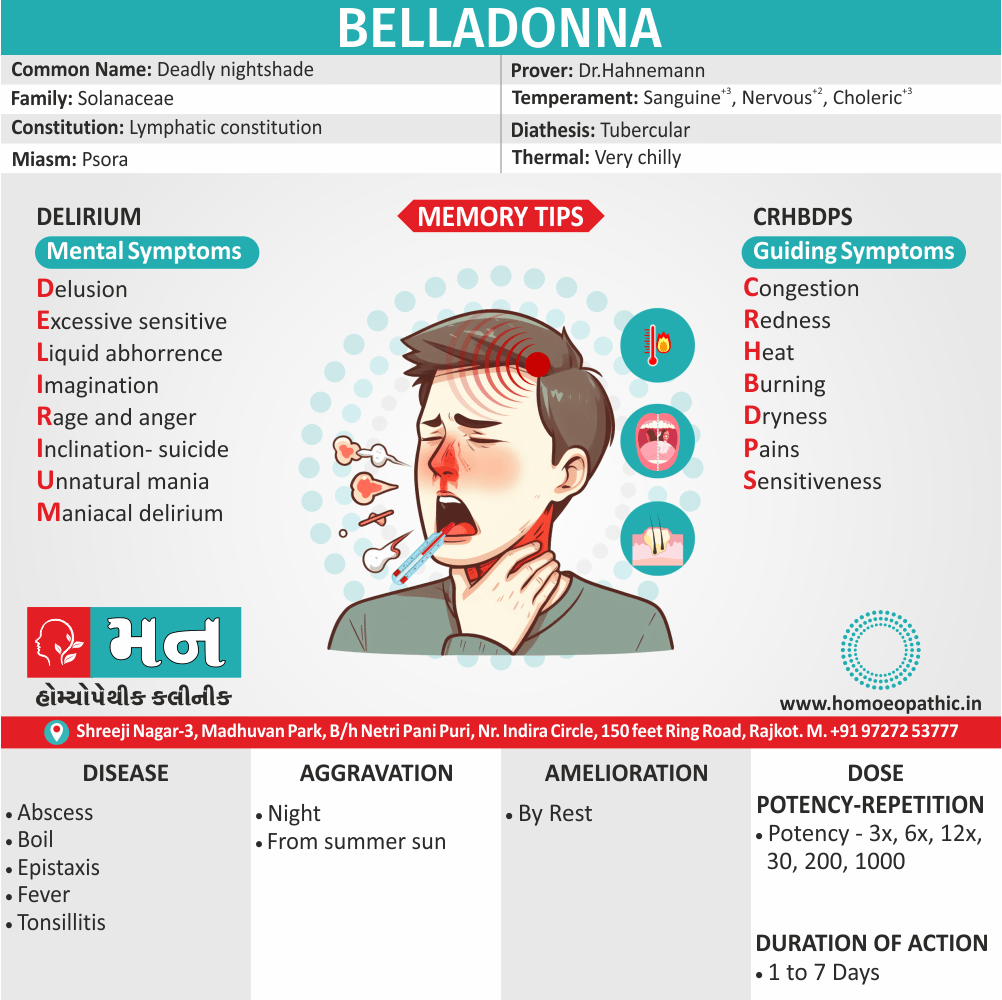
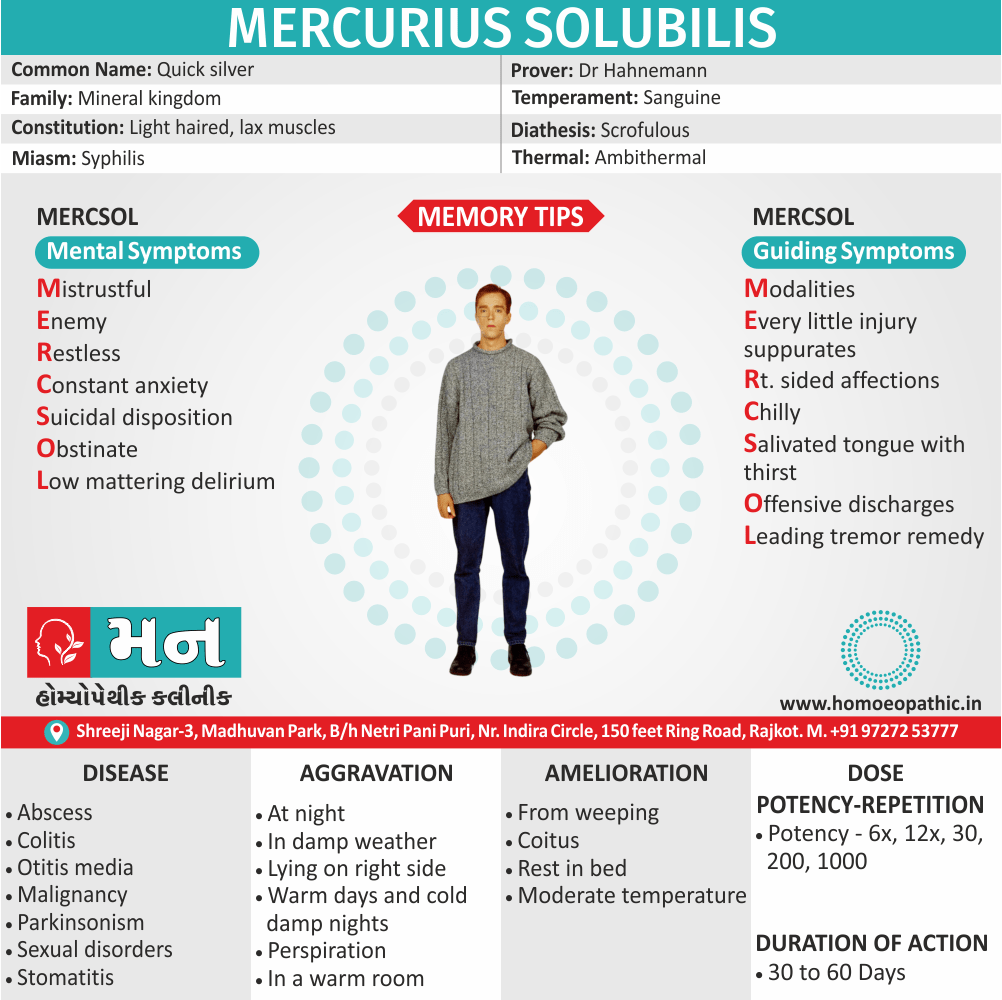
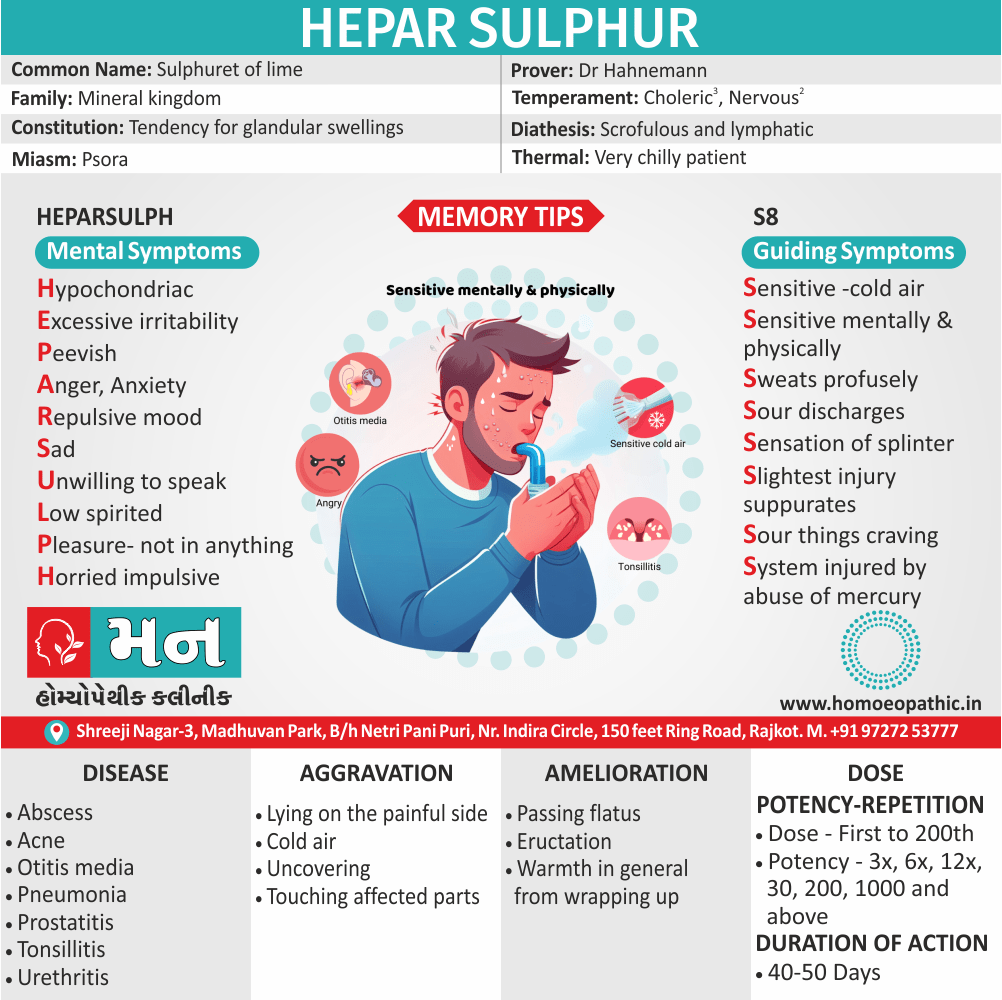
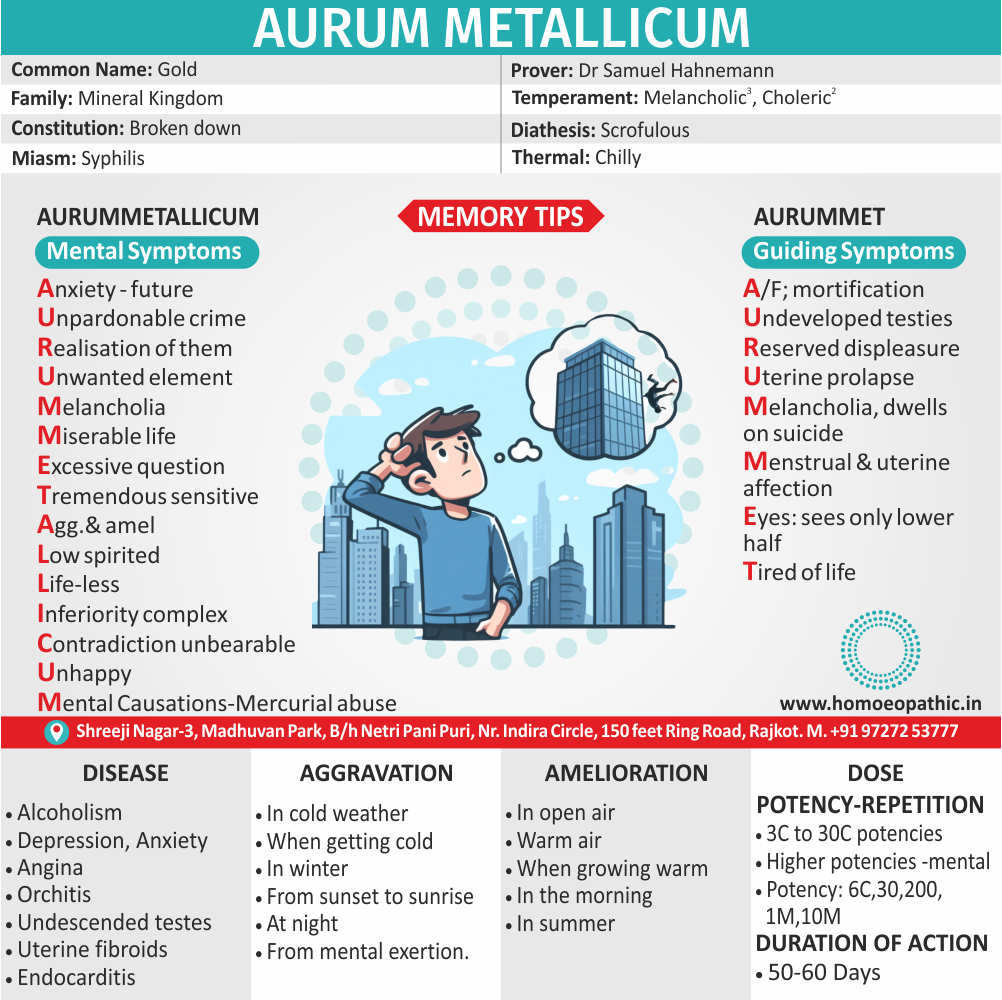
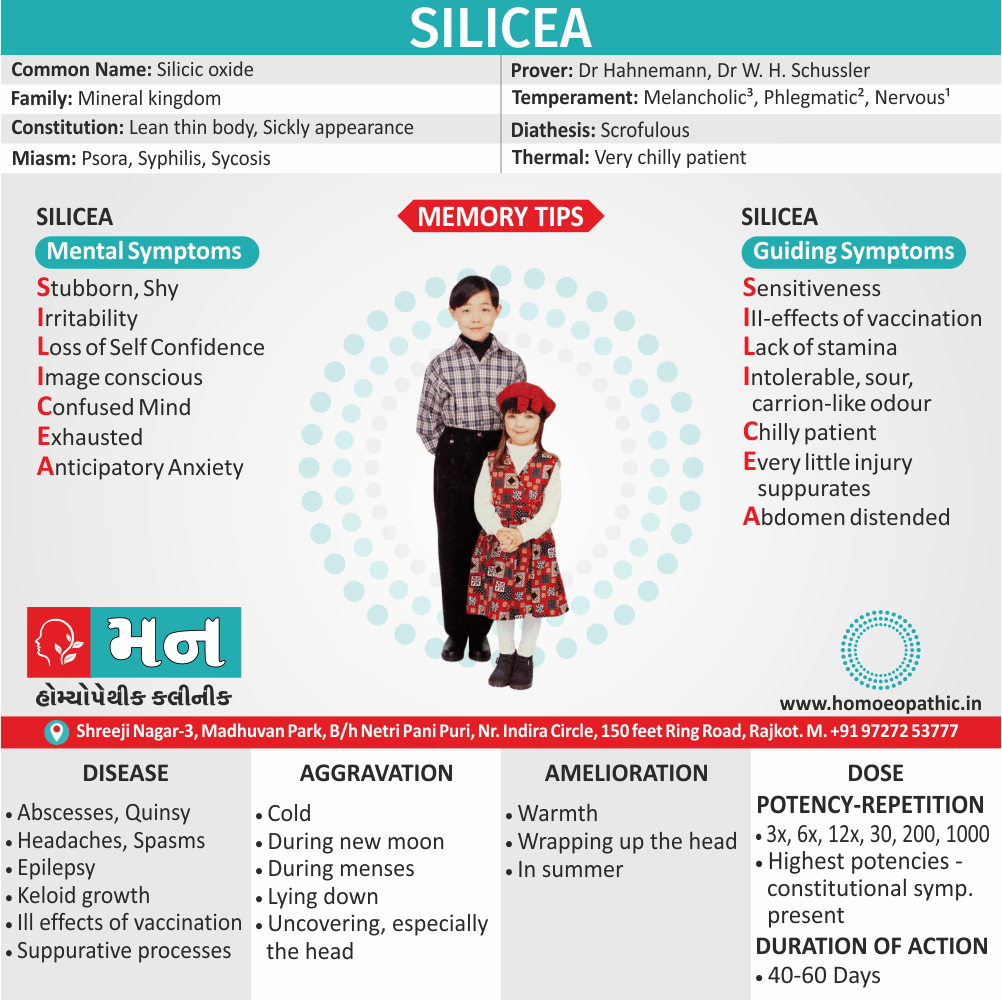
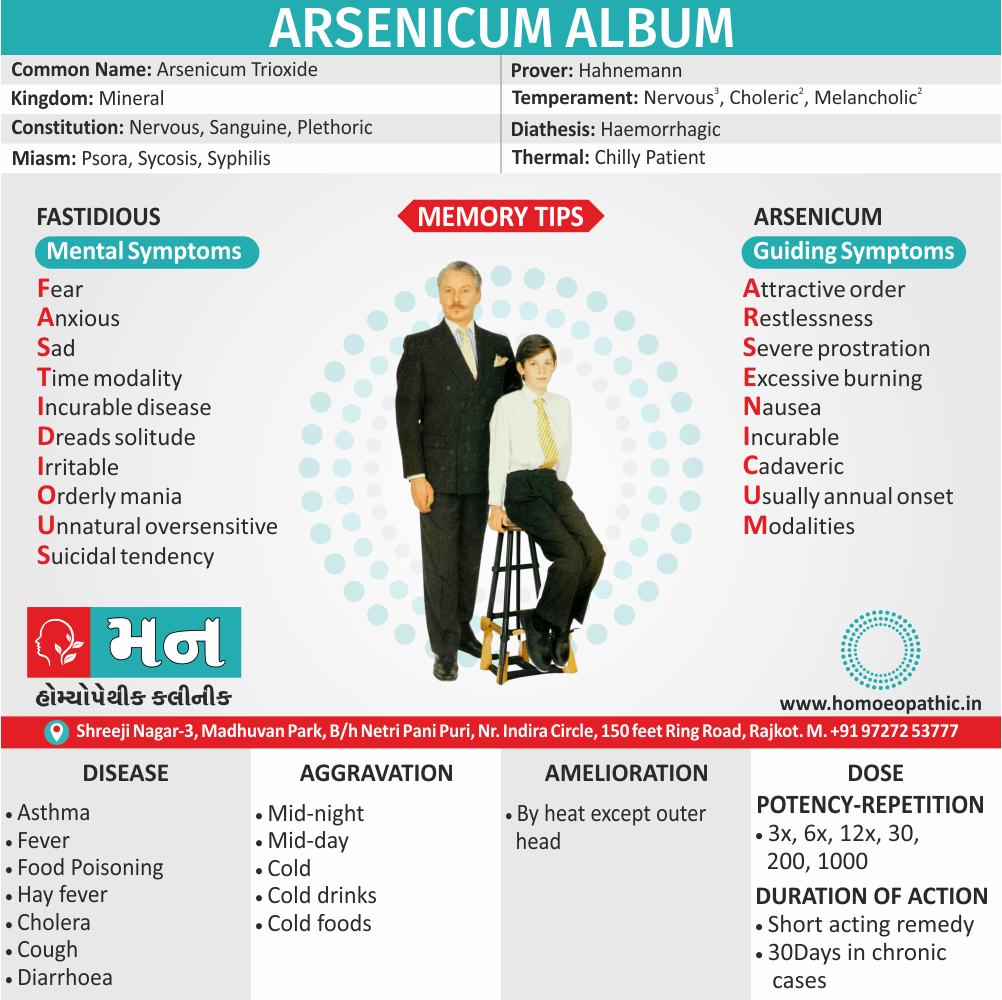
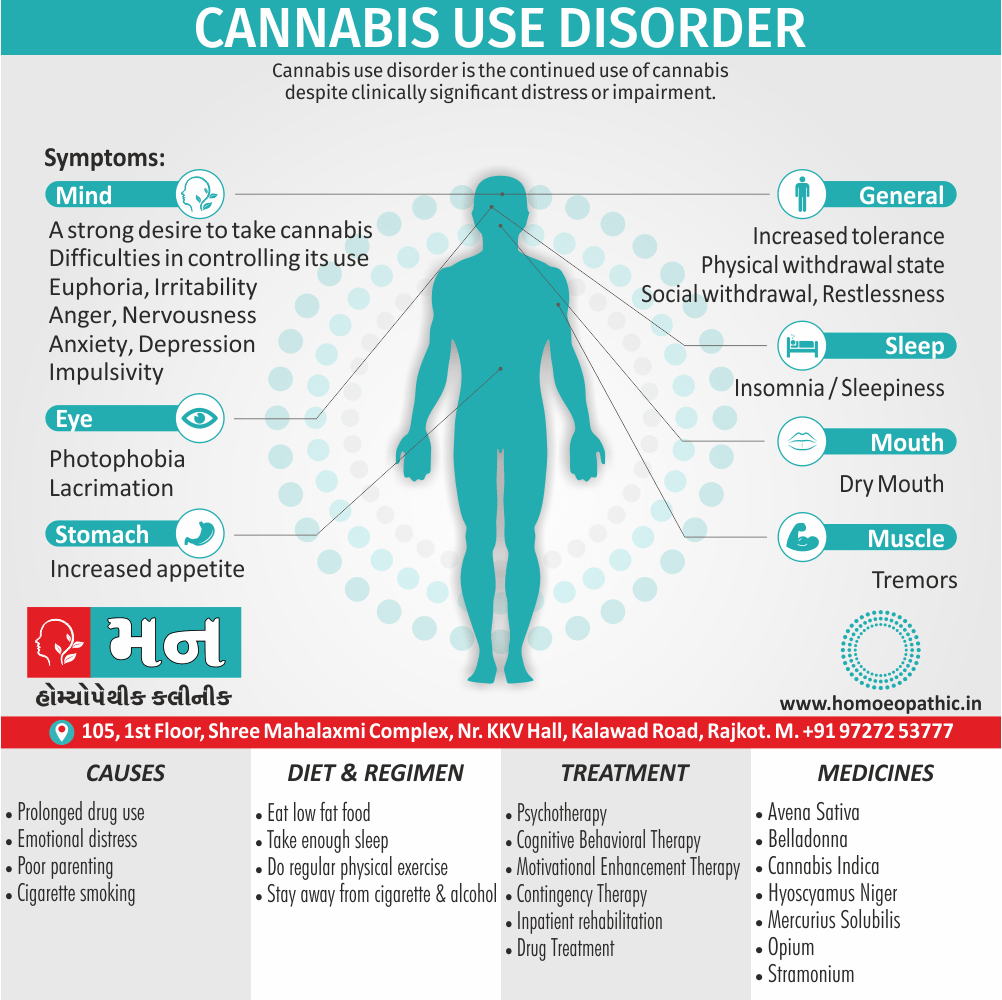
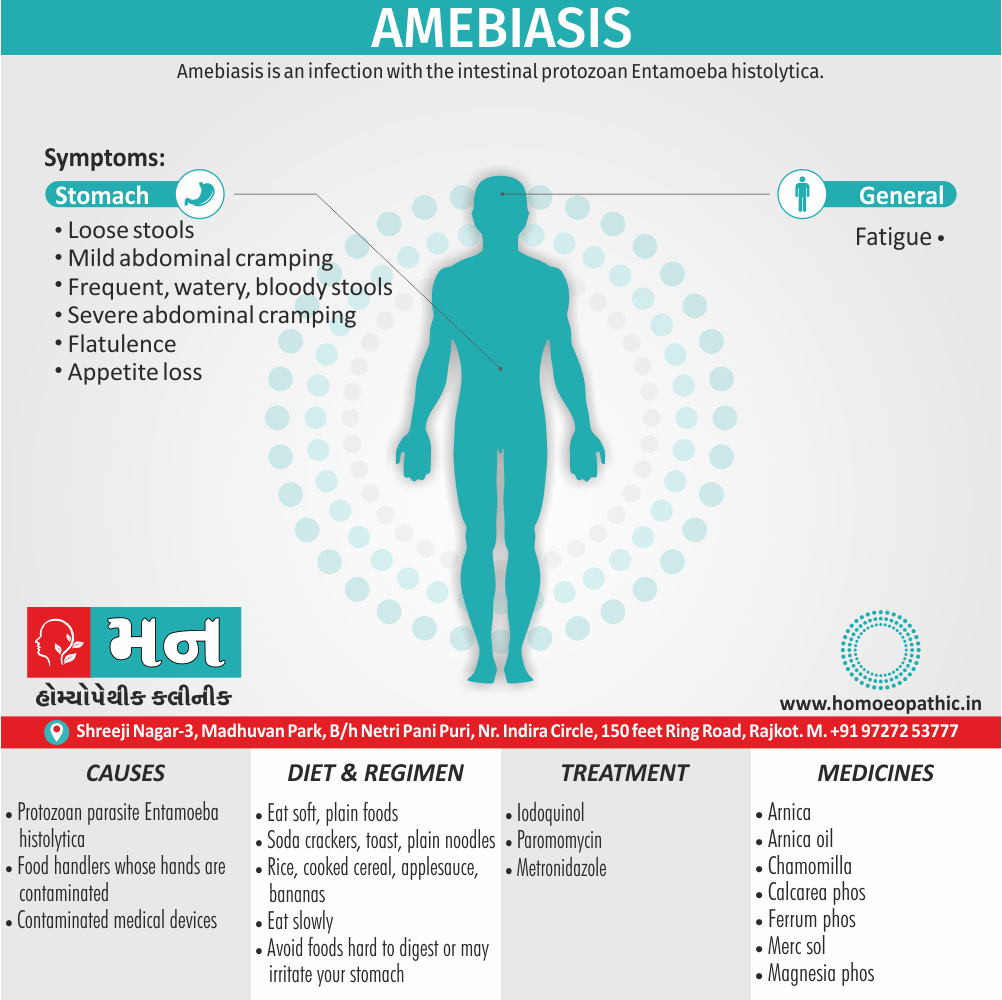
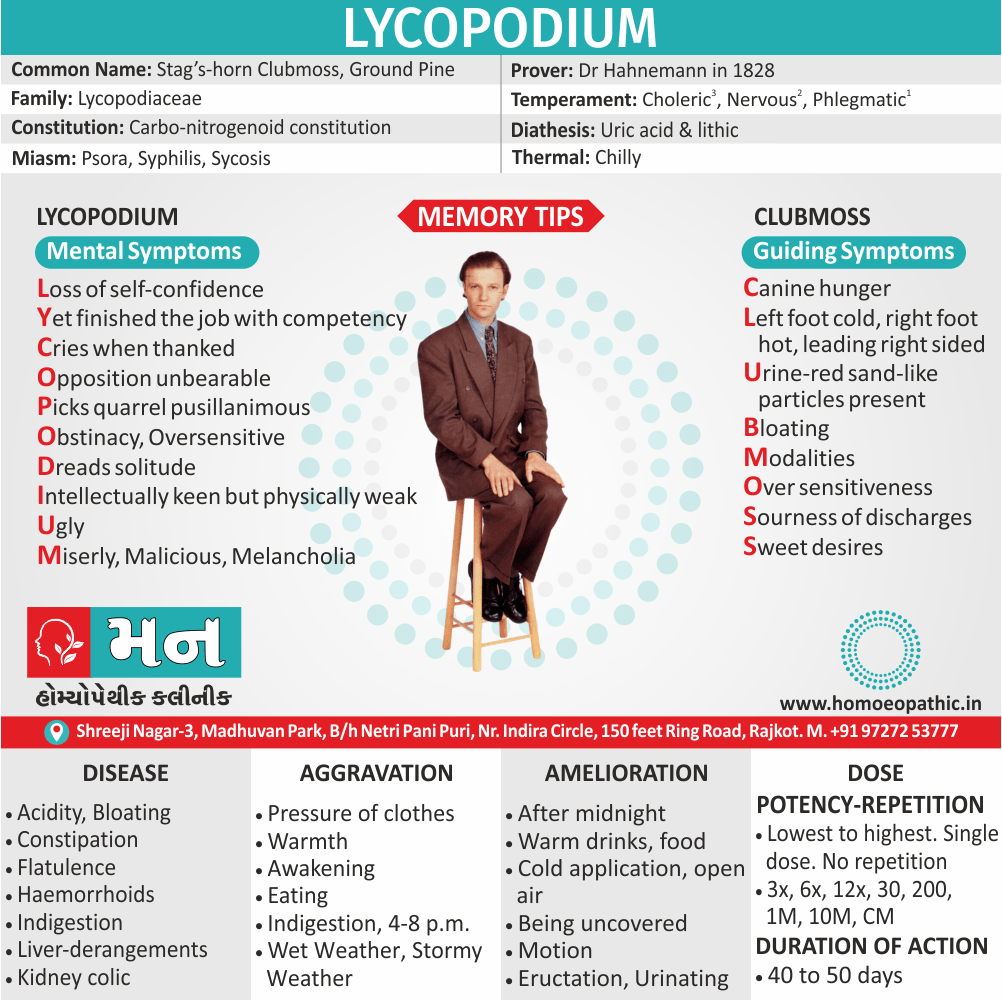
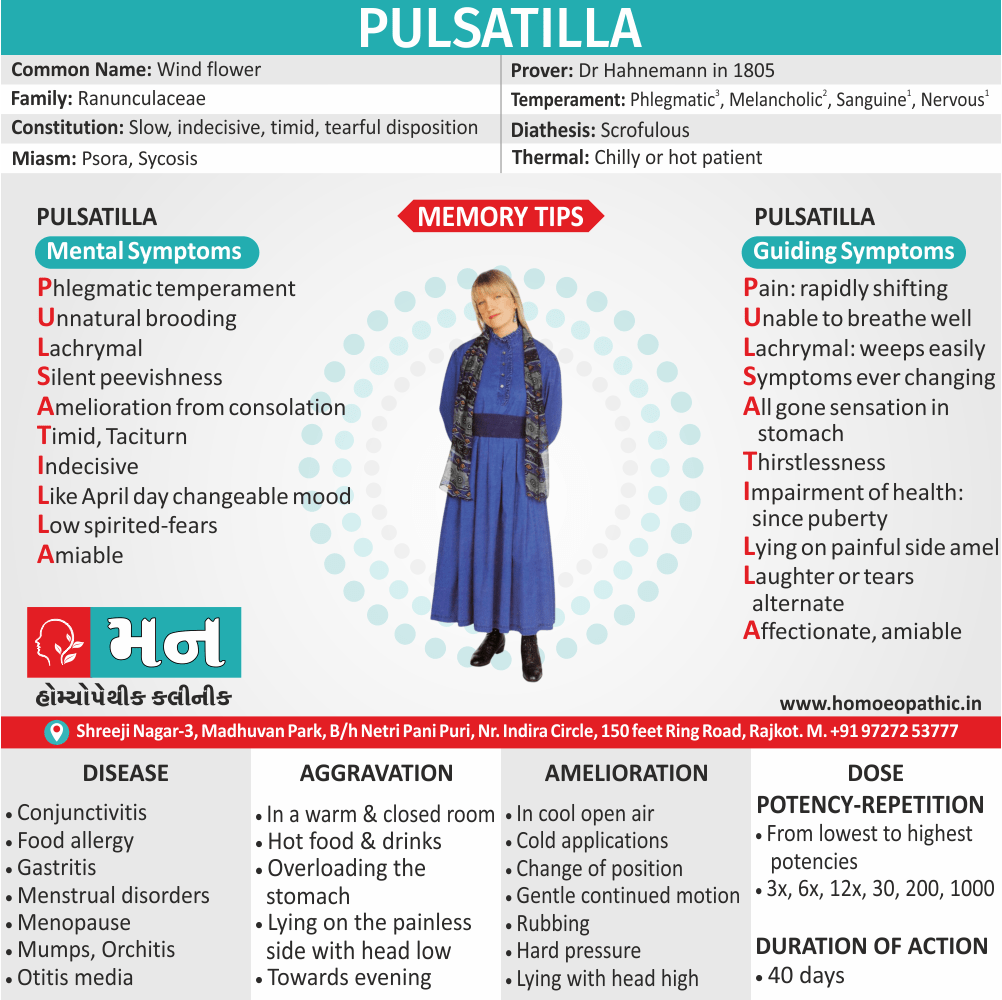
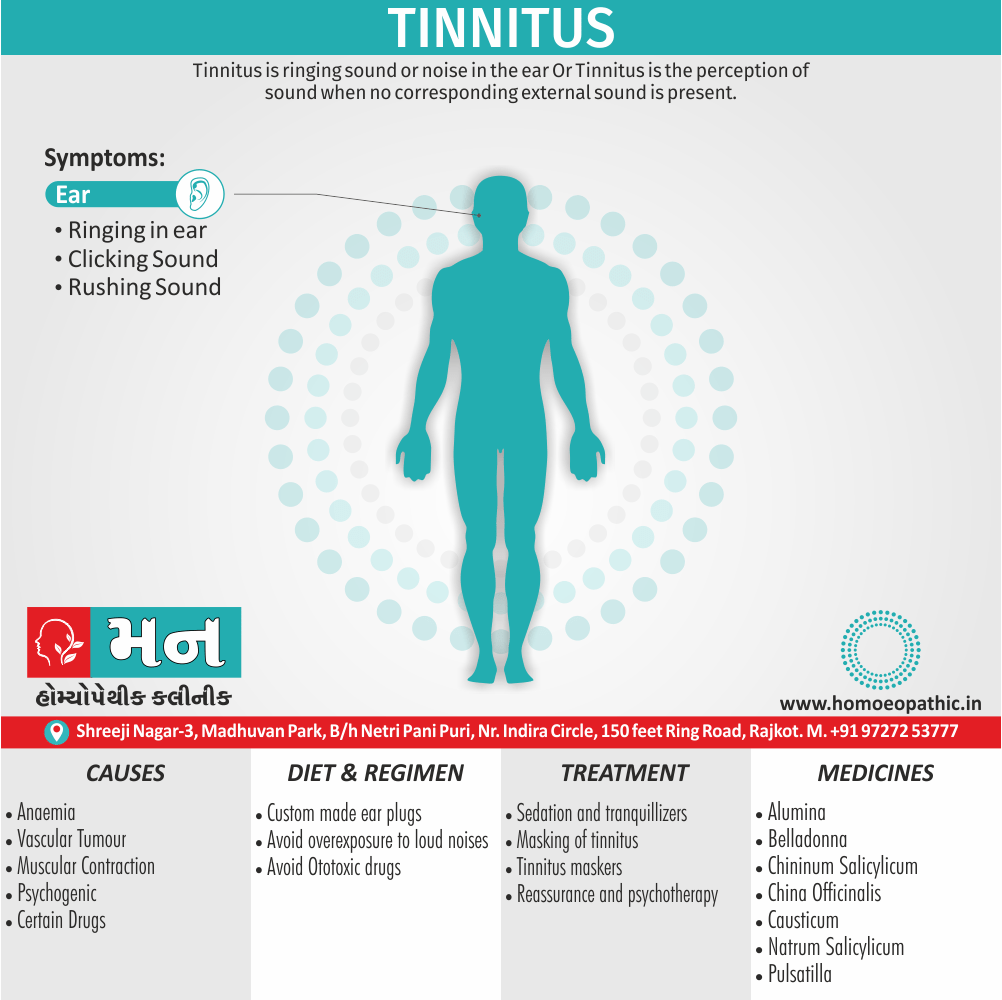
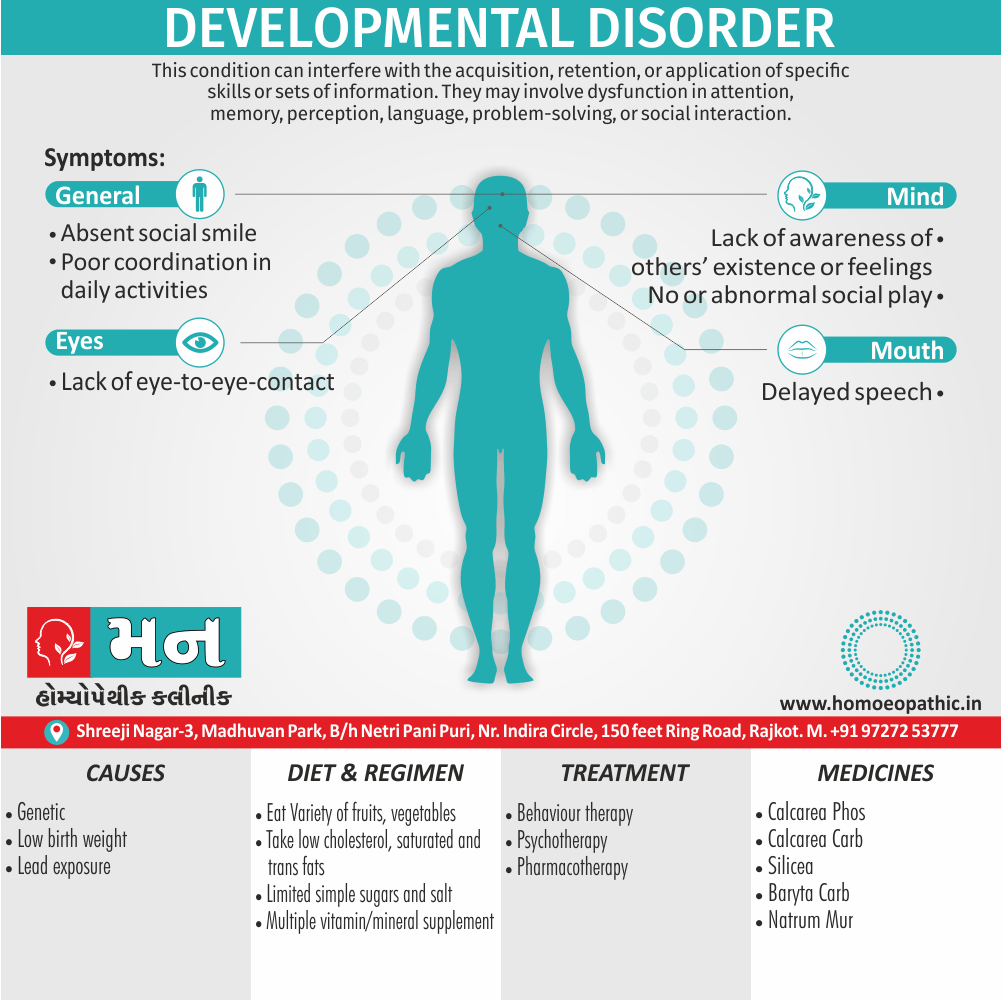
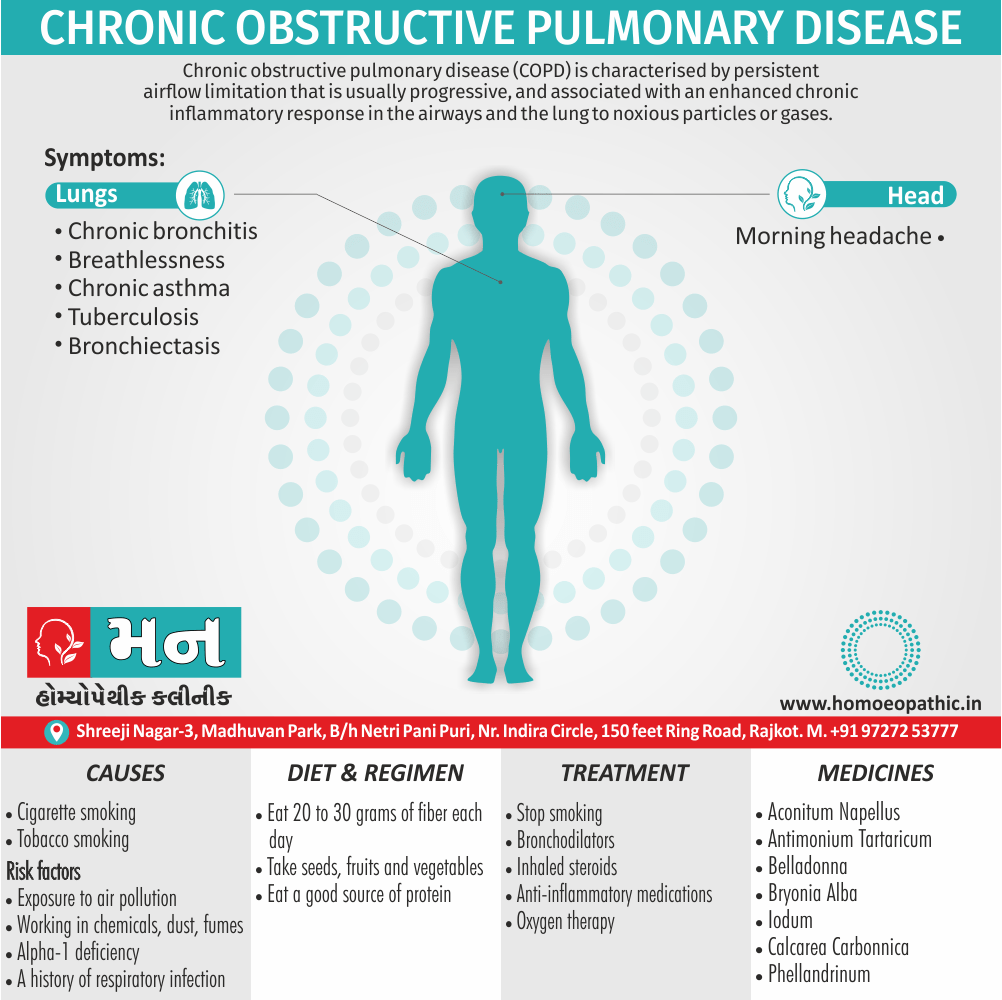
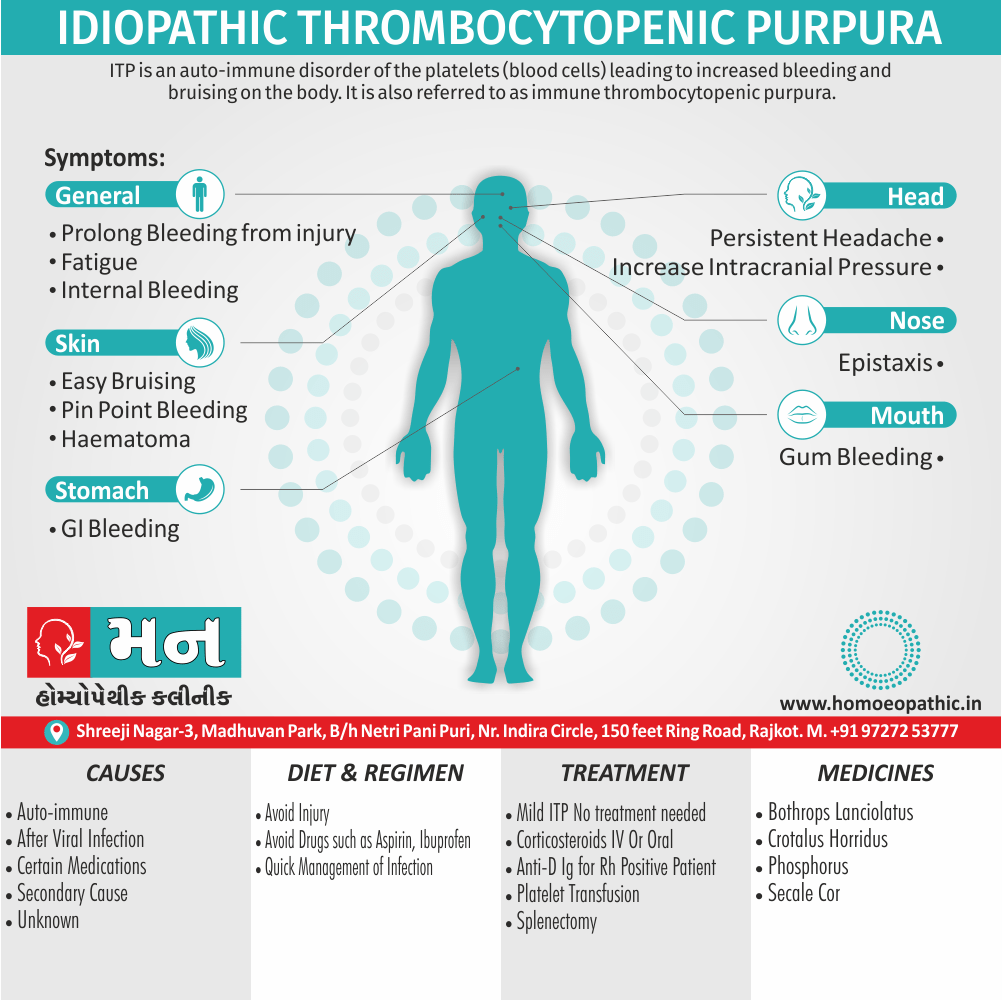
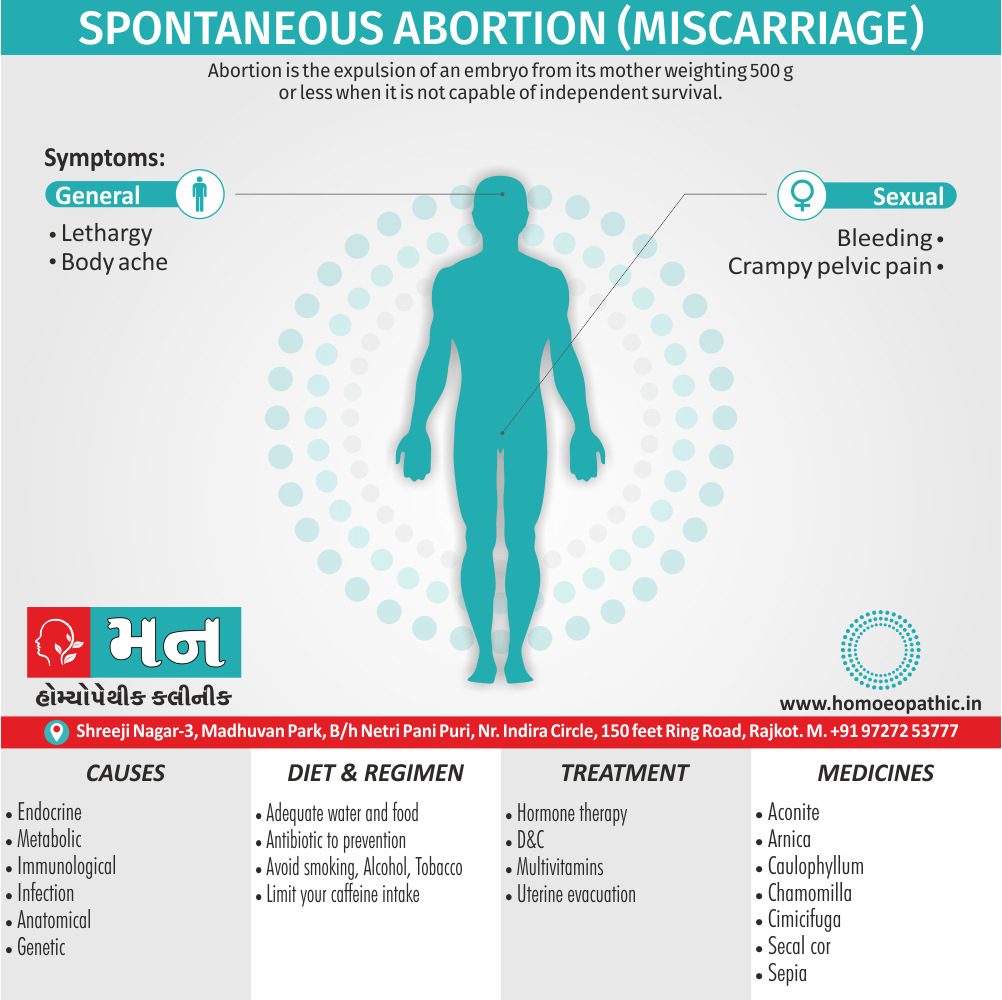
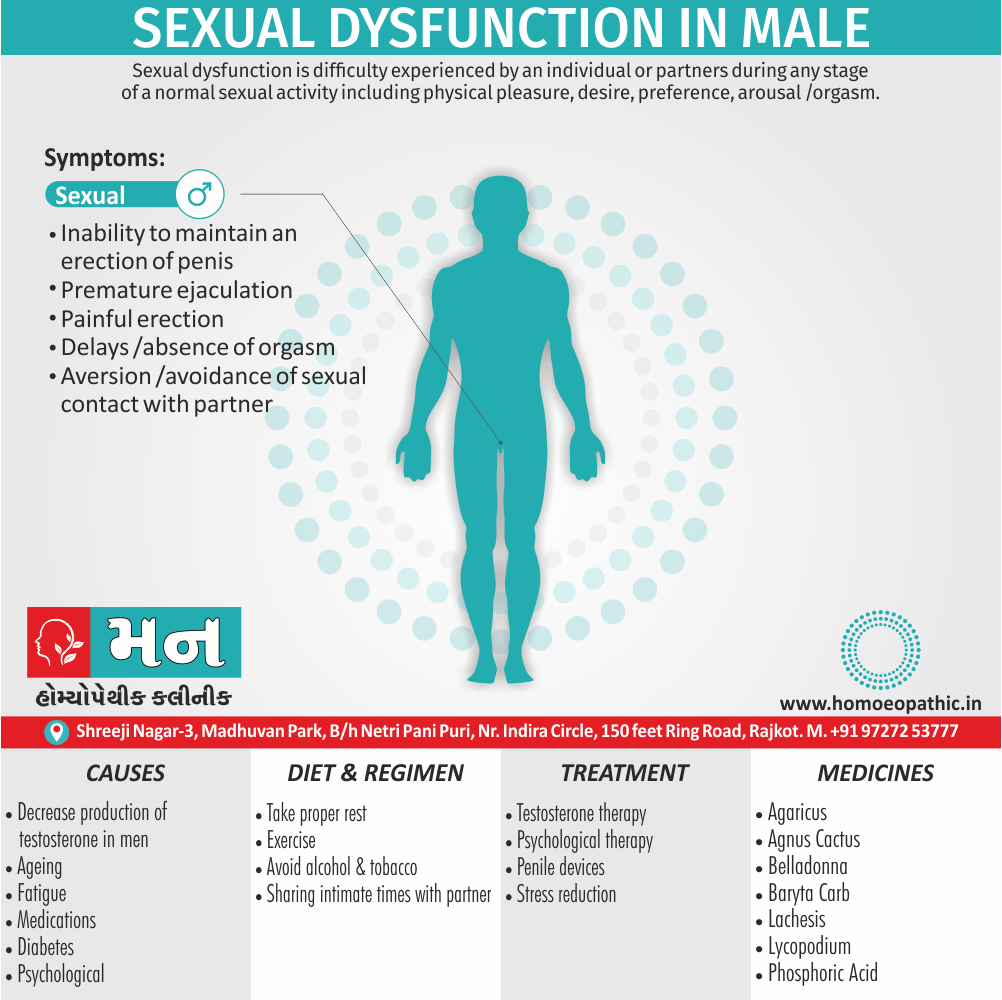
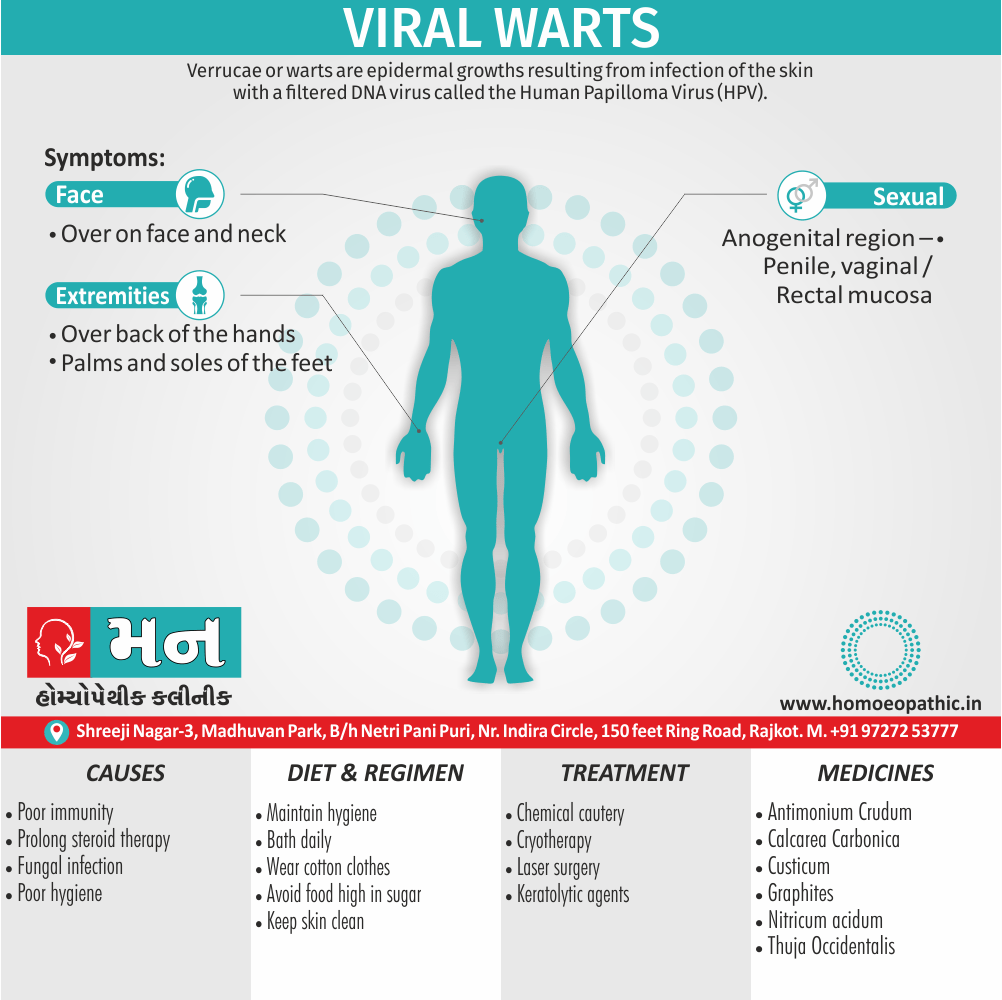
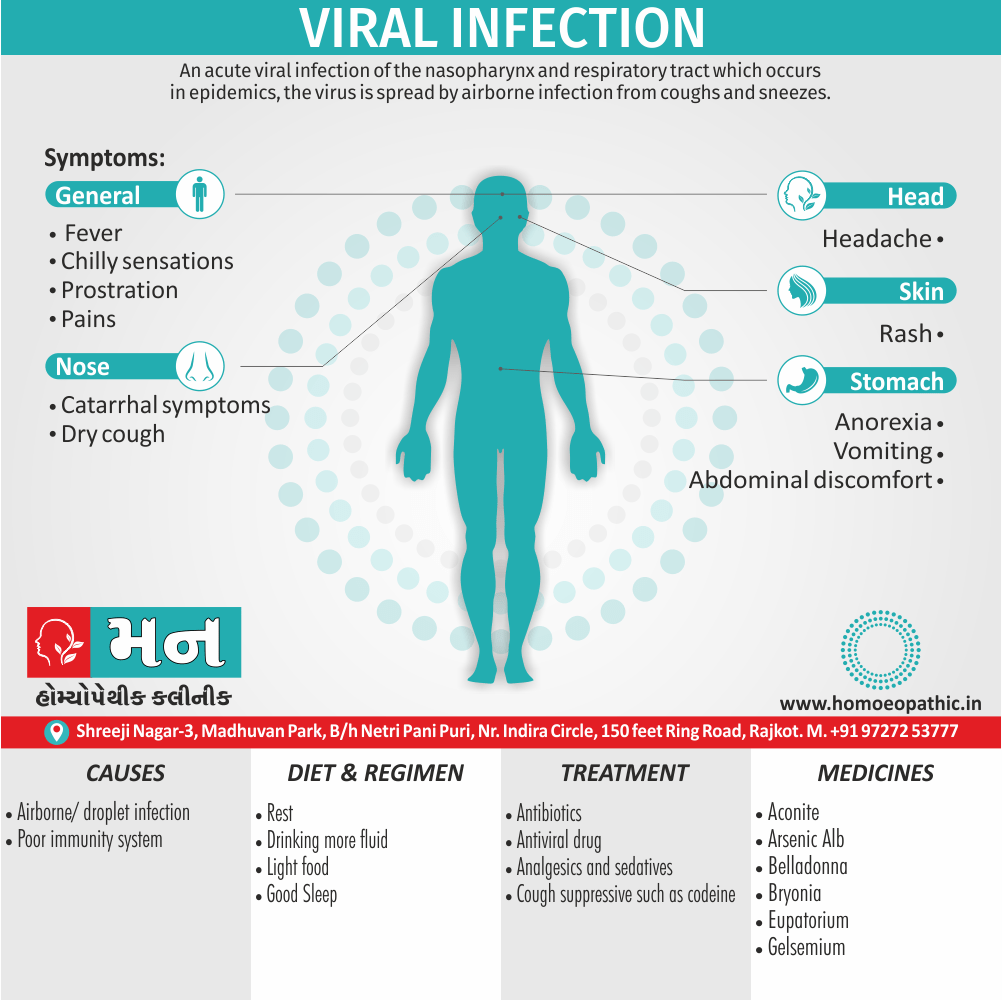
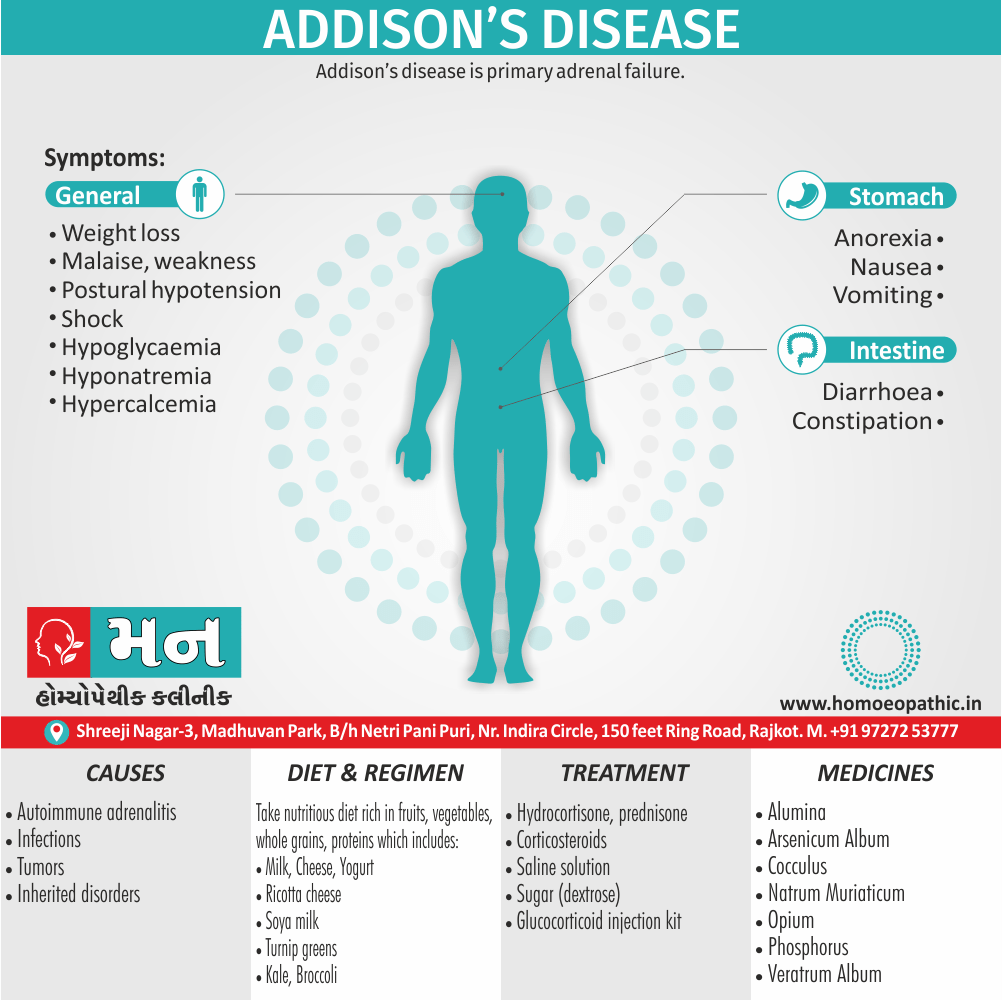
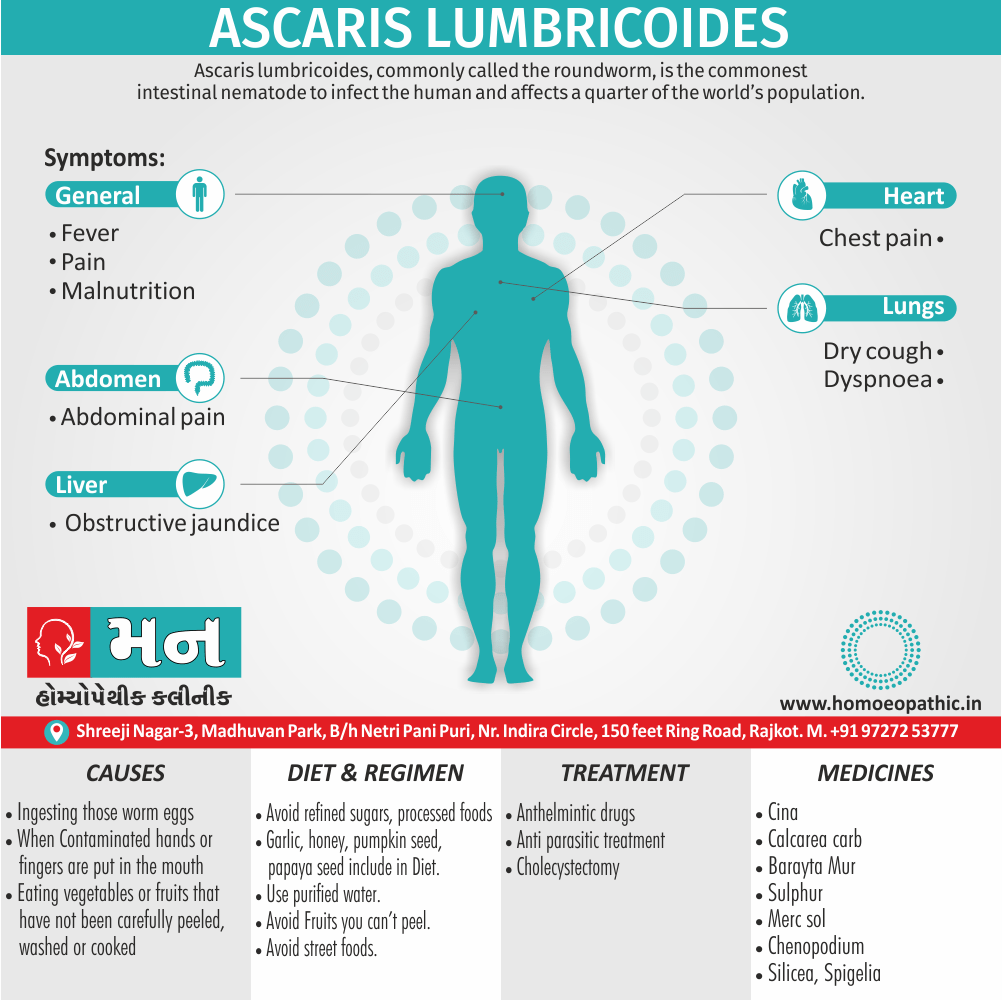
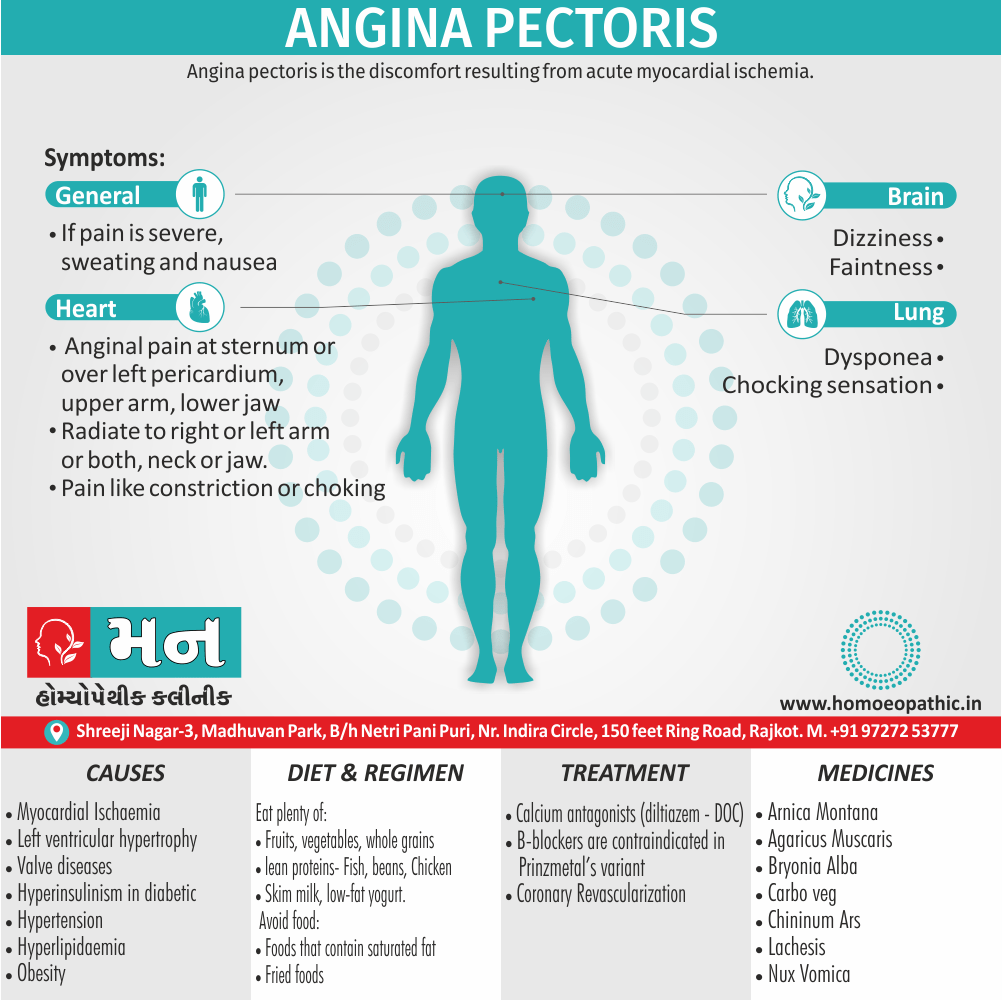
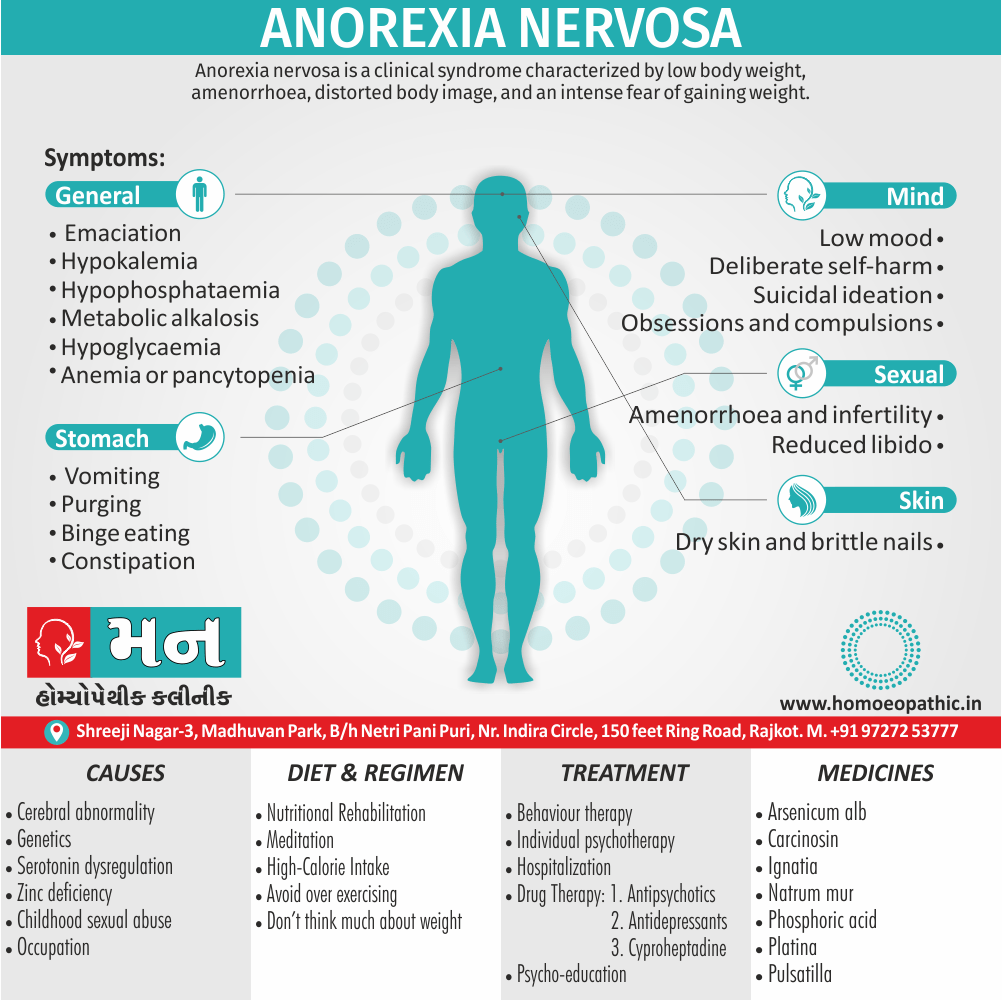
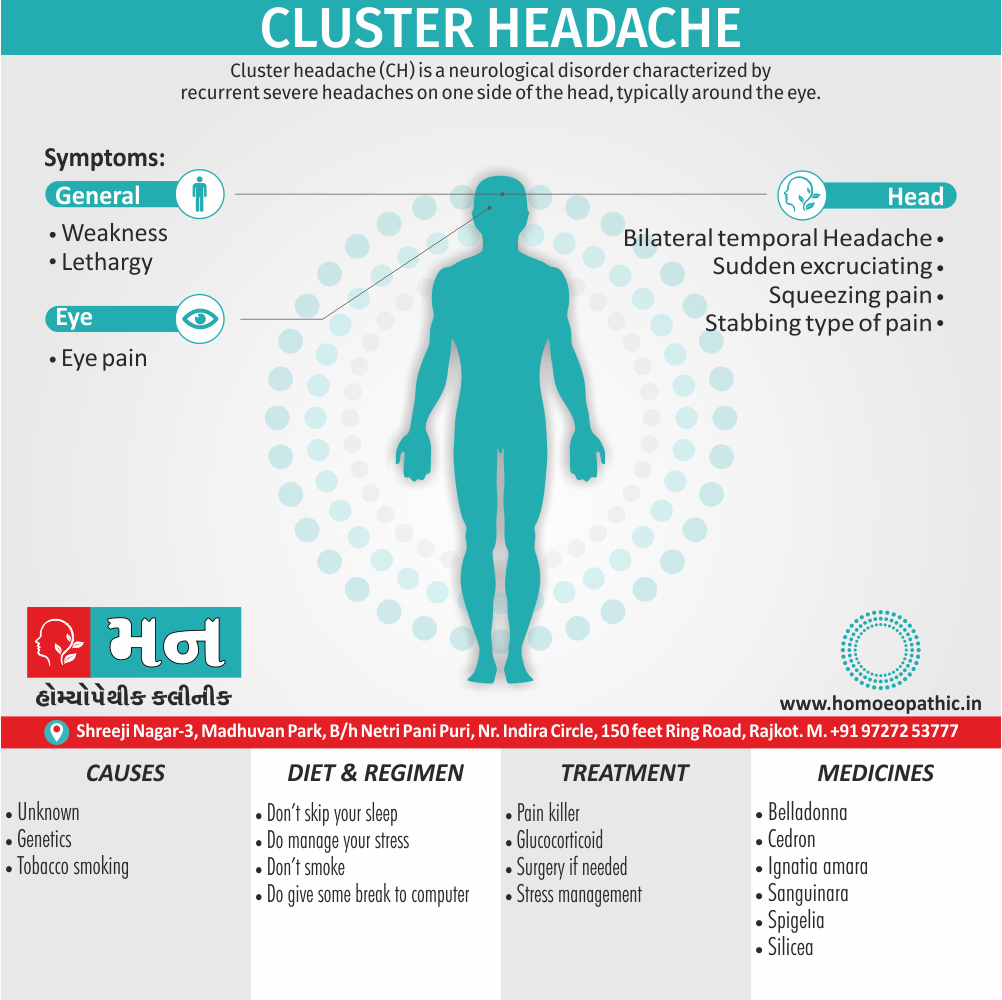
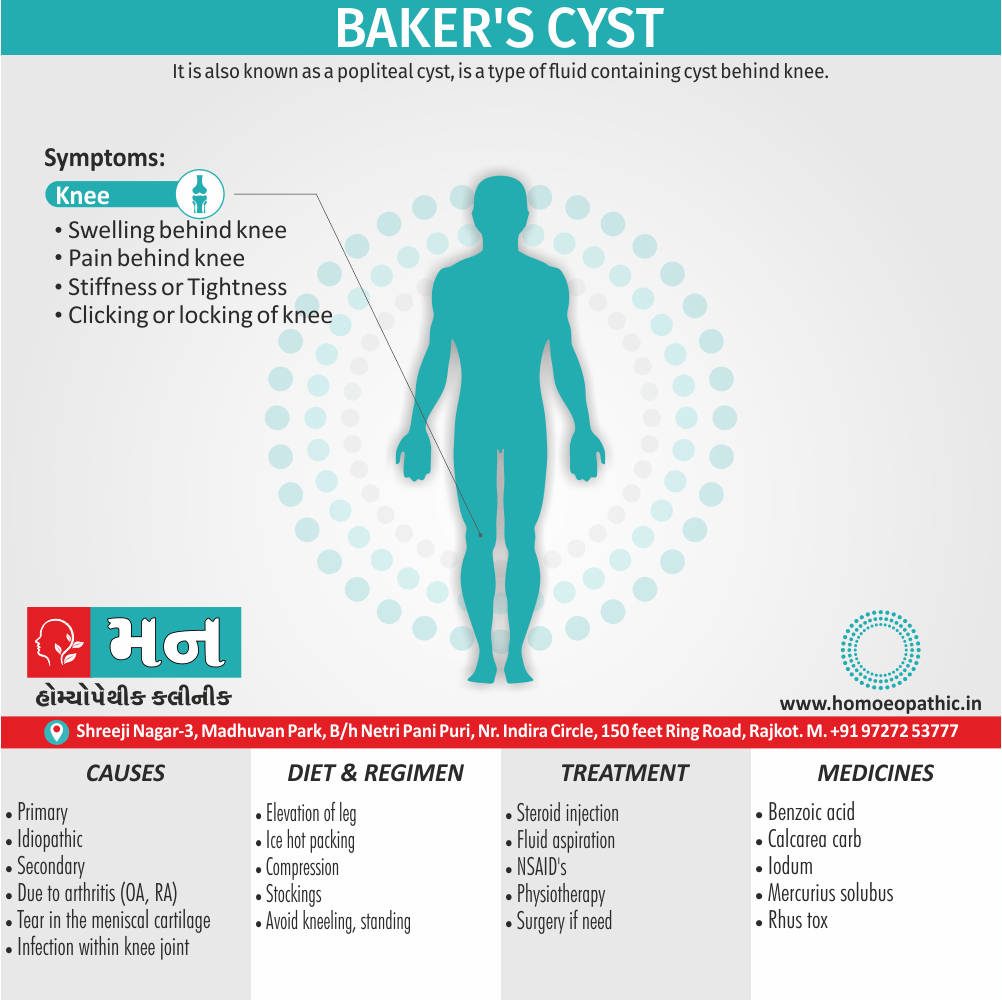
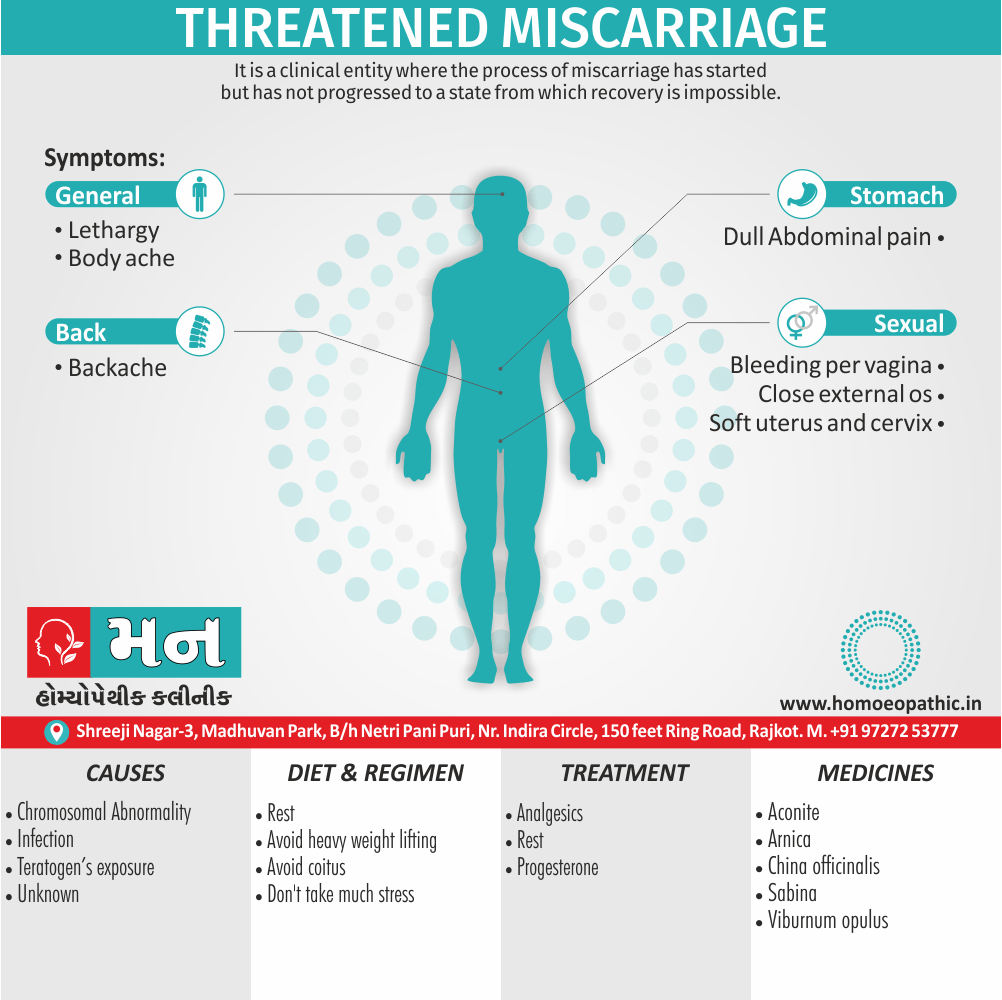
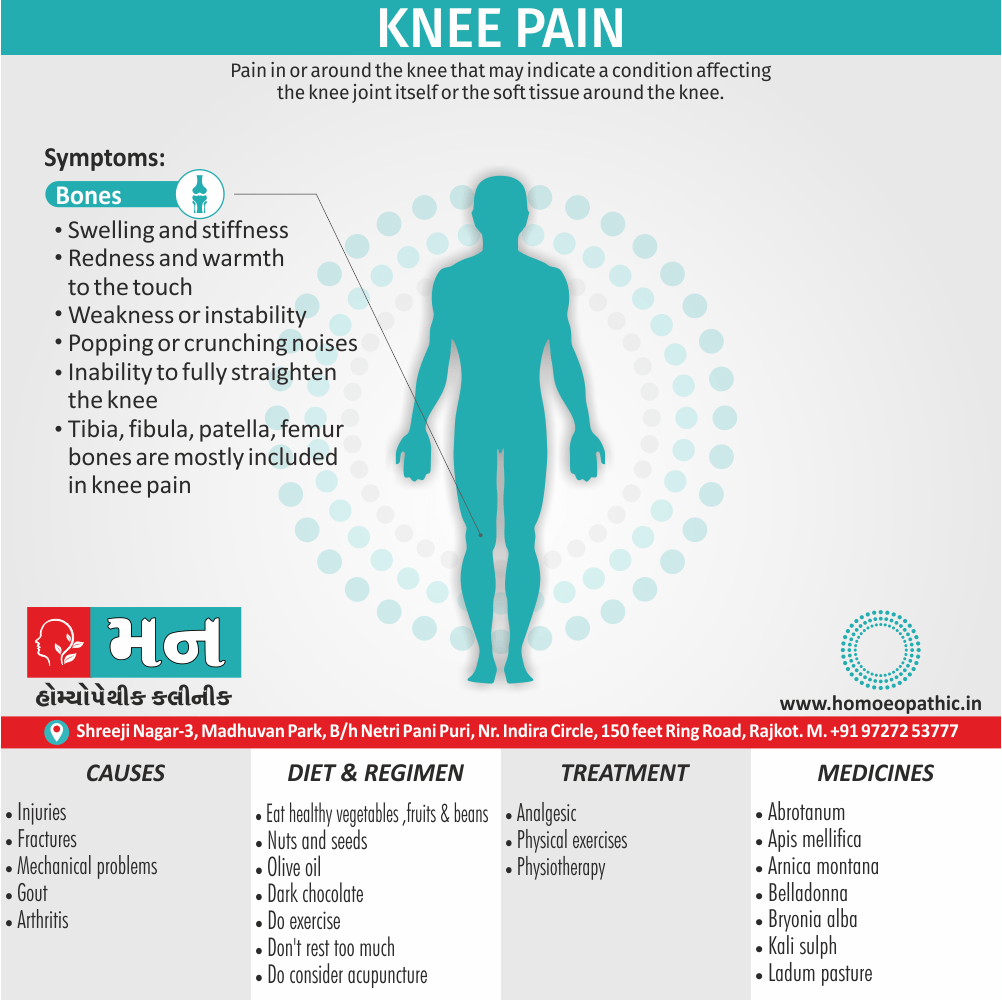
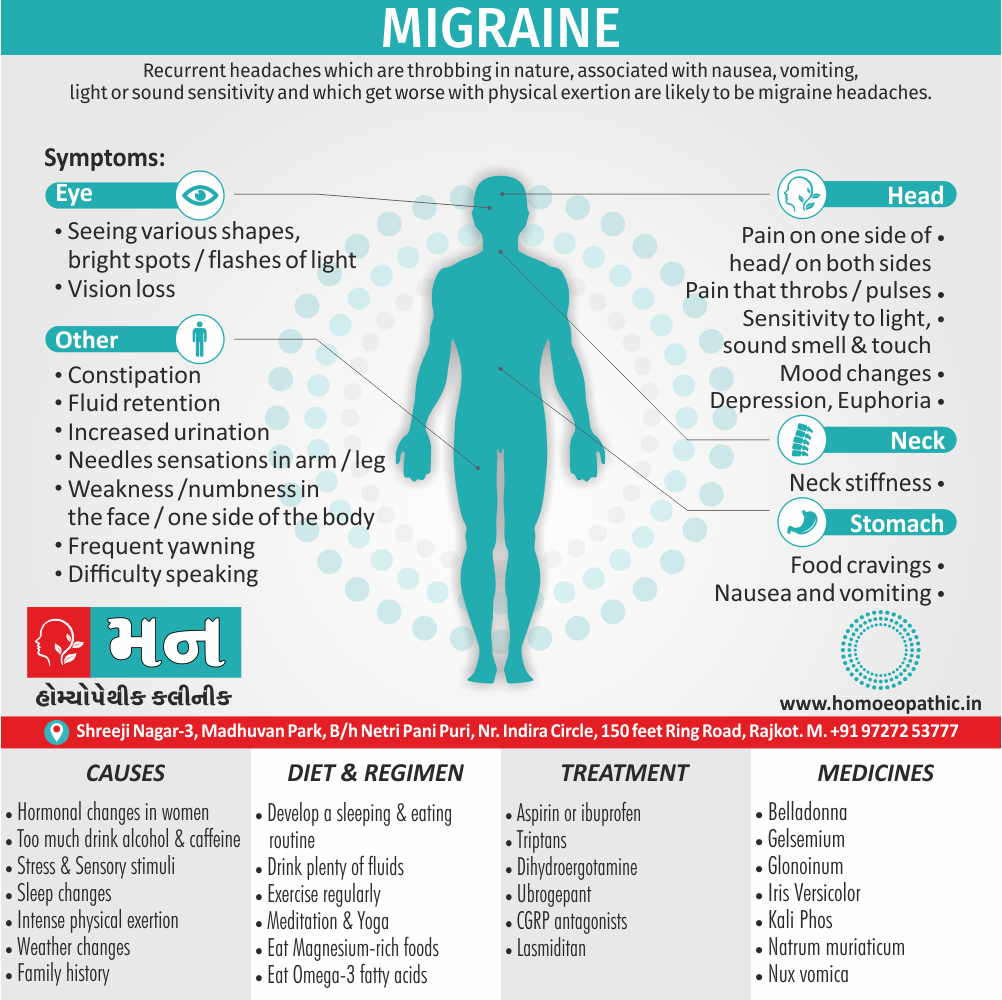
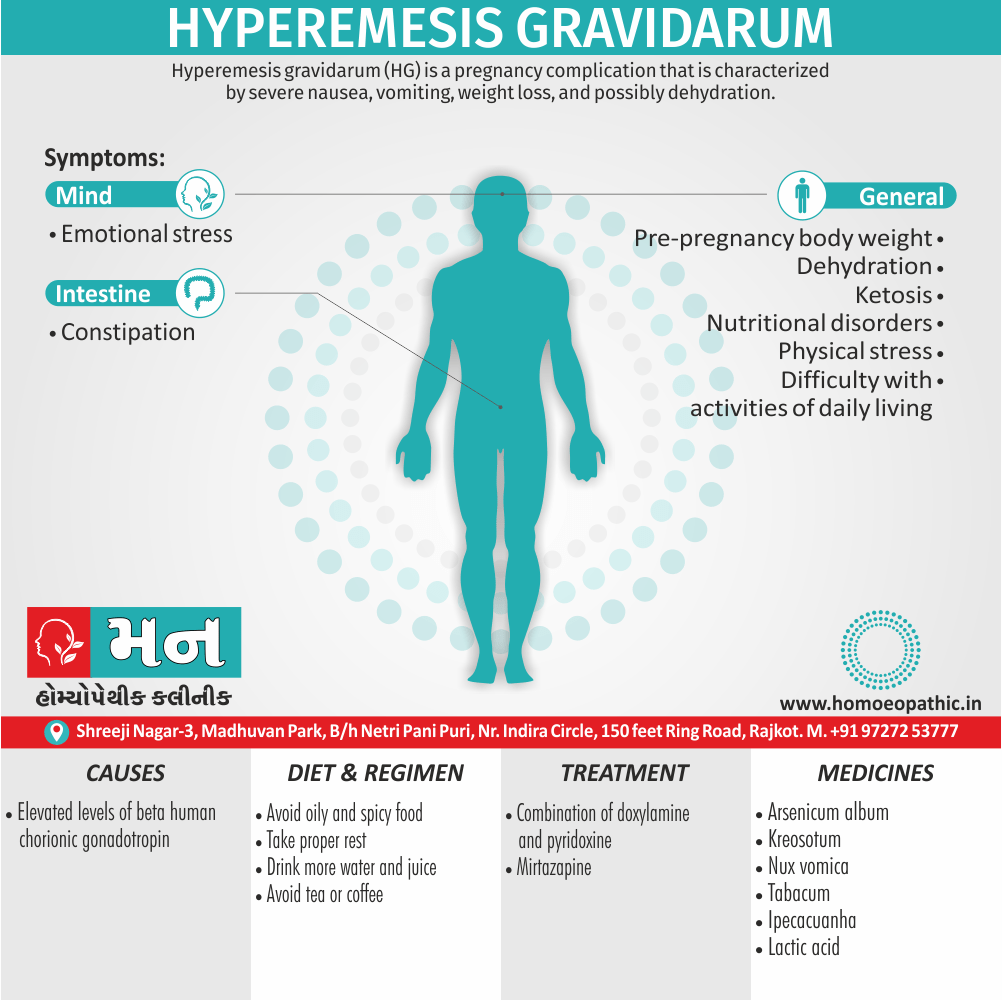
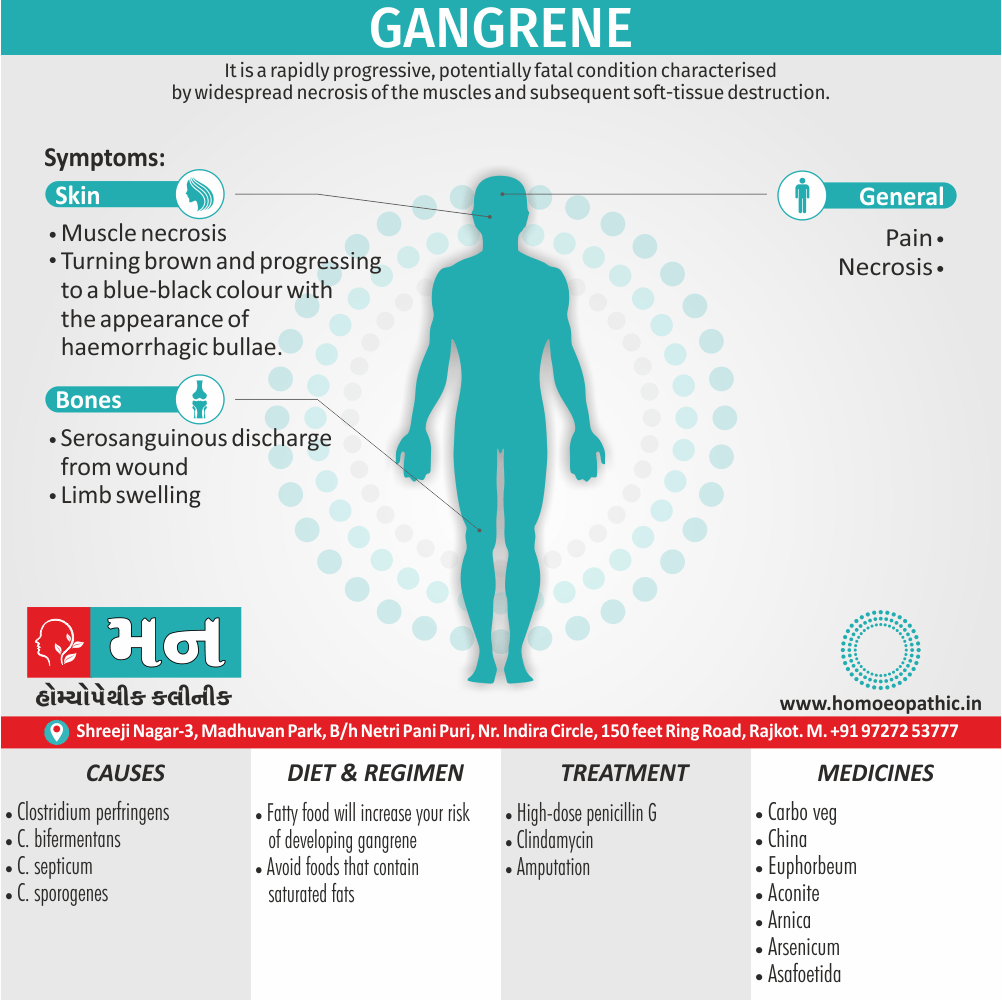
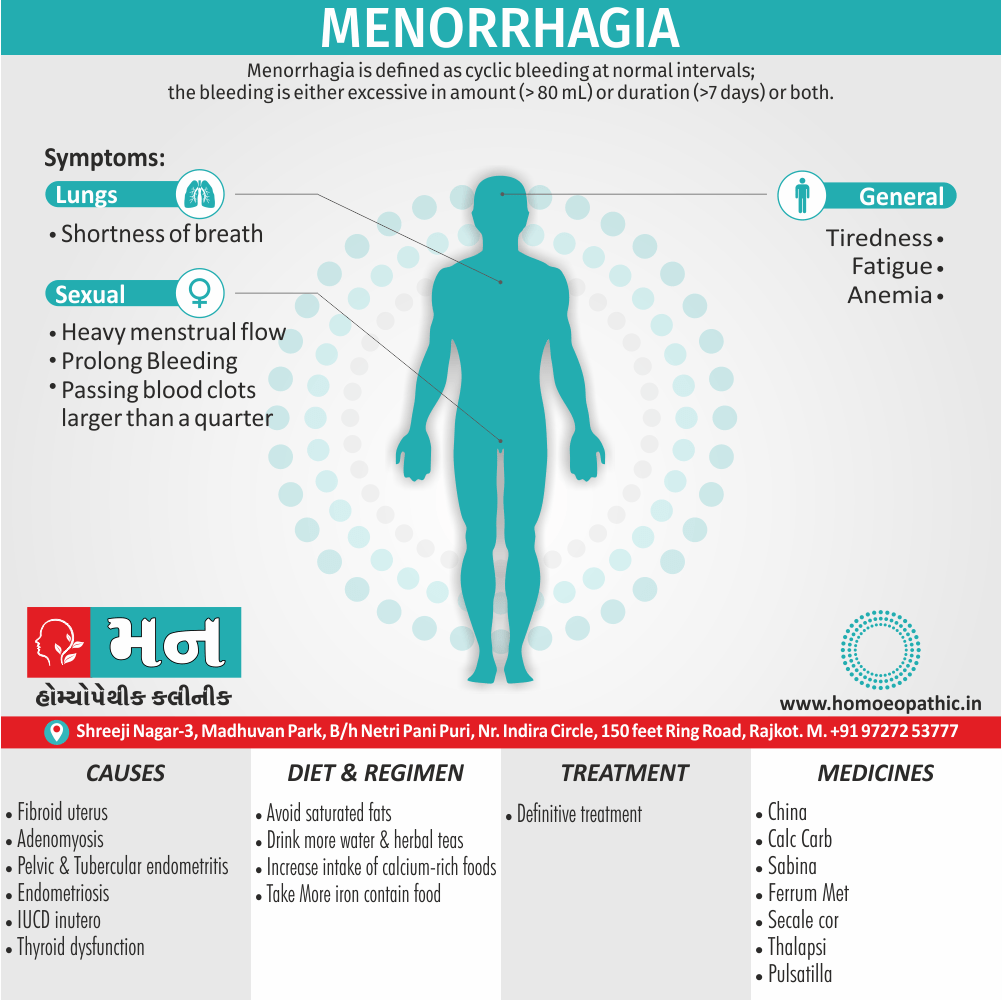
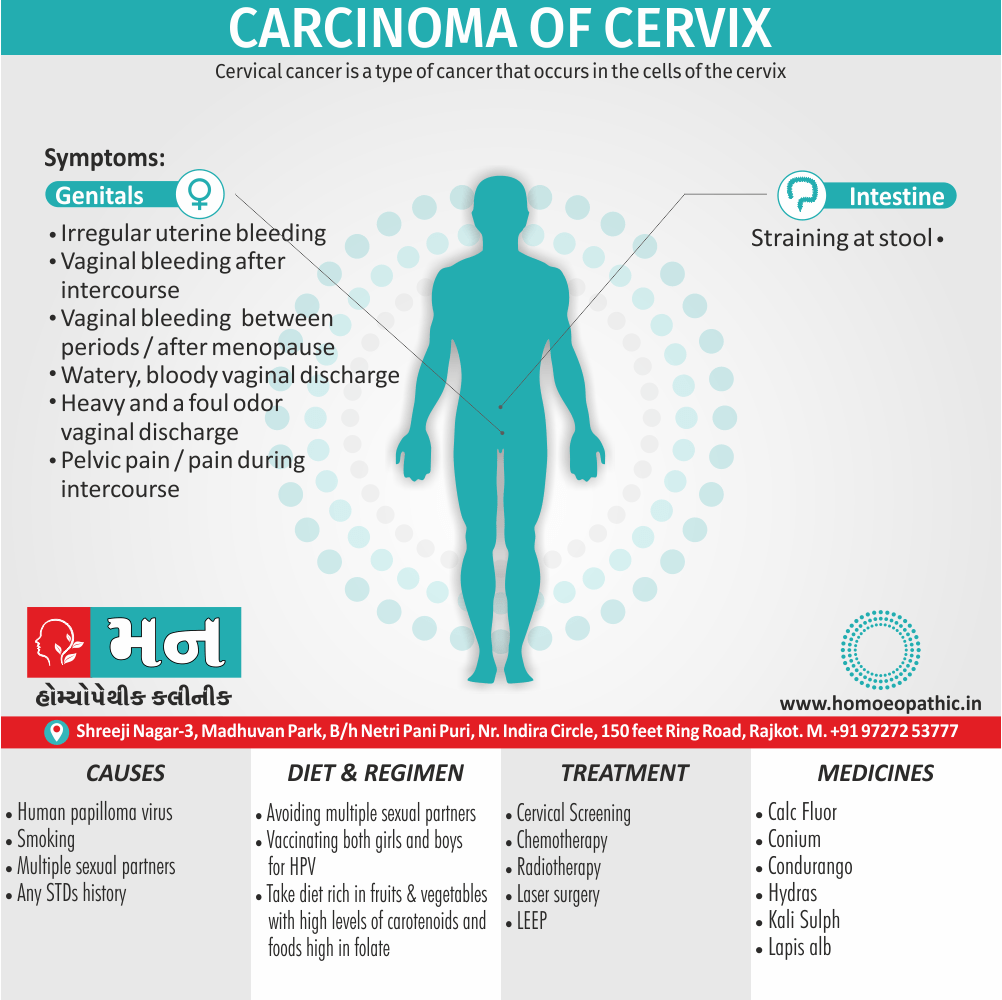
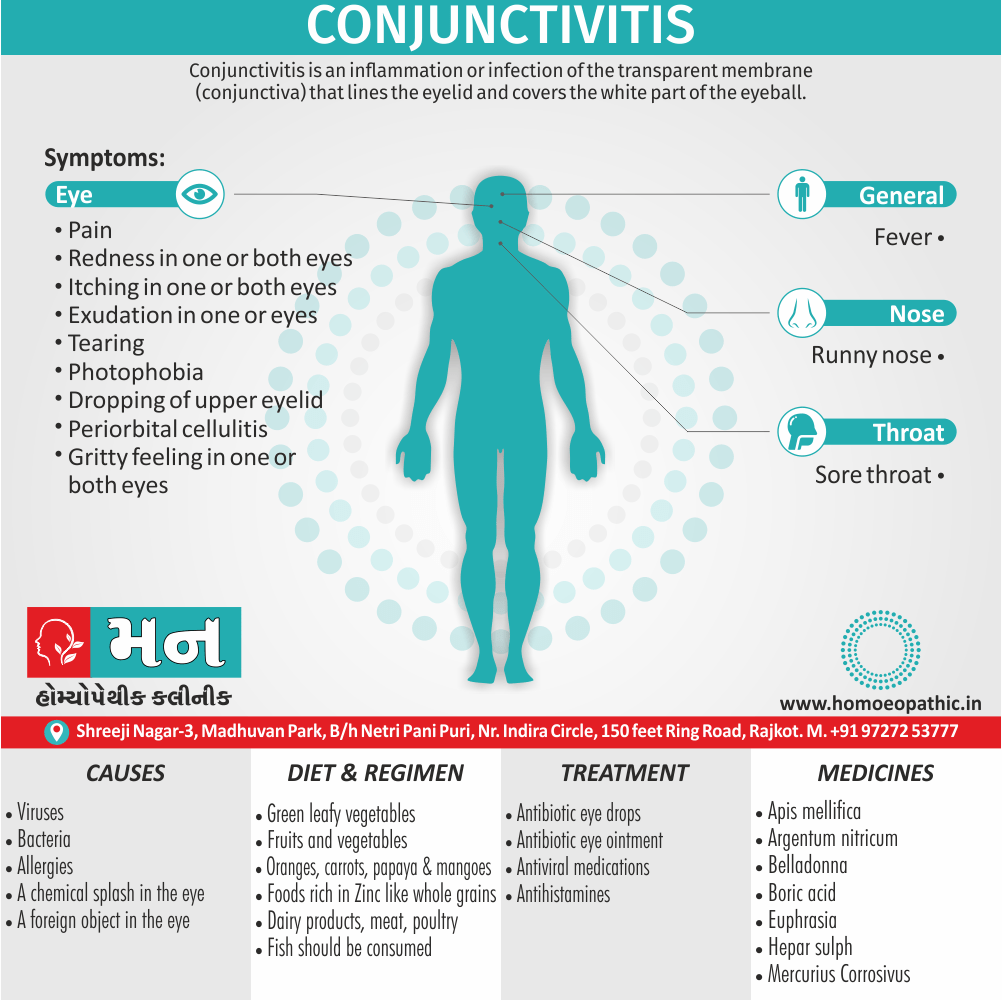
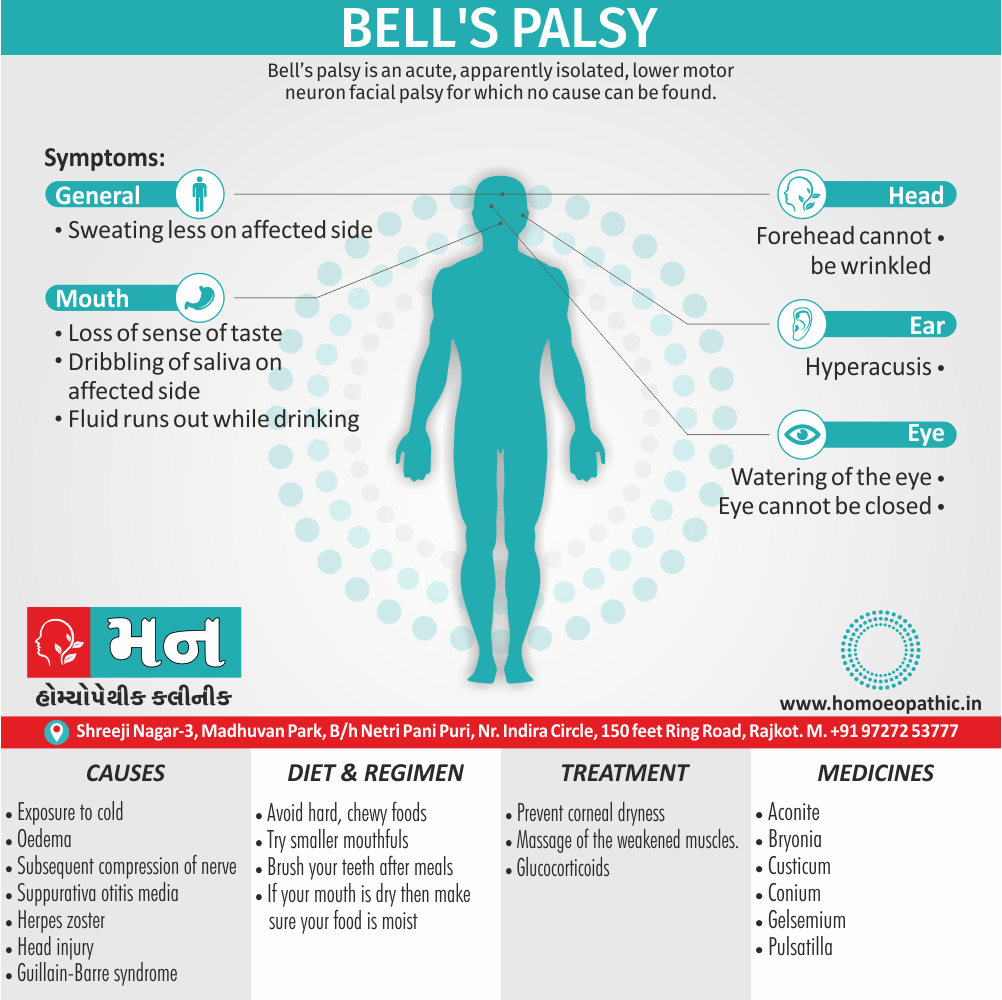
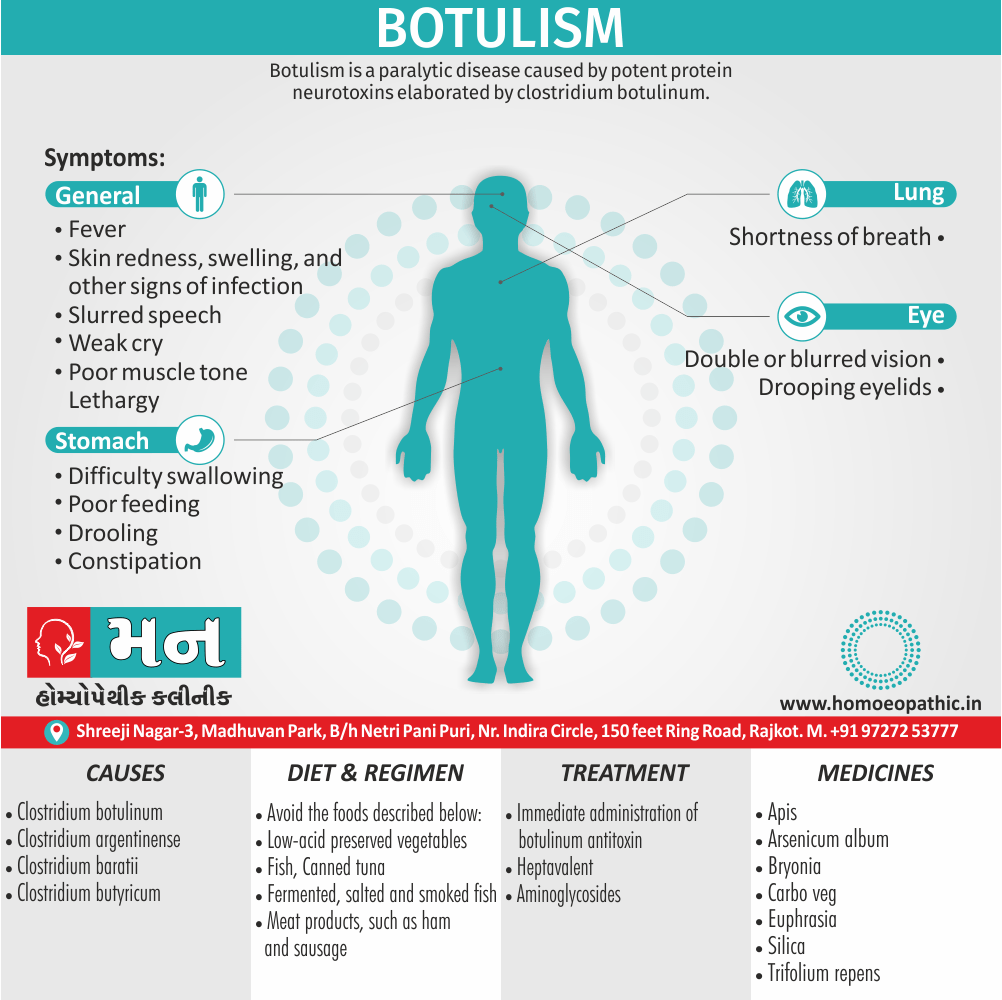
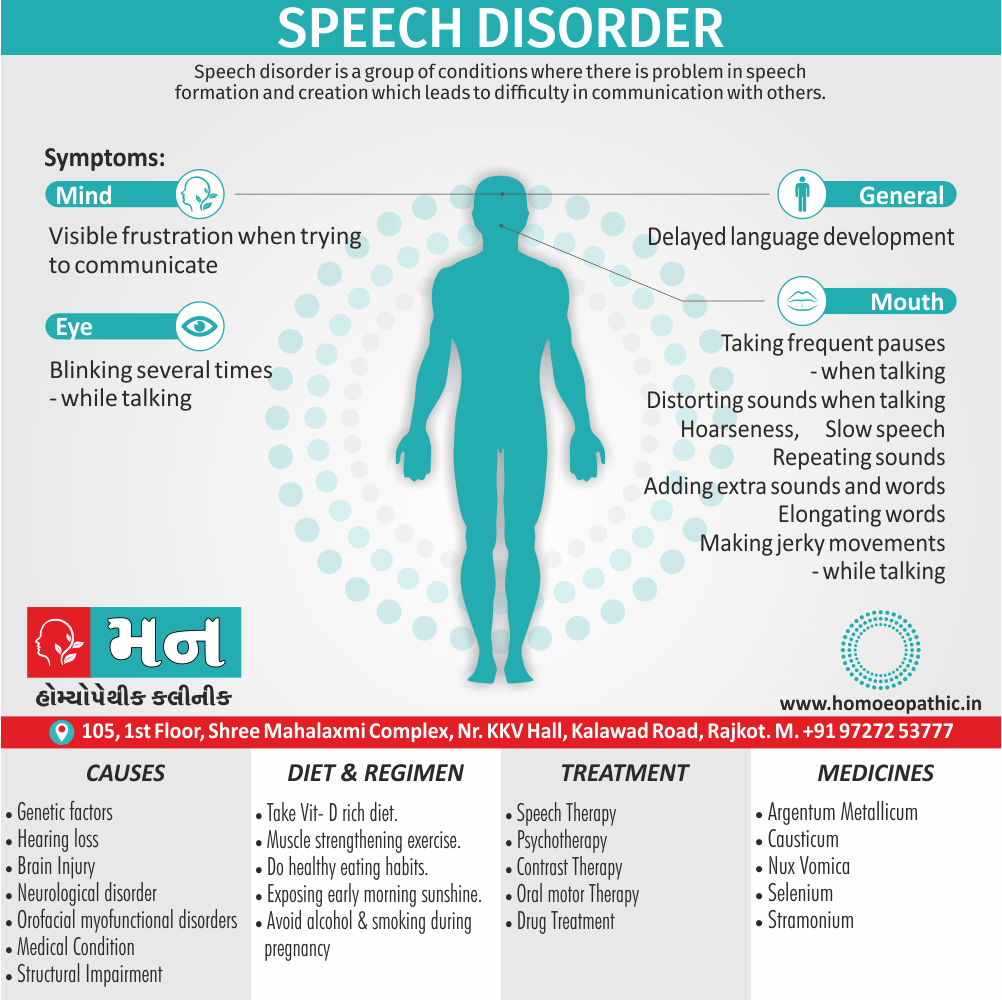
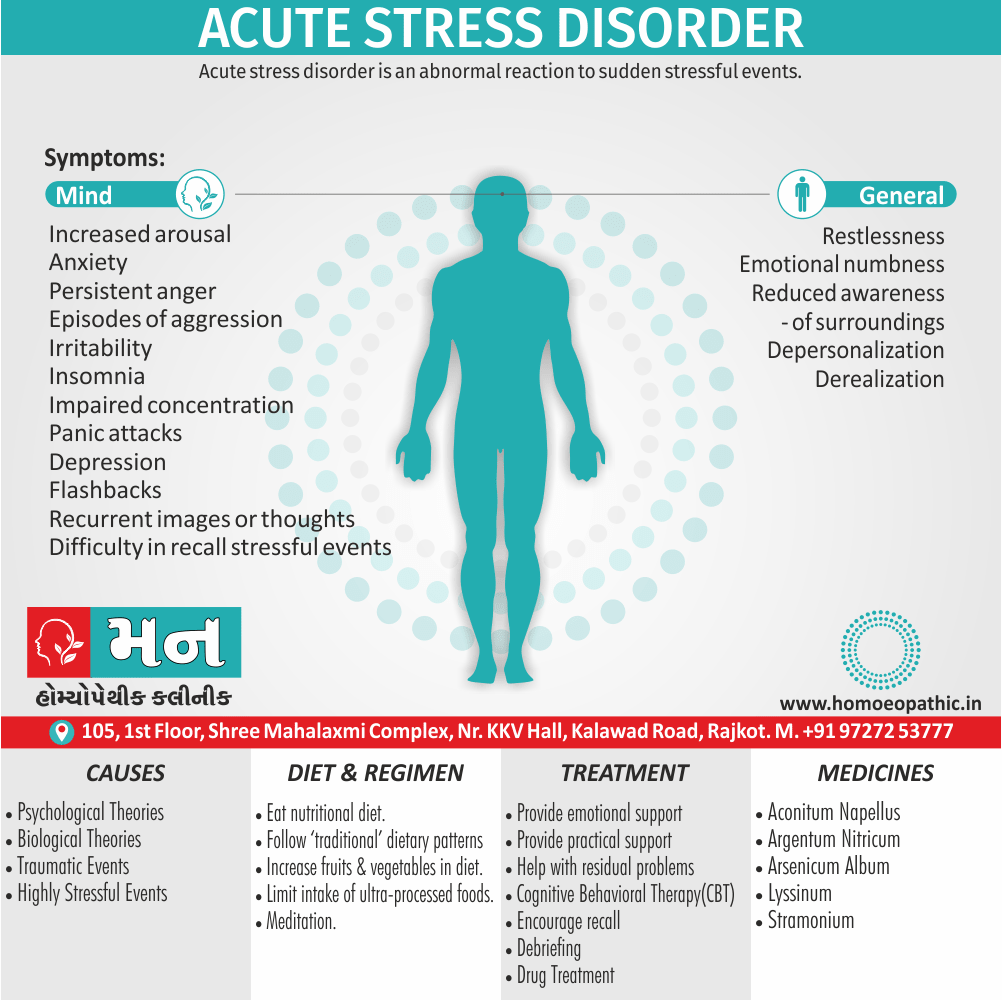
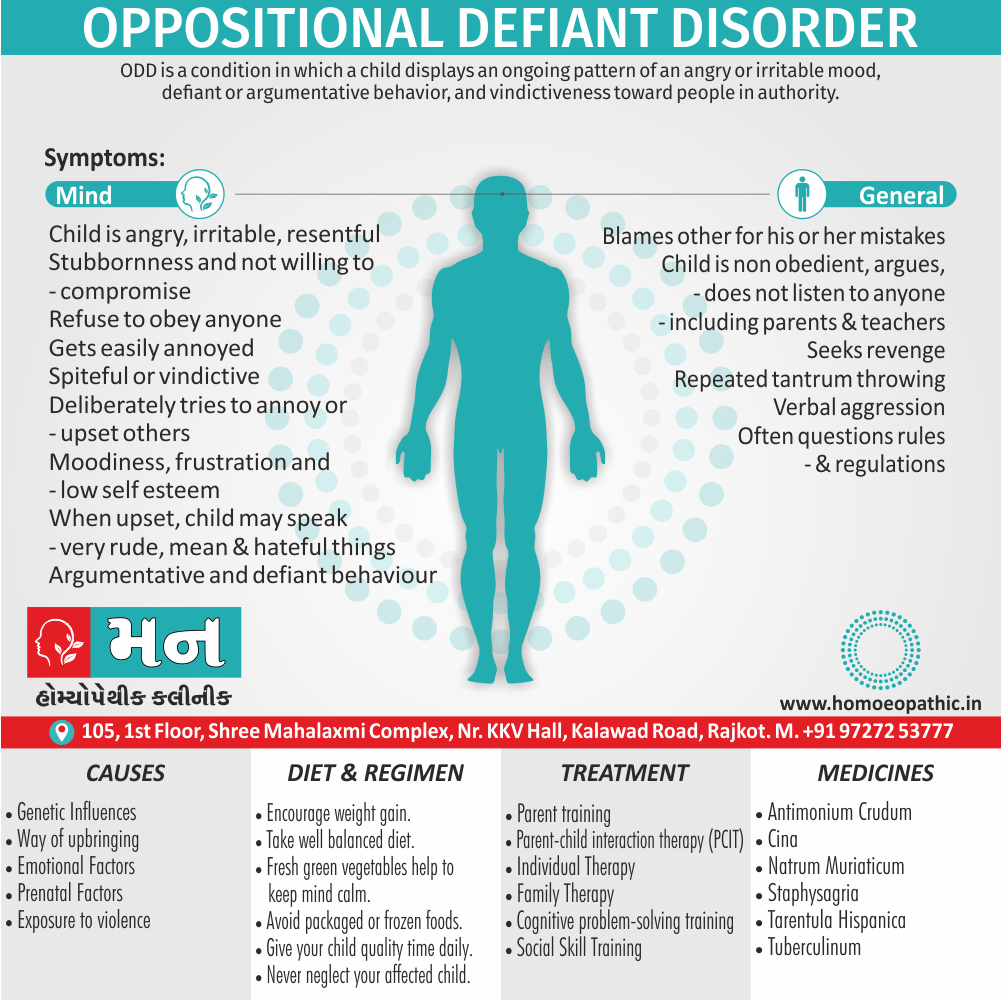
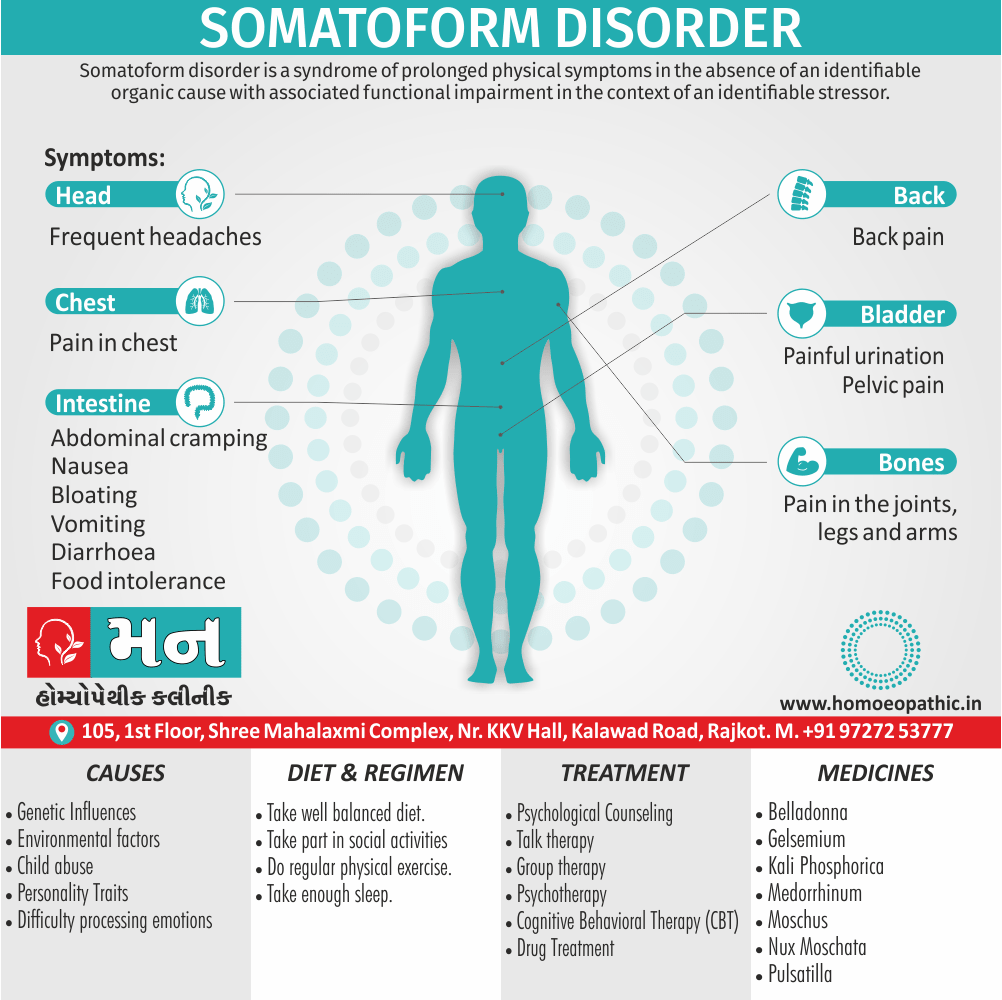
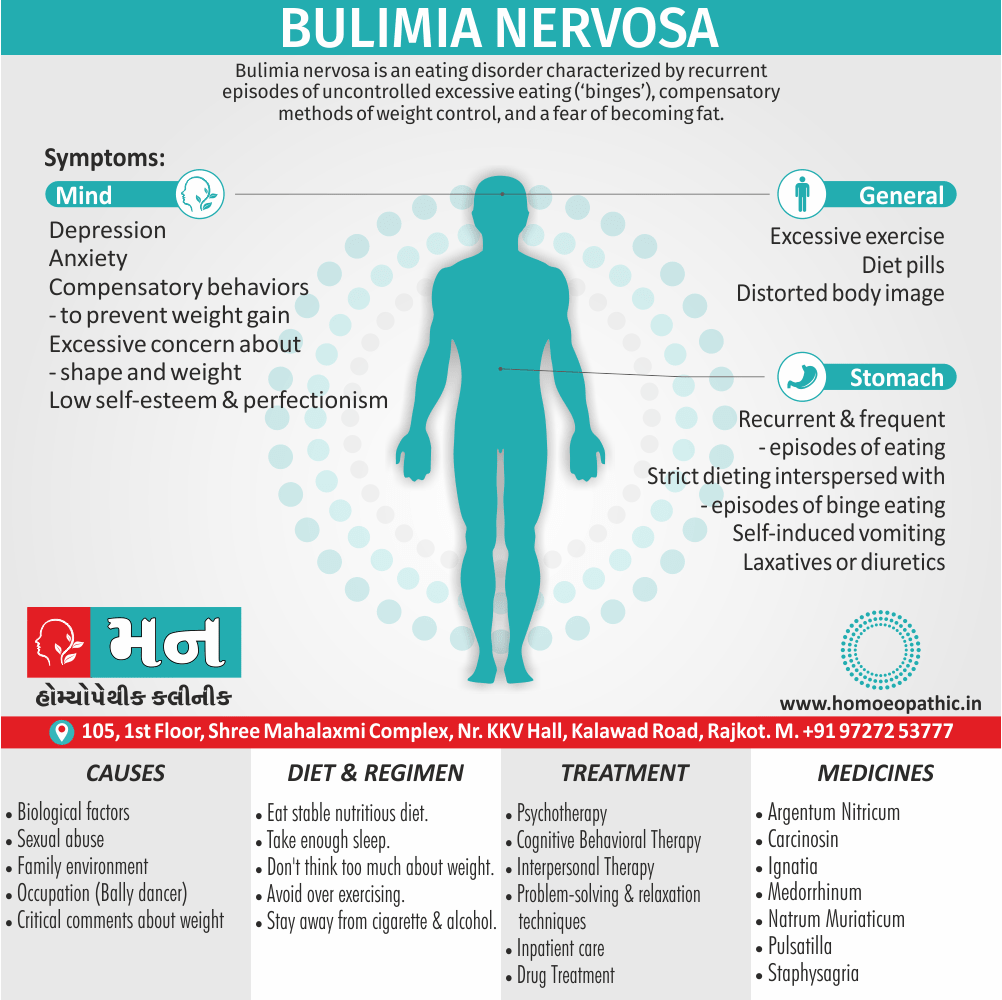
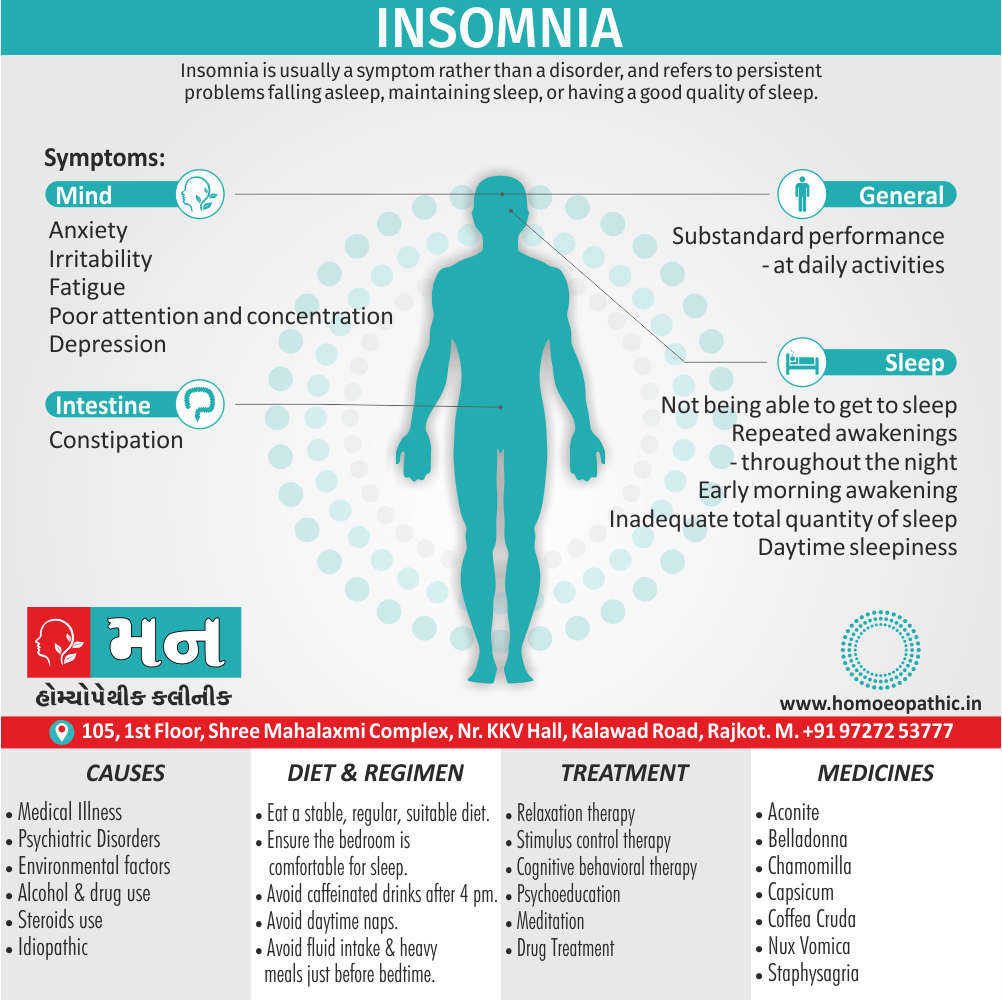
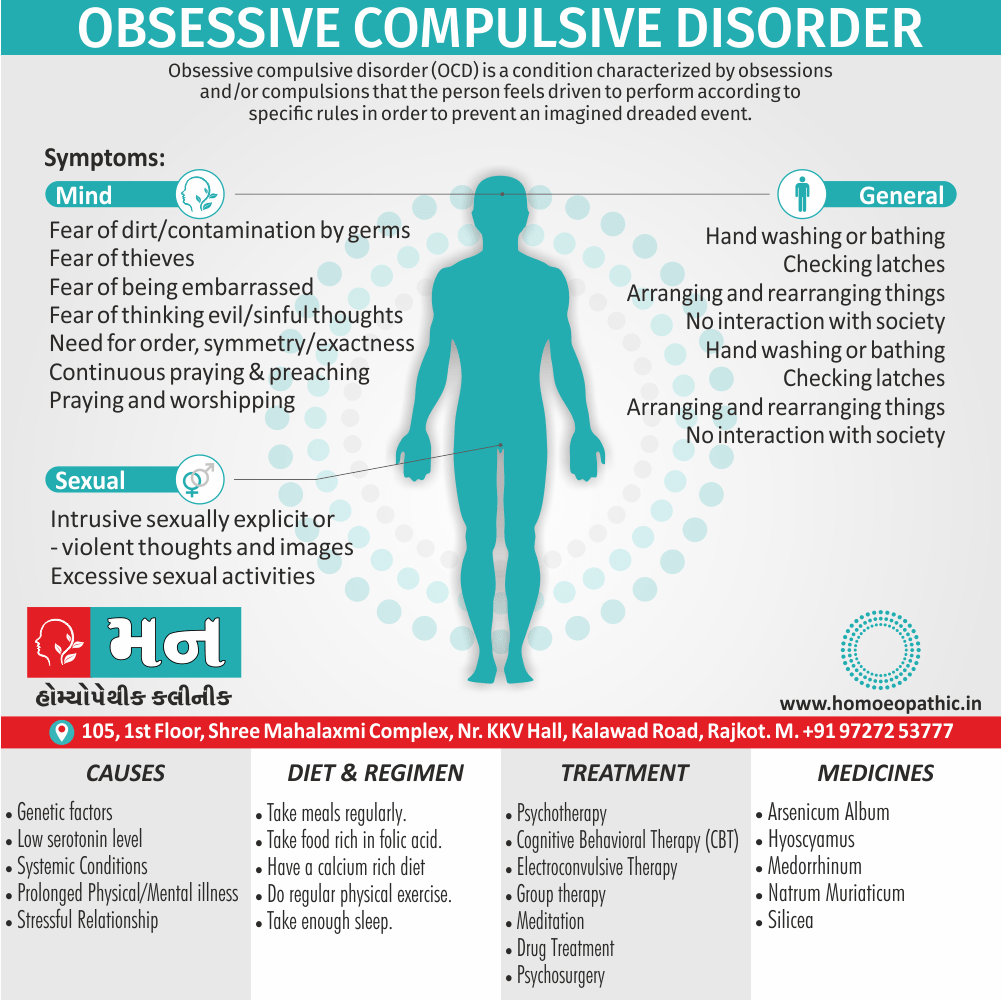
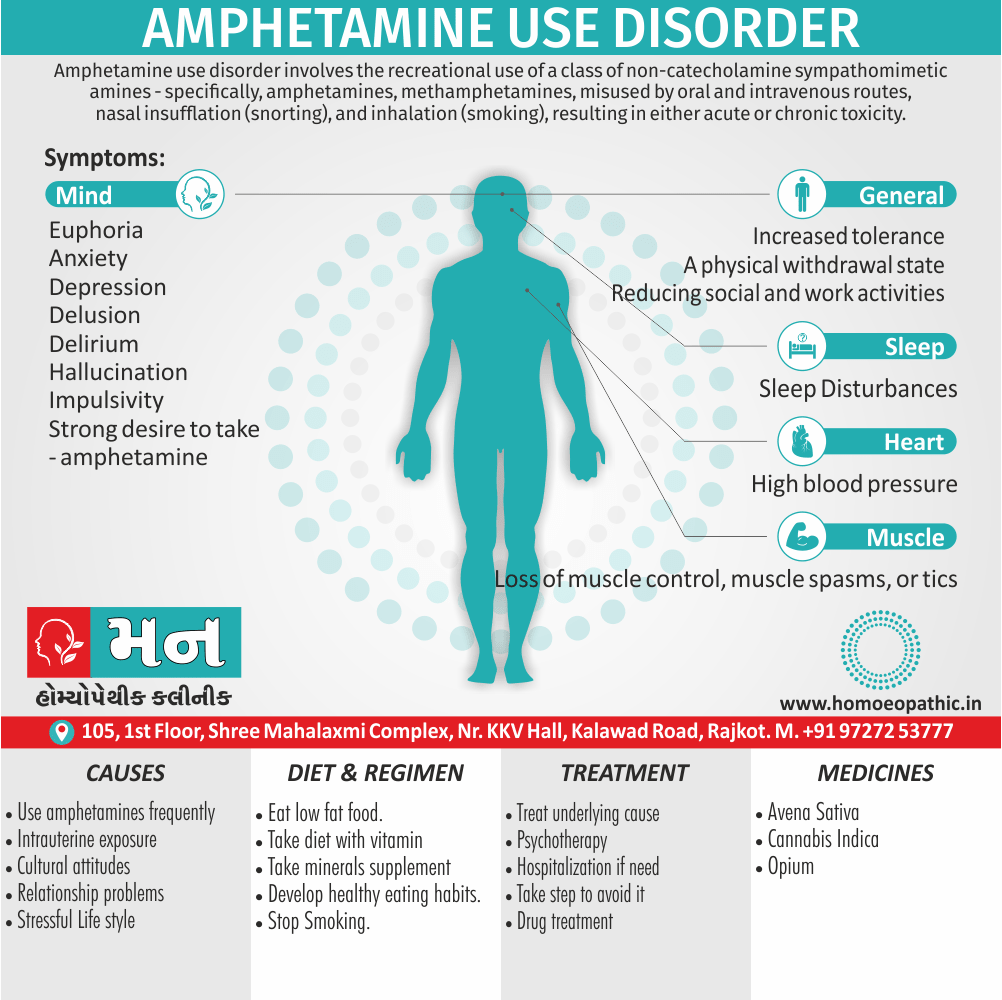
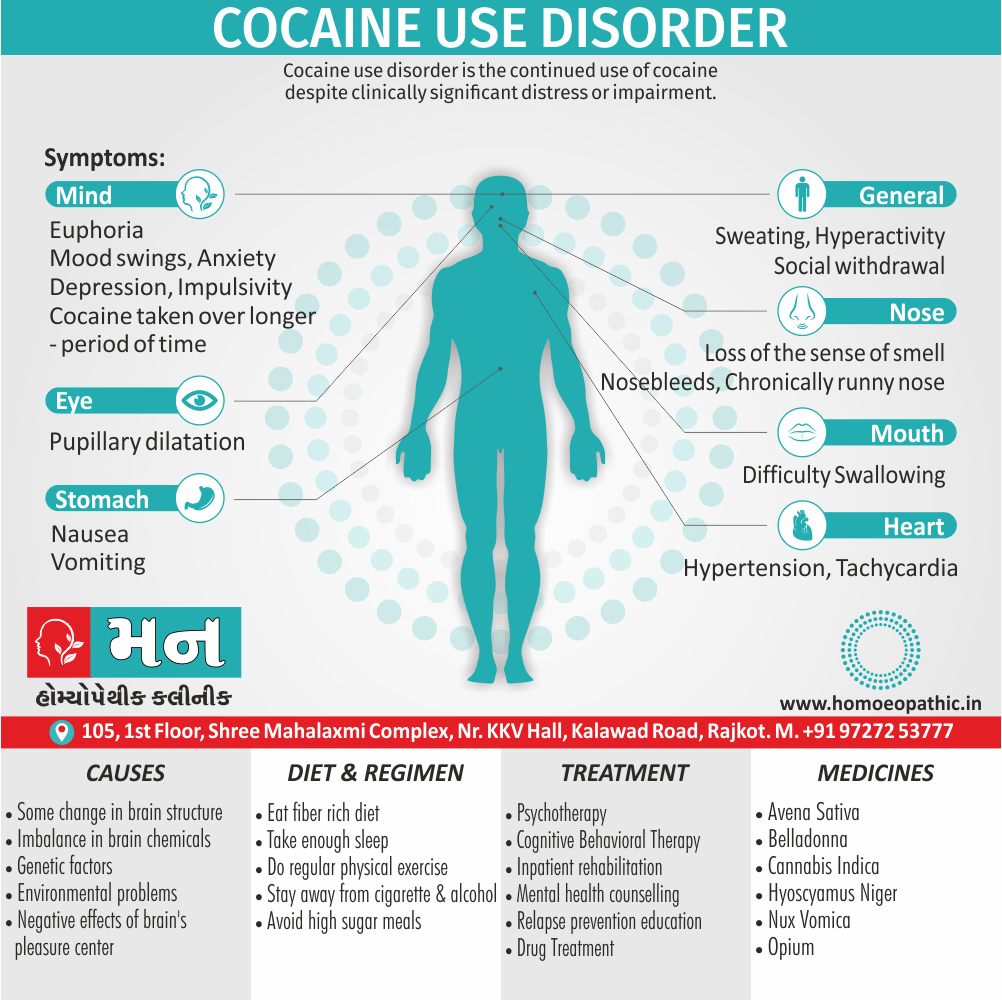
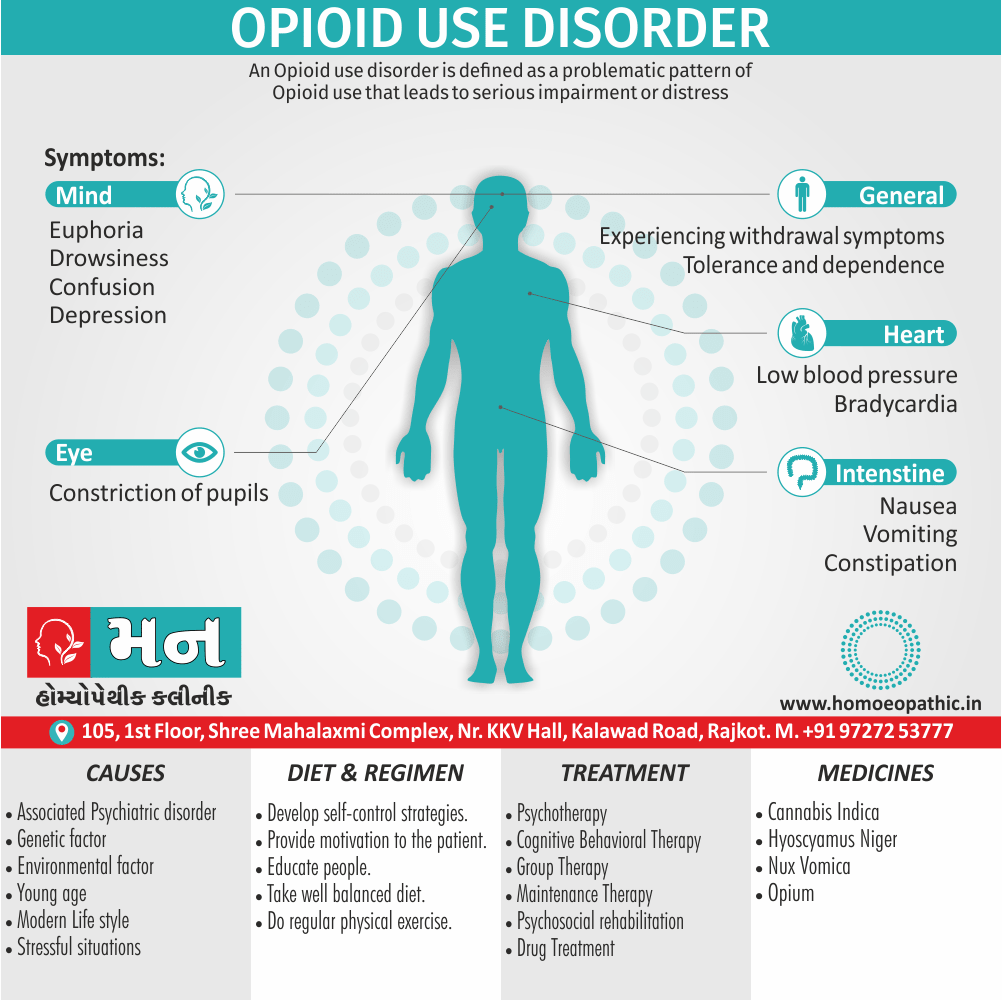
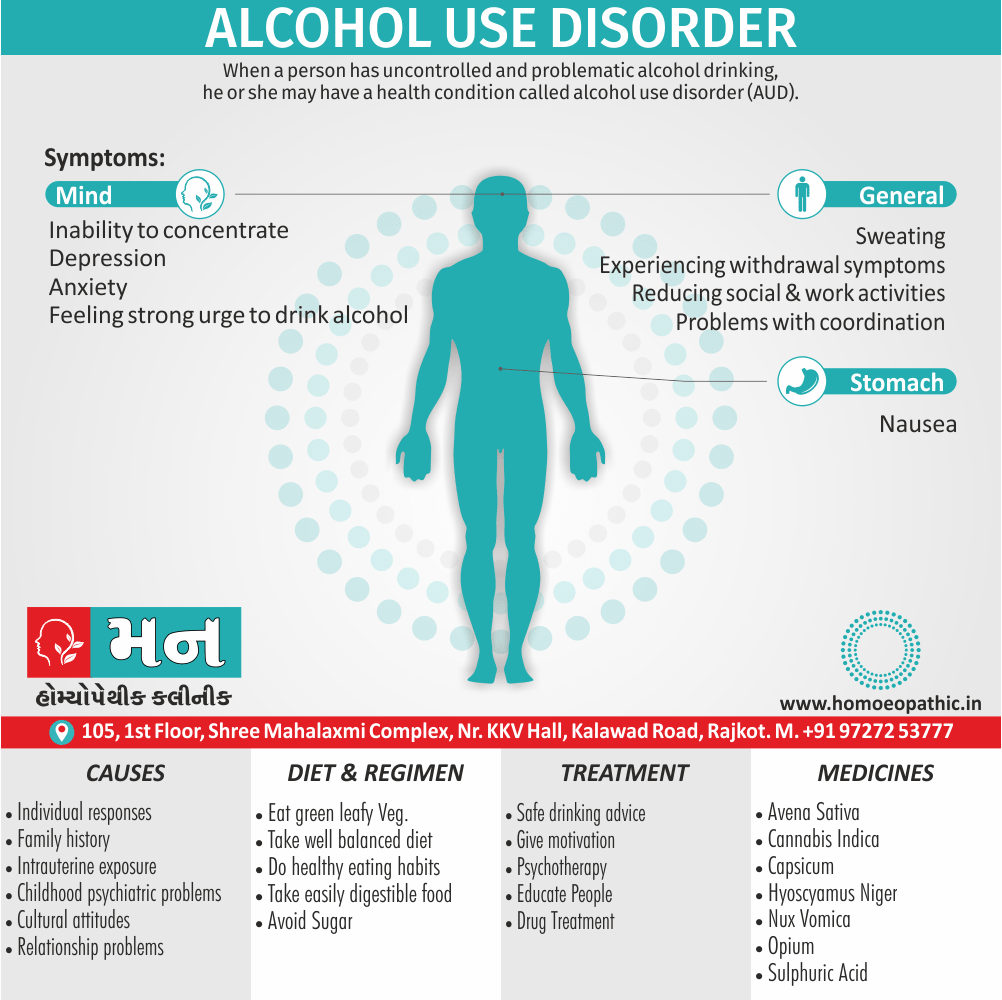
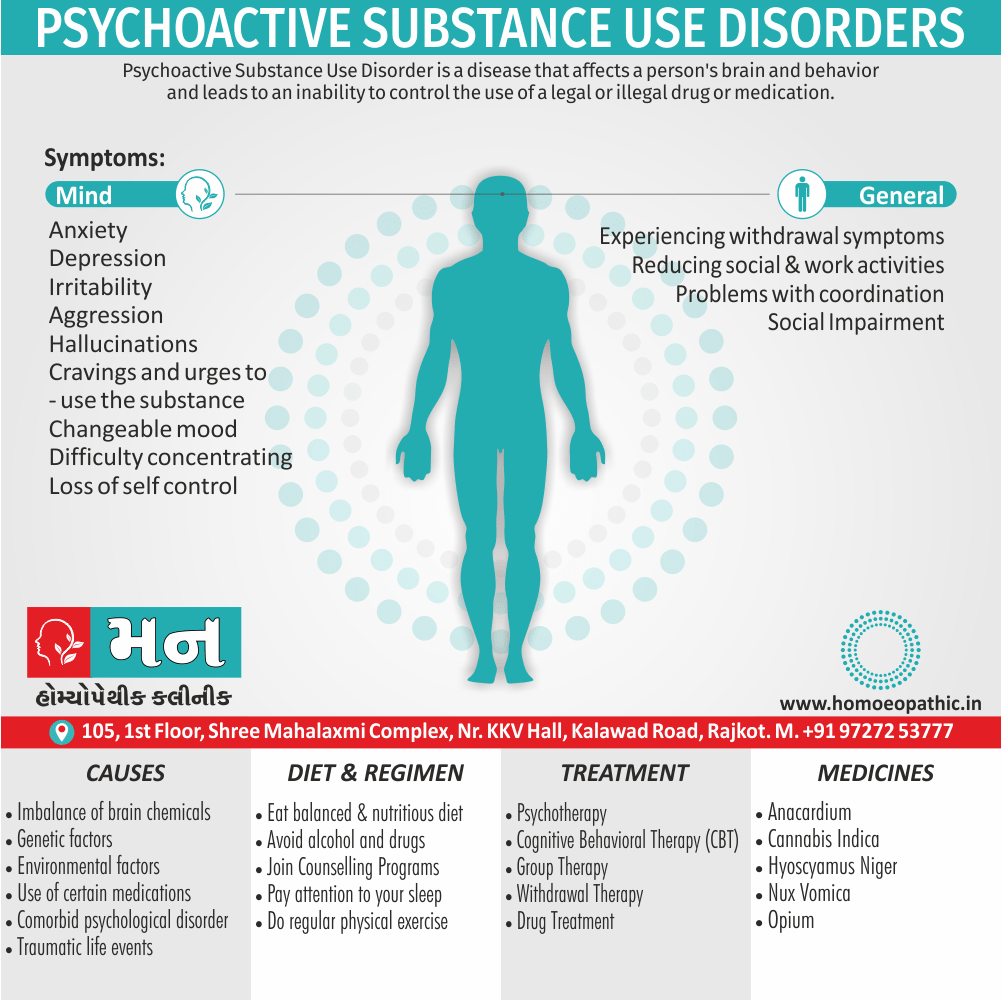
Biostatistics
Learning Objectives
- Define “Biostatistics”
- Describe the range of applications of biostatistics
- Identify situations in which statistics can be misleading.
History of Biostatistics:
The word ‘Statistics’ is derived from Latin word ‘Status’. In German mythology the word ‘Statistik’ was used for the first time in political arrangement. It was Ganfried Acheriwall who used first time this word in medical history.
Pierre C.A Louis (1787-1872), a pioneer of clinical statistics studied 77 patients of Pneumonia. He counted also compared the results of patients treated by ‘Blood Letting’ & concluded that early bleeding was associated with reduced Survival.
William Batesan & Gealton applied Mathematics to Evolution.
In 1959, Robert Ledley & Lee Lusted published-“Reasoning Foundations of Medical Diagnosis”. Additionally, They were the first to provide a mathematical analysis of the reasoning process inherent in medical diagnosis.
Wilfrid Card & Jack Good (1973) wrote on “Mathematical Structure of Clinical Medicine” & “Logical Analysis of Medicine”.
Dr.Hahnemann also mention under the Foot Note of • 145 in his 6th edition of Organon of Medicine “The healing art will then come the mathematical sciences in certainty”
Statistic (singular)
A statistic (or datum ) is a single measure of some attribute of a sample.
e.g., figure such as height of one person, birth weight of a baby,etc. [Etymology: L, status, condition]
Statistics [LL. statisticus] (plural)
Definition :
According to Taber Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary 20thEd
The systematic collection, organization, analysis, interpretation and presentation of numerical data pertaining to any subject.
e.g.figures such as height of 2 persons, birth weight of 5 babies, etc.
In simple word, “Statistics is a science of figures which deals with data in an experimental study”.
Biostatistics is a field dedicated to the precision, facts, observations, measurements, creation of innovative theory and methods for study design, data analysis, and statistical inference, and the promotion of these methods as integral to interdisciplinary research in human health and the life sciences.
According to Webster
“Statistics are the classified facts representing the conditions of the people in a state especially those facts which can be stated in number or in a table of numbers or in any tabular or classified arrangement”.
According to Bowley
“Statistics is a numerical statement of facts in any department of enquiry placed in relation to each other”.
According to Horace Secrist
“By statistics we mean the aggregate of facts affected to a marked extend by multiplicity of causes, numerically expressed, enumerated or estimated according to reasonable standards of accuracy, collected in a systematic manner for a pre-determined purpose and placed in relation to each other.
According to Croxton and Cowden
“Statistics may be defined as a science of collection, presentation, analysis and interpretation of numerical data
In brief, statistics is a method of taking decision on the basis of numerical data properly collected, organized, presented, analyzed and interpreted.
Statistics is the art and science of data. It deals with
-
Planning Research
-
Collecting Data
-
Describing Data
-
Summarizing- Presenting Data
-
Analyzing Data
-
Interpreting Results
-
Reaching decisions or
-
Planning Research
-
Collecting Data
-
Describing Data
-
Summarizing- Presenting Data
-
Analyzing Data
-
Interpreting Results
-
Reaching decisions or discovering new knowledge
Biostatistics Definition
The application of statistical processes and methods to the analysis of biological data.
BIOMETRY
In Greek, Bios = Life and Matron = Measure. So, Biometry is measurement of life.
Health statistics
Health statistics in public health or community health.
Medical statistics
Medical statistics in medicine related to the study of defect, injury, disease, efficacy of drug, serum and line of treatment, etc.
Vital statistics
Vital statistics (SYN:population statistics) in demography pertaining to vital events of births(natality), marriages , disease (morbidity) and deaths(mortality).
These terms are overlapping and not exclusive of each other.
How to study statistics
As Statistics is a logical and systematic science therefore it has its own principles, laws and certain steps. Therefore it should be studied under following stages:
1st stage – Collection of data
2nd stage – Organization of data
3rd stage – Presentation of data
4th stage – Analysis of data
5th stage – Interpretation of data
Characteristics of statistics
- Firstly, Statistics is a quantitative expression also not qualitative expression.
- Secondly, Statistics is the aggregate of facts.
- Thirdly, Statistics is affected especially by multiplicity of causes.
- Fourthly, Statistics is estimated according to reasonable standard of accuracy.
- After that, Statistical data is collected specifically for predetermined purpose.
- Lastly, They should be related to each other.
Limitations Of Statistics
- Firstly, It does not study the qualitative aspects. ‘
- Secondly, Individualistic study is very difficult.
- Thirdly, Statistical studies are based only on an average.
- Fourthly, It lacks mathematical accuracy.
- Lastly, Statistics is only means and not an end of study.
Aims of statistics
The aim of statistics is not only to collect numerical data but also to provide a methodology from which certain conclusion came out.
Utility of statistics in homoeopathy
- It helps in presenting large quantity of data in a simple also classified form. In general, Suppose if we want to show the results of many patients of same disease, we can summarized them into different groups according to age or sex wise also may be present them in tabulation form. Additionally, That means with the help of statistics we can express number of patients or remedies in a smaller form by classifying them.
- Statistics gives the methods of comparison of data also it weighs and judges them in the right perspective e.g. we can use this science for comparison of different Homoeopathic remedies, gradation arid intensity of symptoms can be done with the help of Statistics.
- Furthermore, It assists in arriving at correct views based on facts.
- It helps in finding relationship between the variables. In detail, Many remedies shows relationship at certain state of patient we can use statistics here, which helps in second prescription and follow up study of patients.
- It providers materials I data to researchers which serve as a guide for future planning also programs.
- It is useful in drug proving. (New drug proving as well as verification and reproving of old drugs)
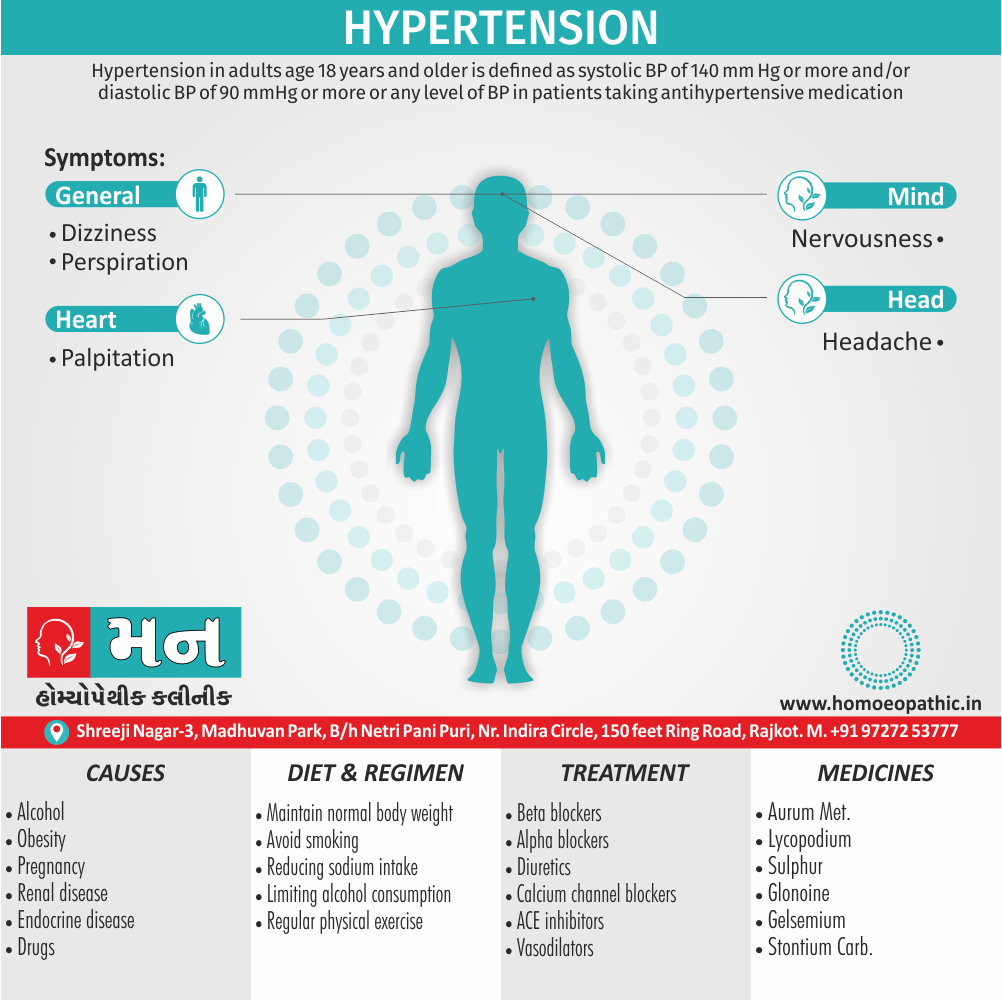
- To asses either normally or healthy state of a person that is to find limits of variables. E.g. Blood pressure. The normal range is 80 – 120 mm of Hg. But it may normal above this range has to ascertain with Statistical tech- ruques.
- To find the correlation between two variables such as Diet and Weight increases or decreases proportionately with diet.
- To find the difference between means and proportions of normal individuals at two different places or at different periods.
Other uses
- It use for Drug proving process that is action of a particular drug both on humans and animals, which helps in ascertaining the pathogenetic and curing power of a particular drug.
- Moreover, It· use to compare the action of same drug on different persons which helps in understanding individualistic characteristic symptoms of that drug patient.
- To compare the efficacy of a particular drug especially by using experimental or control group.
- In detail, To find the Incidence, Prevalence and Progress of symptoms in a disease process – Holistic approach.
- It use in preventive medicine to measure the death rates from vaccinate: or un-vaccinated individuals. and to asses efficacy of a particular drug as: – prophylactic medicine for a specific disease specifically by using appropriate Statistical tests.
- Besides this, In Epidemiological studies the role of causative factors is statistically tested. For Example, deficiency of vitamin C causes Scurvy in a community confirm only after comparing the scurvy cases before and after supplying vitamin-C.
- It use for recording, Birth, Death, Morbidity, etc. Additionally, Rates which are the basic tools in Demography.
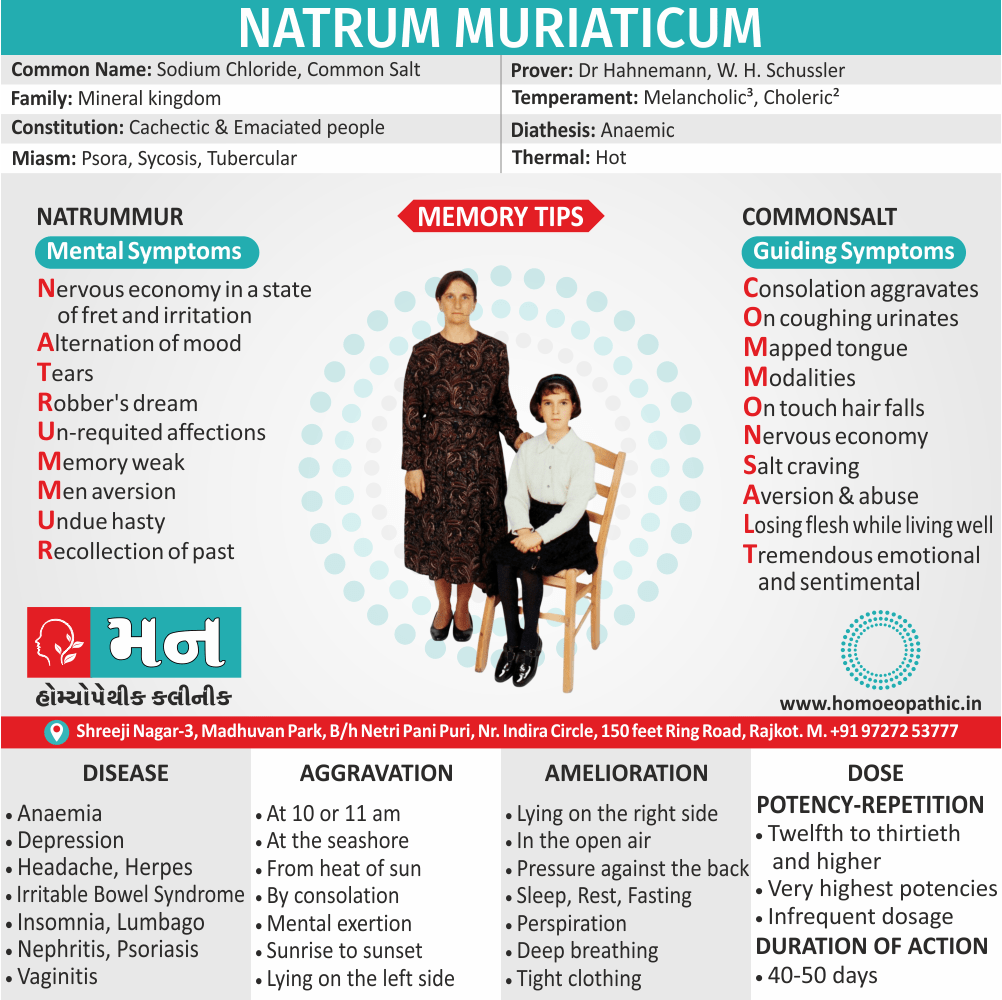
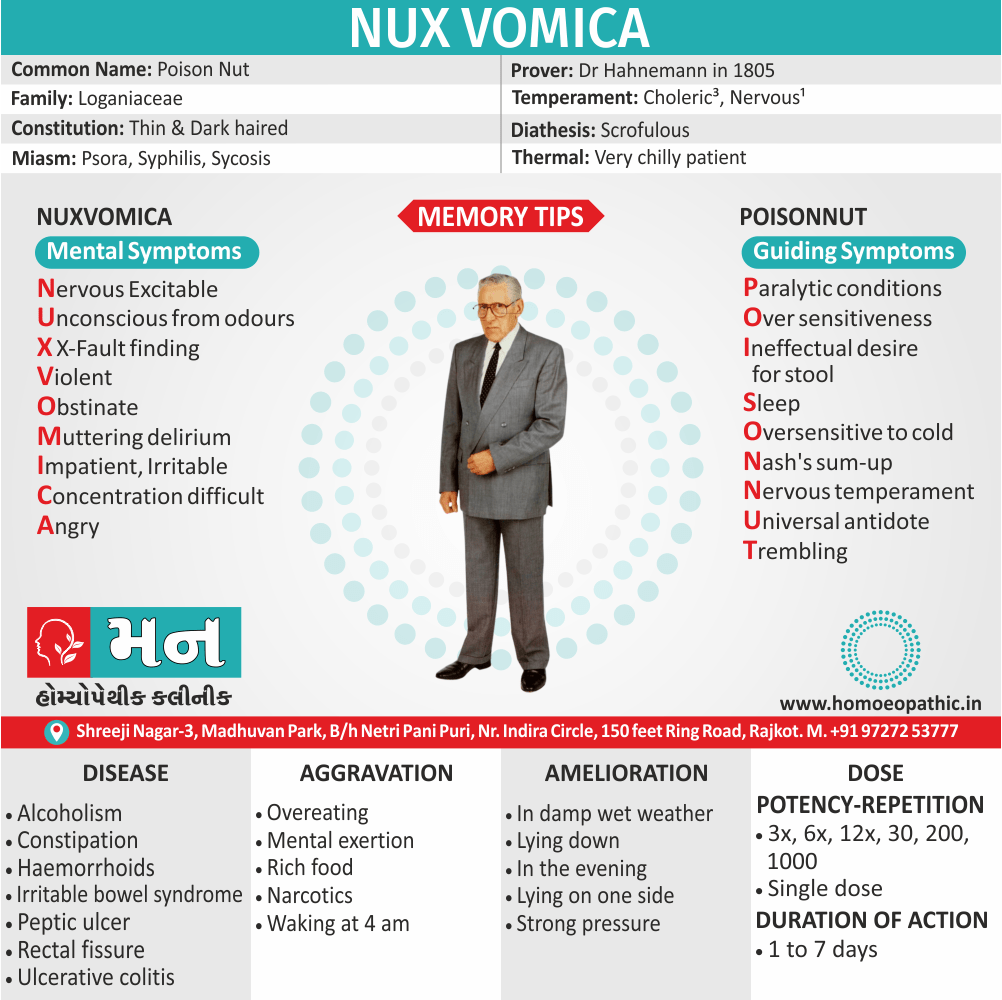
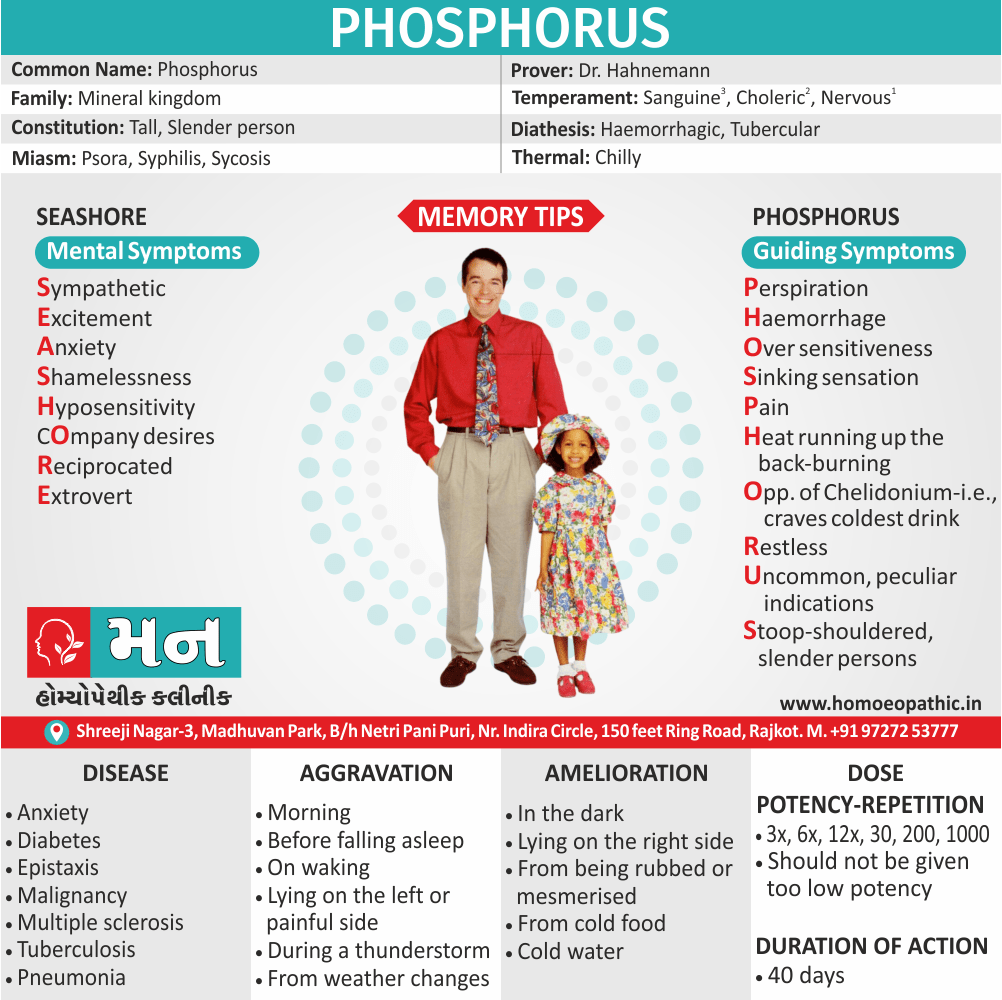
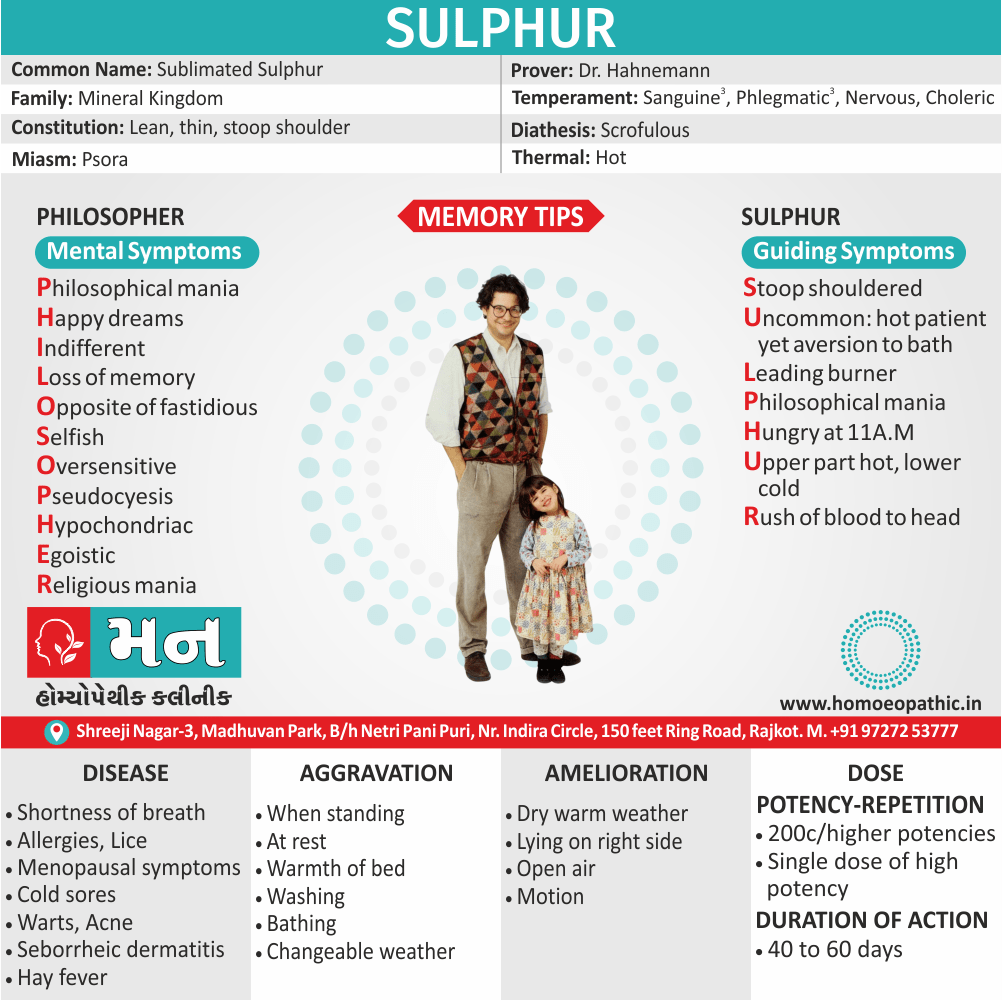
- It use for Analysis of certain components of case taking e.g. Thermal Analysis (Hot/Chilly/Ambithermal), Miasmatic Analysis ( Psora/Sycosis/ Syphilis), etc.